一、SpringBoot多环境配置
1.环境的配置信息
(1)application.properties
#指定默认使用dev的配置
spring.profiles.active=dev(2)application-dev.properties
#开发环境
server.port=8080
branch=dev(3)application-prod.properties
#测试环境
server.port=8081
branch=test
2.测试类
package com.yh.bootev.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author youHui
* 检测当前使用的是哪个环境
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Value("${branch}")
private String branch;
@GetMapping("/branch")
public String test(){
return branch;
}
}
3.打包后在不同环境下运行
java -jar 你打包的jar包名.jar --spring.profiles.active=你要切换的环境
如:java -jar boot-ev-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod二、SpringBoot devtools热部署配置(自动的不建议,对性能消耗大,建议手动的)
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>2.配置plugin :加入 pligin 且配置一个属性 fork 为 true
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>3.开启自动编译
5.重启IDEA即可实现热部署。
三、SpringBoot过滤器
(一)快速了解过滤器
过滤器是基于Servlet实现的,在web开发中可以帮助过滤一些指定的url,可以过滤掉不需要的东西,比如:一些错误的请求。过滤未登录的用户等。
废话不多说直接上代码:
方式一:@WebFilter
1.创建过滤器
package com.yh.bootfilter.filter;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author youHui
* 自定义Filter的方式有两种,一种是@WebFilter,另一种是FilterRegistrationBean
*方式一:
* @WebFilter用于将一个类声明为过滤器,该注解将在部署时被容器处理,
* 容器会根据具体的属性配置将相应的类部署为过滤器
* 其中的来个参数
* urlPatterns = "/api/*":定义要拦截的url路径
* filterName = "myFilter":指定过滤器的名称
**/
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/api/*",filterName = "myFilter")
@Order(1) //这个值用来控制过滤的执行顺序,若同时有多个过滤器,该值越大,越往后执行
public class MyFilter implements Filter {//1.实现Filter接口
//2.重写Filter的三个方法
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("MyFilter被初始化了");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//获取所拦截的接口信息
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String method = request.getMethod();
System.out.println("请求的接口--"+uri+"请求的方法--"+method);
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//只用执行了这个方法,才会丸往下执行
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("MyFilter被销毁");
}
}
2.测试类
package com.yh.bootfilter.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class FilterTestController {
@GetMapping("/user/filter")
public String hello(){
return "我被myFilter过滤器监控了";
}
}
3.注:需要在启动类中加
@ServletComponentScan注解过滤器才会生效
方式二:
通过FilterRegistrationBean注入容器的方式实现
1.创建过滤器类
package com.yh.bootfilter.filter;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author youHui
*FilterRegistrationBean
**/
public class MyFilter2 implements Filter {//1.实现Filter接口
//2.重写Filter的三个方法
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("MyFilter被初始化了");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//获取所拦截的接口信息
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String method = request.getMethod();
System.out.println("请求的接口--"+uri+"请求的方法--"+method);
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//只用执行了这个方法,才会丸往下执行
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("MyFilter被销毁");
}
}
2.创建配置类:目的是为了将过滤器信息注入到Spring容器中去
package com.yh.bootfilter.config;
import com.yh.bootfilter.filter.MyFilter2;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
//将过滤去注入到容器中
@Bean
public MyFilter2 myFilter2(){
return new MyFilter2();
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean getFilterRegistrationBean(MyFilter2 myFilter2){
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(myFilter2);//指定过滤器类
filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(1);//过滤器的顺序
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/api/*");//指定要拦截的接口
filterRegistrationBean.setName("myFilter");//指定过滤器名
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
}
3.测试类
package com.yh.bootfilter.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class FilterTestController {
@GetMapping("/user/filter")
public String hello(){
return "我被myFilter过滤器监控了";
}
}
(二)过滤器在开发中的应用
1.配置开发性接口
在application.properties文件中:
#设置白名单接口:凡是请求地址层级带有open都放行
open.url=/**/open/**2.过滤器
package com.yh.bootfilter.filter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author youHui
*FilterRegistrationBean
**/
public class MyFilter2 implements Filter {//1.实现Filter接口
@Value("${open.url}")
private String openUrl;//获取开发性api
//2.重写Filter的三个方法
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("MyFilter被初始化了");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//获取所拦截的接口信息
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String method = request.getMethod();
System.out.println("请求的接口--"+uri+"请求的方法--"+method);
//判断是是开放性api
AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
if(antPathMatcher.match(openUrl,uri)){
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//放行
}else {
//如果不是开放的接口,就判断它是否有token凭证
String token = request.getHeader("token");//获取token
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(token)){
//跳转到未登录的接口
servletRequest.getRequestDispatcher("/api/open/unLogin").forward(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}else {
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("MyFilter被销毁");
}
}
3.
package com.yh.bootfilter.config;
import com.yh.bootfilter.filter.MyFilter2;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
//将过滤去注入到容器中
@Bean
public MyFilter2 myFilter2(){
return new MyFilter2();
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean getFilterRegistrationBean(MyFilter2 myFilter2){
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(myFilter2);//指定过滤器类
filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(1);//过滤器的顺序
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/api/*");//指定要拦截的接口
filterRegistrationBean.setName("myFilter");//指定过滤器名
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
}
4.测试类
package com.yh.bootfilter.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class FilterTestController {
@GetMapping("/user/filter")
public String hello(){
return "我被myFilter过滤器监控了";
}
//开放性接口
@GetMapping("/home/open/info")
public String setHome(){
return "欢迎进入首页";
}
@GetMapping("/open/unLogin")
public String setUnLogin(){
return "登录失效,请重新登录";
}
}
四、SpringBoot拦截器Interceptor
简单来说,拦截器就是一道阀门,在某个方法被访问之前进行拦截,然后在之前或者之后加入某些操作,拦截器是AOP的一种实现策略。
(一)Interceptor基础
1.自定义拦截器类
package com.yh.bootinterceptor.interceptor;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {//1.实现HandlerInterceptor接口
//2.重写它的三个方法
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截方法访问之前调用");
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();//获取被拦截的接口
System.out.println(requestUri+"接口被拦截了");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截方法访问之后调用");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("整个流程结束调用");
}
}
2.定义开放的接口
#开发性接口
open.url=/**/open/**3.创建配置类,用来配置拦截器的cel
package com.yh.bootinterceptor.config;
import com.yh.bootinterceptor.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Configuration
public class WebApplicationConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {//1.实现WebMvcConfigurer
//注入开放性api
@Value("${open.url}")
private String openUrl;
//声明一个拦截器并注入到容器中
@Bean
public MyInterceptor myInterceptor(){
return new MyInterceptor();
}
//2.重写addInterceptors方法
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry){
/**
* 配置拦截策略
* addInterceptor(myInterceptor()):指定用哪一个拦截器
* addPathPatterns("/api/**"):所要拦截的接口
* excludePathPatterns(openUrl):开放接口
*/
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/api/**").excludePathPatterns(openUrl);
}
}
4.测试类
package com.yh.bootinterceptor.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class InterceptorController {
@GetMapping("/home/open/info")
public String home(){
return "欢迎访问首页";
}
@GetMapping("/user/interceptor")
public String userInfo(){
return "已经被拦截器监控";
}
}
(二)拦截器在用户登录中的应用
1.配置类
package com.yh.bootinterceptor.config;
import com.yh.bootinterceptor.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Configuration
public class WebApplicationConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {//1.实现WebMvcConfigurer
//注入开放性api
@Value("${open.url}")
private String openUrl;
//声明一个拦截器并注入到容器中
@Bean
public MyInterceptor myInterceptor(){
return new MyInterceptor();
}
//2.重写addInterceptors方法
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry){
/**
* 配置拦截策略
* addInterceptor(myInterceptor()):指定用哪一个拦截器
* addPathPatterns("/api/**"):所要拦截的接口
* excludePathPatterns(openUrl):开放接口
*/
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/api/**").excludePathPatterns(openUrl);
}
}
2.拦截器类
package com.yh.bootinterceptor.interceptor;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {//1.实现HandlerInterceptor接口
//2.重写它的三个方法
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截方法访问之前调用");
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();//获取被拦截的接口
System.out.println(requestUri+"接口被拦截了");
//判断用户是否携带凭证
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(token)){
request.getRequestDispatcher("/api/open/unLogin").forward(request,response);
return false;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截方法访问之后调用");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("整个流程结束调用");
}
}
3.测试类
package com.yh.bootinterceptor.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class InterceptorController {
@GetMapping("/home/open/info")
public String home(){
return "欢迎访问首页";
}
@GetMapping("/user/interceptor")
public String userInfo(){
return "已经被拦截器监控";
}
@GetMapping("/open/unLogin")
public String getUnLogin(){
return "登录失效,请重新登录";
}
}
五、SpringBoot整合JSP
1.添加jsp相关依赖
<!--jsp标签库支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--springBoot内置的tomcat对jsp的支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>2.jsp相关配置
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
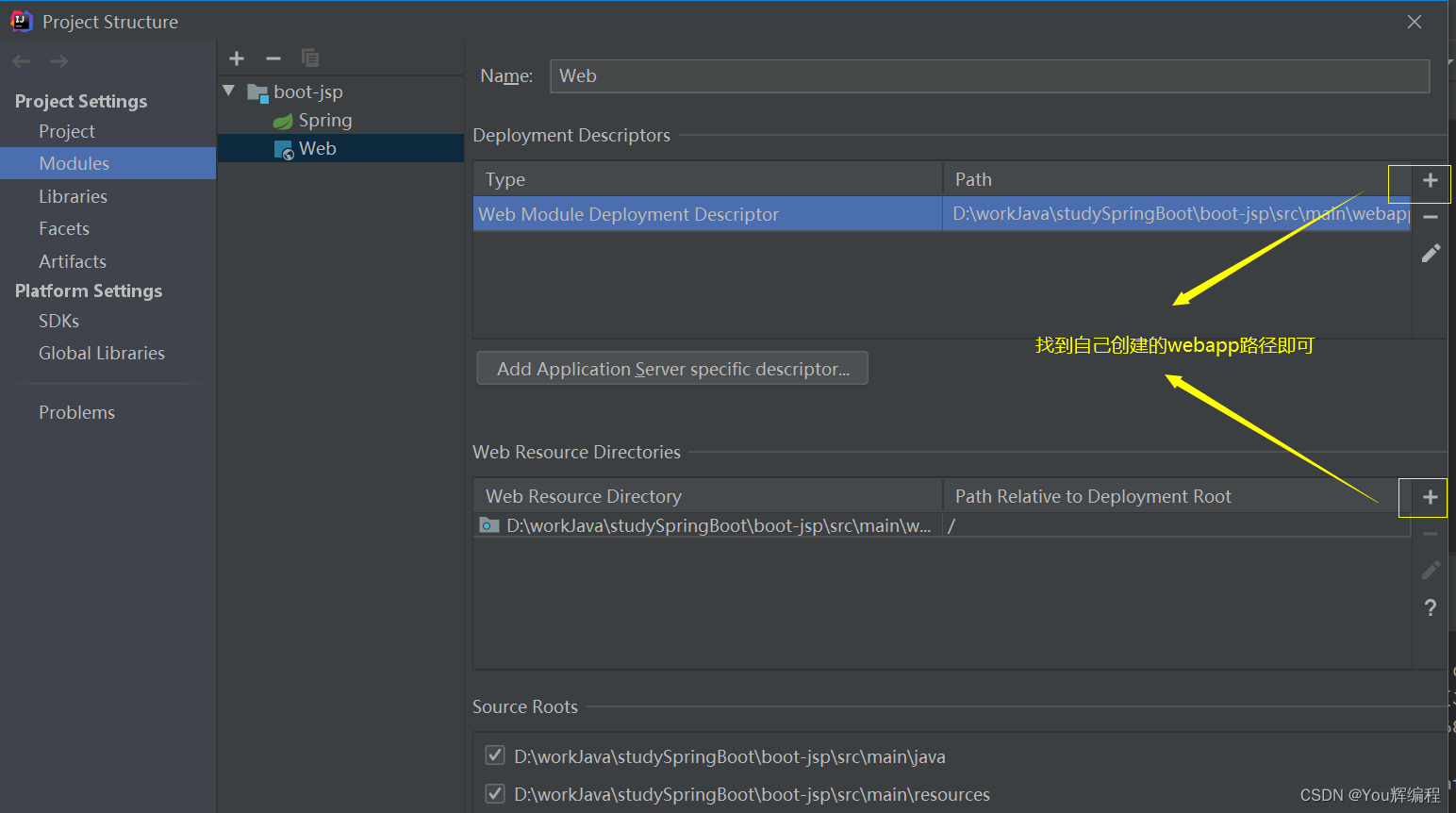
server.port=80883.配置webapp的路径(创建在main目录下)
4.在jsp文件夹下新建index.jsp文件
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;font-weight: bold;">成功整合jsp</h1>
</body>
</html>
5.测试类
package com.yh.bootjsp.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Controller
@RequestMapping
public class JspController {
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(){
return "index";//返回jsp页面
}
}
六、SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf
1.Thymeleaf配置
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.servlet.content-type=text/html2.Thymeleaf依赖
在项目创建时勾选Thymeleaf或到网上找相关依赖引入即可。
3.在templates下创建模板index.html文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'hello:'+${username}"></p>
</body>
</html>4.测试类
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model){
model.addAttribute("username","zhangsan");
return "hello";
}
}七、SpringBoot整合Freemarker
我这里有提到(123条消息) You辉编程_Java框架之SpringBoot_You辉编程的博客-CSDN博客
八、SpringBoot集成Druid监控数据源
其实就是一个平台,通过配置进入平台查看一些数据。
推展认识:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>(2)相关配置
#数据库配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.druid.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_mybatis?
useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.druid.username=root
spring.datasource.druid.password=root
################## 连接池配置 ################
#连接池建立时创建的初始化连接数
spring.datasource.druid.initial-size=5
#连接池中最大的活跃连接数
spring.datasource.druid.max-active=20
#连接池中最小的活跃连接数
spring.datasource.druid.min-idle=5
# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间
spring.datasource.druid.max-wait=60000
# 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小
spring.datasource.druid.pool-prepared-statements=true
spring.datasource.druid.max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size=20 spring.datasource.druid.validation-query=SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
spring.datasource.druid.validation-query-timeout=30000
#是否在获得连接后检测其可用性
spring.datasource.druid.test-on-borrow=false
#是否在连接放回连接池后检测其可用性
spring.datasource.druid.test-on-return=false
#是否在连接空闲一段时间后检测其可用性
spring.datasource.druid.test-while-idle=true
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
spring.datasource.druid.time-between-eviction-runs-millis=60000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
spring.datasource.druid.min-evictable-idle-time-millis=300000
# 监控后台账号和密码
spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet.login-username=admin
spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet.login-password=66666
spring.devtools.restart.poll-interval=3000ms
spring.devtools.restart.quiet-period=2999ms(3)访问Druid:http://localhost:8080/druid
九、SpringBoot集成Swagger2
(一)使用
1.引入依赖
<!--swagger2 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
</dependency>2.创建配置
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket createDocket(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
//要暴露的接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.xxx.xxx.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
.globalOperationParameters(parameterList)
}
//信息的描述
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder().
title("Swagger api") //标题
.description("spring boot 2.x 集成Swagger") //描述
.version("1.0") //版本
.build();
}
}
3.描述
@Data
public class SwaggerReqVO {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "账号") //描述
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "密码")
private String password;
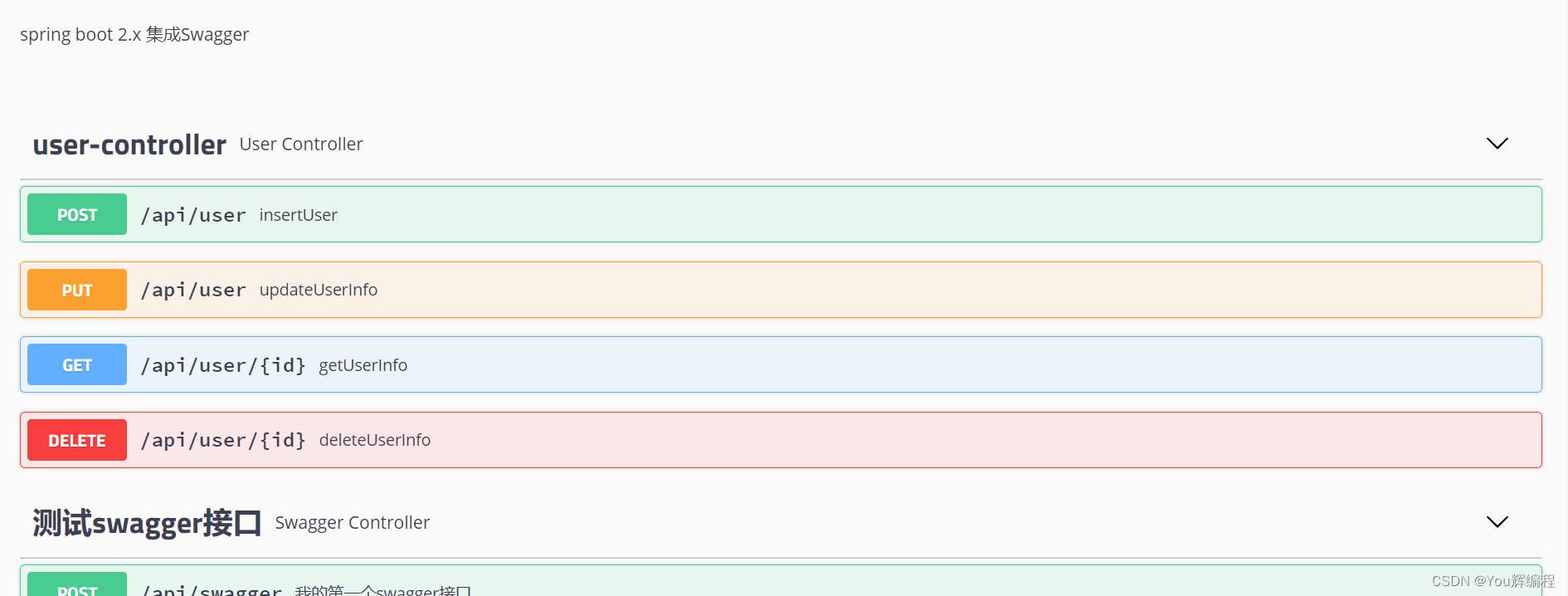
}4.测试类
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
@Api(tags = "测试swagger接口") //描述
public class SwaggerController {
@ApiOperation(value = "我的第一个swagger接口")
@PostMapping("/swagger")
public SwaggerReqVO testSwagger(@RequestBody SwaggerReqVO vo){
return vo;
}
}
(二)Swagger常用注解
1.@Api:对一个类进行说明。可以标记一个 Controller 类作为 Swagger 文档资源。
@Api(tags = "用户模块",description = "用户模块相关接口") 2.@ApiModel:对一个类进行说明。一般用于接受前端参数的实体类上。
@ApiModel(value = "实体类的相对路径",description = "接收更新用户数据VO")public class UpdateUserReqVO {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "用户id")//对每个属性进行描述
private String id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "账号")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "密码")
private String password;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "性别(1.男 2.女)")
private Integer sex;
}3.@ApiParam:主要用于Controller中方法参数的说明
value:参数说明
required:是否是必须的
@GetMapping("/getUser")
public SysUser getUser(@ApiParam(value = "需要传用户id",required = true) @RequestParam(required = true) String id){
return userService.getUserInfo(id);
}4.@ApiOperation:对controller方法的作用进行说明。
@ApiOperation(value = "获取一个用户")
5.@ApiResponse和ApiResponses
@ApiResponse用来说明响应的是哪些信息,ApiResponses表示组装了多个@ApiResponse
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code = 0,message = "响应成功",response = SysUser.class)
})6.@ApiImplicitParam和@ApiImplicitParams
用于方法,为单独的请求参数进行说明。
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name="id",value = "用户id",dataType = "String",paramType = "query",required = true,
defaultValue = "1001")
})(三)Swagger安全配置
有的环境并不需要Swagger,这时我们可以将其关掉。
1.配置
#swagger 开关
swagger2.enable=true2.将其注入配置类
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Value("${swagger2.enable}")
private boolean enable;
@Bean
public Docket createDocket(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
//要暴露的接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.xxx.xxx.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
.globalOperationParameters(parameterList)
.enable(enable);
}
//信息的描述
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder().
title("Swagger api") //标题
.description("spring boot 2.x 集成Swagger") //描述
.version("1.0") //版本
.build();
}
}
(四)Swagger的全局配置
如果想Swagger也能像PostMan一样可以加一些头部信息的话,就需要对Swagger进行全局配置
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Value("${swagger2.enable}")
private boolean enable;
@Bean
public Docket createDocket(){
List<Parameter> parameterList=new ArrayList<>();
ParameterBuilder parameterBuilder=new ParameterBuilder();//头部信息
parameterBuilder.name("token").description("swagger调试(模拟传入用户认证凭证)").modelRef(new ModelRef("String"))
.parameterType("header").required(false);
parameterList.add(parameterBuilder.build());
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
//要暴露的接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.yingxue.lesson.web.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
.globalOperationParameters(parameterList)
.enable(enable);
}
//信息的描述
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder().
title("Swagger api") //标题
.description("spring boot 2.x 集成Swagger") //描述
.version("1.0") //版本
.build();
}
}
十、SpringBoot封装整合Redis
1.初始Redis:You辉编程_Redis数据库_You辉编程的博客-CSDN博客
2.Srpingboot+jedis
jedis集成了redis的命令擦操作,jedis是redis官方推荐面向Java操作Redis的客户端 。
(1)引入相关依赖
<!--springboot封装redis的组件依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jedis客户端-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>(2)配置jedisPool连接池管理jedis
#jedisPool的配置开始
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
redis.maxIdle=30
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
redis.minIdle=1
#连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
redis.maxTotal=100
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)10秒redis.maxWait=10000
# Redis服务器地址
redis.host=localhost
# Redis服务器连接端口
redis.port=6379
# Redis链接超时时间 10秒
redis.timeout=10000(3)配置类
package com.yh.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.maxIdle}")
private int maxIdle;
@Value("${redis.minIdle}")
private int minIdle;
@Value("${redis.maxTotal}")
private int maxTotal;
@Value("${redis.timeout}")
private int timeout;
@Value("${redis.maxWait}")
private int maxWait;
@Value("${redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${redis.port}")
private int port;
/**
* 把 jedisPool连接池注入到spring容器中
* @return
*/
@Bean
public JedisPool getJedisPool(){
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(maxIdle);
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(minIdle);
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(maxTotal);
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWait);
JedisPool jedisPool = new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig,host,port,timeout);
return jedisPool;
}
}
(4)创建RedisService类,jedis企业开发工具类的封装
package com.yh.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Service
public class RedisService {
//注入连接池
@Autowired
private JedisPool jedisPool;
public boolean exists(String key){
Jedis jedis = null;
boolean result;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
result = jedis.exists(key);
} finally {
if(jedis != null){
jedis.close();
}
}
return result;
}
public Long del(final String... keys){
Jedis jedis = null;
Long result;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
result = jedis.del(keys);
} finally {
if(jedis != null){
jedis.close();
}
}
return result;
}
}
(5)测试
@Autowired
private RedisService redisService;
@Test
public void testRedis(){
redisService.exists("name");
redisService.del("name","name1");
}3.SpringBoot+RedisRedisTemplate工具类封装自定义序列化方式
RedisTemplate类是对Redis api进一步进行封装,使操作Redis更加便捷。
(1)引入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>(2)配置
# Redis 服务器地址
spring.redis.host=localhost
# Redis 服务器连接端⼝
spring.redis.port=6379
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)默认 8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=100
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)默认 -1 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=PT10S
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接默认 8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=30
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接默认 0
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=1
#链接超时时间
spring.redis.timeout=PT10S(3)测试
SpirngBoot已经自动把RedisTemplate注入到Spring容器中,直接拿来用即可。并提供了一下方法
@Test
public void testRedis(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
//指定序列化,使它的key,value可读即显示正常的字符
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","赵六");
}注:RedisTemplate默认只支持String类型的数据,要想支持除String以外的数据,则要自己定义序列化方式(需要引入fast json依赖)。
<!--fastJson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.49</version>
</dependency>自定义序列化方式代码
public class MyStringRedisSerializer implements RedisSerializer<Object> {
private final Charset charset;
public MyStringRedisSerializer() {
this(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
public MyStringRedisSerializer(Charset charset) {
Assert.notNull(charset, "Charset must not be null!");
this.charset = charset;
}
@Override
public String deserialize(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes == null ? null : new String(bytes, charset));
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(Object object) {
if (object == null) {
return new byte[0];
}
if(object instanceof String){
return object.toString().getBytes(charset);
}else {
String string = JSON.toJSONString(object);
return string.getBytes(charset);
}
}
}
封装成工具类
package com.yh.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Service
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate;
public boolean hasKey(String key){
if(key == null){
return false;
}
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
}
配置类
package com.yh.config;
import com.yh.serializer.MyStringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new MyStringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new MyStringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
}
异常类
package com.yh.exception;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
public class BusinessExcception extends RuntimeException{
private final int messageCode;
private final String messageDefault;
public BusinessExcception(String message,int messageCode) {
super(message);
this.messageCode = messageCode;
this.messageDefault = message;
}
public int getMessageCode() {
return messageCode;
}
public String getMessageDefault() {
return messageDefault;
}
}
测试
@Autowired
private RedisService redisService;
@Test
public void testRedis(){
// redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
// //指定序列化,使它的key,value可读即显示正常的字符
// redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","赵六");
System.out.println(redisService.hasKey("name"));
}4.SpringBoot redis实战-分布式Session共享
实现思路
用户提交用户名+密码--->登录成功后生成token--->把用户信息存入Redis(key就是token,value就是userId)--->设置key的过期时间(模拟Session的过期时间,一般我1h)--->拦截器拦截请求校验sessionId
boot-redis-session: redis实行分布式session共享 (gitee.com)
十一、SpringBoot集成定时任务、异步调用
1.定时任务实现方式
注:需要在启动类中加
@EnableScheduling //开启定时任务
package com.yh.bootschedule.task;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Component
public class SchedulerTask {
private static final SimpleDateFormat f=new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
/**
* @Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) :上一次开始执行时间点之后5秒再执行
* @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000) :上一次执行完毕时间点之后5秒再执行
* @Scheduled(initialDelay=1000, fixedRate=5000) :第一次延迟1秒后执行,之后按fixedRate的规则每5秒执行一次
*/
//方式一
//定时任务5秒执行一次
// @Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)
// public void processFixedRate(){
// System.out.println("processFixedRate方式:开始定时任务,现在的时间是:"+f.format(new Date()));
// }
/**
* cron 一共有七位,最后一位是年,Spring Boot 定时方案中只需要设置六位即可:
* 第一位,表示秒,取值 0 ~ 59; 第二位,表示分,取值 0 ~ 59; 第三位,表示小时,取值 0 ~ 23; 第四位,日期天/日,取值 1 ~
* 31; 第五位,日期月份,取值 1~12; 第六位,星期,取值 1 ~ 7,星期一,星期二...,注,1 表示星期 天,2 表示星期一; 第七位,
* 年份,可以留空,取值 1970 ~ 2099。 cron 中,还有一些特殊的符号,含义如下: (*)星号,可以理解为每的意思,每秒、每分、
* 每天、每月、每年...。 (?)问号,问号只能出现在日期和星期这两个位置,表示这个位置的值不确定。 (-)减号,表达一个范围,
* 如在小时字段中使用“10 ~ 12”,则表示从 10 到 12 点,即 10、11、12。 (,)逗号,表达一个列表值,如在星期字段中使用“1、2、
* 4”,则表示星期一、星期二、星期四。 (/)斜杠,如 x/y,x 是开始值,y 是步⻓长,比如在第一位(秒),0/15 就是从 0 秒开始,
* 每隔 15 秒执 行一次。 下面列举几个常用的例子。 0 0 1 * * ? :每天凌晨1 点执行; 0 5 1 * * ?:每天 凌晨1 点 5 分执行;
* 以上就是 Spring Boot 自定的定时方案,使用起来非常的简单方便。
*/
//方式二
@Scheduled(cron="*/5 * * * * ?")
private void processCron(){
System.out.println("processCron方式:定时任务开始运行,现在时间:" + f.format(new Date()));
}
}
2.SpringBoot使用@Async实现异步调用-异步回调结果
注:需要在启动类中添加@EnableAsync注解
package com.yh.task;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
/**
* 这是同步
*/
public static Random random=new Random();
@Async
public Future<String> doTaskOne() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始任务一");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前时间
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100000));
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("完成任务一消耗的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一已完成");
}
@Async
public Future<String> doTaskTwo() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始任务二");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前时间
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100000));
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("完成任务二消耗的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一已完成");
}
@Async
public Future<String> doTaskThree() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始任务三");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前时间
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100000));
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("完成任务三消耗的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一已完成");
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testTask() throws Exception{
Future<String> taskOne=asyncTask.doTaskOne();
Future<String> taskTwo=asyncTask.doTaskTwo();
Future<String> taskThree=asyncTask.doTaskThree();
while (true){
if(taskOne.isDone()&&taskTwo.isDone()&&taskThree.isDone()){
//代处理完后统一返回结果集
break;
}
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
3.SpringBoot使用@Async实现异步调用-自定义线程池
使用@EnableAsync+@Async默认实现SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor 不是真的线程池,这个类不重用线程,每次调用 都会创建一个新的线程,非常的消耗资源。
(1)注入线程池对象
package com.yh;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BootAsyncApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BootAsyncApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Executor myTaskExecutor(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//创建线程池,并初始化线程数量
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
//最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(15);
//用来缓冲执行任务的队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(200);
//当超过核心先线程数之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后就会被销毁
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
//设置好之后可以方便定位处理任务所在的线程池
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("myTask");
//用来设置线程池关闭的时候等待所有任务都完成再继续销毁其他的Bean
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
//该方法用来设置线程池中任务的等待时间,如果超过这个时候还没有销毁就强制销毁,以确保应用最后能够被关闭,而不是阻塞住。
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
//线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略:这里采用了CallerRunsPolicy策略,当线程池没有处理能力的时候,该策略会直接在execute 方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务;如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}
package com.yh.task;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
/**
* 这是同步
*/
public static Random random=new Random();
@Async("myTaskExecutor")
public Future<String> doTaskOne() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始任务一");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前时间
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100000));
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("完成任务一消耗的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一已完成");
}
@Async("myTaskExecutor")
public Future<String> doTaskTwo() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始任务二");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前时间
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100000));
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("完成任务二消耗的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一已完成");
}
@Async("myTaskExecutor")
public Future<String> doTaskThree() throws Exception{
System.out.println("开始任务三");
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前时间
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(100000));
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("完成任务三消耗的时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一已完成");
}
}
@Test
public void testTask() throws Exception{
Future<String> taskOne=asyncTask.doTaskOne();
Future<String> taskTwo=asyncTask.doTaskTwo();
Future<String> taskThree=asyncTask.doTaskThree();
while (true){
if(taskOne.isDone()&&taskTwo.isDone()&&taskThree.isDone()){
//代处理完后统一返回结果集
break;
}
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
十二、SpringBoot权限框架Shiro
subject:主体,可以是用户也可以是程序,主体要访问系统,系统需要对主体进行认证、授权。
security Manager:安全管理器,主体进行认证和授权都是通过securityManager进行。
authenticator:认证器,主体进行认证最终通过authenticator进行的。
authorizer:授权器,主体进行授权最终通过authorizer进行的。
sessionManager:web应用中一般是用web容器对session进行管理,shiro也提供一套session管理的方式。
SessionDao: 通过SessionDao管理session数据,针对个性化的session数据存储需要使用sessionDao。
cache Manager:缓存管理器,主要对session和授权数据进行缓存,比如将授权数据通过cacheManager进行缓存管理,和
ehcache整合对缓存数据进行管理。
Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库,而不是明文存储。
realm:域,领域,相当于数据源,通过realm存取认证、授权相关数据。
记住一点,Shiro 不会去维护用户、维护权限;这些需要我们自己去设计/提供;然后通过相应的接口注入给Shiro 即可。 <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>(2)用户认证
public void authentication(){
/*****************安全管理器环境**************************/
//构建安全管理器环境SecurityManager环境
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//创建数据源
SimpleAccountRealm simpleAccountRealm=new SimpleAccountRealm();
simpleAccountRealm.addAccount("zhangwuji","666666");
//设置到安全管理器
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(simpleAccountRealm);
//把安全管理器配置到工具包里
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
/*****************安全管理器环境**************************/
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//获取主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建主体提交时需要携带的token(由用户名密码组成)
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken=new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangwuji","666666");
try {
//主体提交验证
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//验证通过返回true,不通过返回false
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
//退出
subject.logout();
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
}catch (UnknownAccountException uae){
System.out.println("用户不存在");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (LockedAccountException lae){
System.out.println("账号已经被锁定");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}
}
(2)用户授权
public void authorization(){
/*****************安全管理器环境**************************/
//构建安全管理器环境SecurityManager环境
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//创建数据源
SimpleAccountRealm simpleAccountRealm=new SimpleAccountRealm();
simpleAccountRealm.addAccount("zhangwuji","666666","admin","test");//更具角色授权
//设置到安全管理器
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(simpleAccountRealm);
//把安全管理器配置到工具包里
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
/*****************安全管理器环境**************************/
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//获取主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建主体提交时需要携带的token(由用户名密码组成)
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken=new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangwuji","666666");
try {
//主体提交验证
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//验证通过返回true,不通过返回false
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
//判断该用户是否拥有这个角色
subject.checkRoles("admin","user");
//退出
subject.logout();
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
}catch (UnknownAccountException uae){
System.out.println("用户不存在");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (LockedAccountException lae){
System.out.println("账号已经被锁定");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (UnauthorizedException e){
System.out.println("该用户没有该权限访问");
}
}(3)SpringBoot使用IniRealm进行认证授权
SimpleAccountRealm写死了用户数据,不够灵活,IniRealm是Shiro提供一种Realm实现。用户、角色、权限等信息集中在一个.ini文件里。
①配置.ini文件
在resources目录下创建一个shiro.ini文件(角色的配置文件)
[users] ----->用户的角色
test=666666,test
admin=66666,admin
[roles]------->用户的权限
test=user:list,user:edit
admin=*②读取角色信息并认证授权
public void testIniRealm(){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//读取配置文件的内容
IniRealm iniRealm=new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini");
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(iniRealm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//获取主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建主体提交时需要携带的token(由用户名密码组成)
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken=new UsernamePasswordToken("test","666666");
try {
//主体提交验证
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//验证通过返回true,不通过返回false
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
//判断该用户是否拥有这个角色
subject.checkRoles("test");
//校验是否拥有其权限
subject.checkPermissions("user:list");//是否拥有用户列表的权限
//退出
subject.logout();
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
}catch (UnknownAccountException uae){
System.out.println("用户不存在");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (LockedAccountException lae){
System.out.println("账号已经被锁定");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (UnauthorizedException e){
System.out.println("该用户没有该权限访问");
}
}(4)SpringBoot使用JdbcRealm进行认证授权
IniRealm虽然可以通过.ini文件进行配置然后读取其安全信息,但还是得提前写好相关信息,还是不够灵活,JdbcRealm可以直接从db中读取信息,然后再认证授权认证。
①加入数据库相关依赖
<!--数据库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--数据源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>②用户权限信息
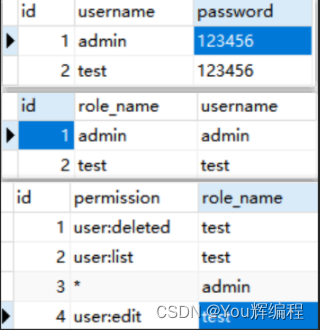
③认证授权
public void testJdbcRealm(){
//配置数据源
DruidDataSource druidDataSource=new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro");
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
druidDataSource.setUsername("root");
druidDataSource.setPassword("666666");
//配置文件中的用户权限信息
JdbcRealm jdbcRealm=new JdbcRealm();
jdbcRealm.setDataSource(druidDataSource);
//开启权限开关
jdbcRealm.setPermissionsLookupEnabled(true);
//构建SecurityManager环境
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//设置Realm
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(jdbcRealm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//获取主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建主体提交时需要携带的token(由用户名密码组成)
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken=new UsernamePasswordToken("test","123456");
try {
//主体提交验证
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//验证通过返回true,不通过返回false
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
//判断该用户是否拥有这个角色
subject.checkRoles("test");
//校验是否拥有其权限
subject.checkPermissions("user:deleted","role:list");//是否拥有用户列表的权限
//退出
subject.logout();
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
}catch (UnknownAccountException uae){
System.out.println("用户不存在");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (LockedAccountException lae){
System.out.println("账号已经被锁定");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (UnauthorizedException e){
System.out.println("该用户没有该权限访问");
}
}
(5)Springboot使用自定义Realm进行认证授权
JdbcRealm虽然能从数据库读取用户授权信息,但其底层已经固定写好了sql语句,一旦数据库名或表名发生改变有得重新改写底层sql这样一来就造成不灵活,自定义Realm可以解决这个问题。
Realm只需要继承:AuthorizingRealm重写doGetAuthenticationfo(用户认证)、doGetAuthorizationInfo(用户授权)这两个方法即可。
①自定义Realm
package com.yh.shiro;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.swing.text.SimpleAttributeSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
/**
* mock用户信息
* @param principalCollection
* @return
*/
/************************数据*************************/
private Map<String,String> userMap=new HashMap<>();
{
userMap.put("admin","123456");
userMap.put("test","123456");
}
/************************数据*************************/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//用户授权
String username = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
//获取角色信息
List<String> roles=getRolesByUserName(username);
List<String> permissions=getPermissionsByUsername(username);
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info=new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addRoles(roles);
info.addStringPermissions(permissions);
return info;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
//获取用户数据
String username = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
String password = getPasswordByUsername(username);
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(password)){
return null;
}
//用户认证
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info=new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,password,getName());
return info;
}
//通过用户名获取到密码
private String getPasswordByUsername(String username){
return userMap.get(username);
}
//通过用户名获取角色信息
private List<String> getRolesByUserName(String username){
List<String> roles=new ArrayList<>();
if(username.equals("admin")){
roles.add("admin");
}else {
roles.add("test");
}
return roles;
}
//通过用户名获取权限信息
private List<String> getPermissionsByUsername(String username){
List<String> permissions=new ArrayList<>();
if(username.equals("admin")){
permissions.add("*");//权限为所有
}
permissions.add("user:list");
permissions.add("user:deleted");
permissions.add("user:edit");
return permissions;
}
}
②认证授权
public void testCustomRealm(){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//创建域
CustomRealm customRealm=new CustomRealm();
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(customRealm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//获取主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建主体提交时需要携带的token(由用户名密码组成)
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken=new UsernamePasswordToken("test","123456");
try {
//主体提交验证
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//验证通过返回true,不通过返回false
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
//判断该用户是否拥有这个角色
subject.checkRoles("test");
//校验是否拥有其权限
subject.checkPermissions("user:deleted","role:list");//是否拥有用户列表的权限
//退出
subject.logout();
System.out.println("用户认证的状态"+subject.isAuthenticated());
}catch (UnknownAccountException uae){
System.out.println("用户不存在");
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (LockedAccountException lae){
System.out.println("账号已经被锁定");
}catch (AuthenticationException ae){
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
}catch (UnauthorizedException e){
System.out.println("该用户没有该权限访问");
}
}
(6)SpringBoot整合shiro——盐值加密
①自定义Realm
package com.yh.shiro;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.Md5Hash;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.swing.text.SimpleAttributeSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author youHui
**/
public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
/**
* mock用户信息
* @param principalCollection
* @return
*/
/************************数据*************************/
private Map<String,String> userMap=new HashMap<>();
{
userMap.put("admin","123456");
userMap.put("test","123456");
}
/************************数据*************************/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//用户授权
String username = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
//获取角色信息
List<String> roles=getRolesByUserName(username);
List<String> permissions=getPermissionsByUsername(username);
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info=new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addRoles(roles);
info.addStringPermissions(permissions);
return info;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException {
//获取用户数据
String username = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
String password = getPasswordByUsername(username);
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(password)){
return null;
}
//用户认证
// info=new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,password,getName());
//SimpleAuthenticationInfo info=new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,getEncPassword(password),getName());
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info=new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(
username,getEncPassword(password,username),getName());
//设置盐值
info.setCredentialsSalt(ByteSource.Util.bytes(username));
return info;
}
//通过用户名获取到密码
private String getPasswordByUsername(String username){
return userMap.get(username);
}
//通过用户名获取角色信息
private List<String> getRolesByUserName(String username){
List<String> roles=new ArrayList<>();
if(username.equals("admin")){
roles.add("admin");
}else {
roles.add("test");
}
return roles;
}
//通过用户名获取权限信息
private List<String> getPermissionsByUsername(String username){
List<String> permissions=new ArrayList<>();
if(username.equals("admin")){
permissions.add("*");//权限为所有
}
permissions.add("user:list");
permissions.add("user:deleted");
permissions.add("user:edit");
return permissions;
}
//返回密文密码
private String getEncPassword(String password,String salt){
return new Md5Hash(password,salt,3).toString();
}
//private String getEncPassword(String password){
//return new Md5Hash(password,null,3).toString();
//}
}
②认证授权
public void testSaltMatcher(){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
CustomRealm customRealm = new CustomRealm();
//指定解密得方式
HashedCredentialsMatcher matcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
matcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");//md5加密
matcher.setHashIterations(3);//加密得次数
//配置到域中
customRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(matcher);
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(customRealm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//获取主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建主体提交时需要携带的token(由用户名密码组成)
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("test", "123456");
try {
//主体提交验证
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
/*****************主体提交验证**************************/
//验证通过返回true,不通过返回false
System.out.println("用户认证的状态" + subject.isAuthenticated());
//判断该用户是否拥有这个角色
subject.checkRoles("test");
//校验是否拥有其权限
subject.checkPermissions("user:deleted", "role:list");//是否拥有用户列表的权限
//退出
subject.logout();
System.out.println("用户认证的状态" + subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
System.out.println("用户不存在");
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
System.out.println("账号已经被锁定");
} catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
System.out.println("用户名密码不匹配");
} catch (UnauthorizedException e) {
System.out.println("该用户没有该权限访问");
}
}




















 377
377











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








