目录
1. 多窗口买票
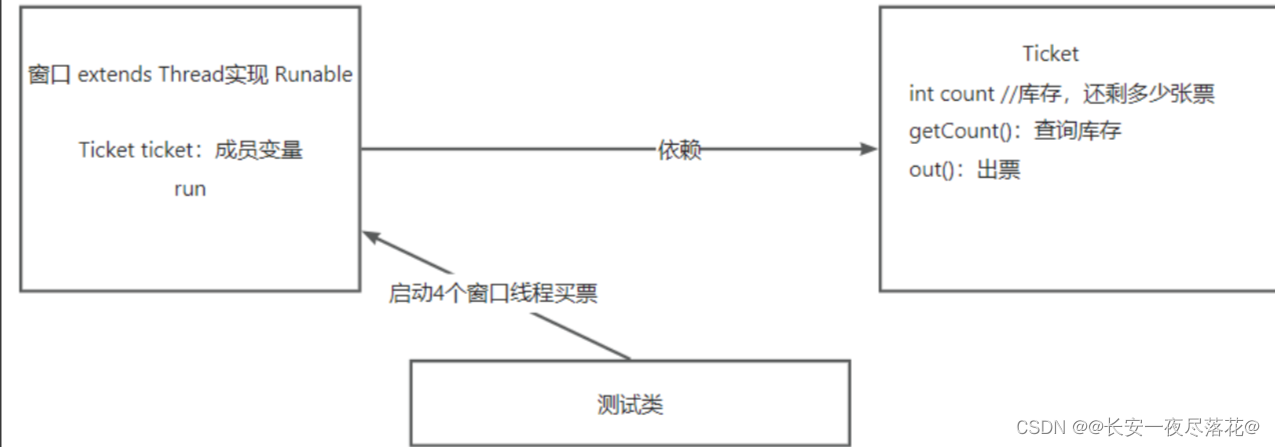
多窗口售票问题
问题:剩余票数为负数
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
ticket.setCount(100);
TicketTask ticketTask = new TicketTask(ticket);
Thread t1 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口3");
Thread t4 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口4");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();//同时启动四个线程
}
}
public class Ticket {
private int count;
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public int checkCount(){
return this.count;
}
public void outTicket(){
this.count--;
}
}
public class TicketTask implements Runnable {
private Ticket ticket;
public TicketTask() {
}
public TicketTask(Ticket ticket) {
this.ticket = ticket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (ticket.checkCount() <= 0)
break;
try {
Thread.sleep(550);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket.outTicket();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 剩余票数:" + ticket.checkCount());
}
}
}
结果为:
窗口3 剩余票数:7
窗口2 剩余票数:4
窗口1 剩余票数:3
窗口3 剩余票数:2
窗口4 剩余票数:4
窗口4 剩余票数:1
窗口3 剩余票数:-2
窗口1 剩余票数:-1
窗口2 剩余票数:-1
理想状态是当票零时,停止出售,买票任务不安全
- 超卖问题的原因:当多条语句在操作同一个线程共享数据时,一个线程对多条语句只执行了一部分,还没有执行完,另一个线程参与进来执行。导致共享数据的错误。
- 解决办法:对多条操作共享数据的语句,只能让一个线程都执行完,在执行过程中,其他线程不可以参与执行。
2. 临界区代码块
临界区代码段是每个线程中访问临界资源的那段代码,多个线程必须互斥地对临界区资源进行访问。线程进入临界区代码段之前,必须在进入区申请资源,申请成功之后进行临界区代码段,执行完成之后释放资源。临界区代码段(Critical Section)的进入和退出即:多个线程同时访问的代码块,比如上面的例子:
while (true) {
if (ticket.checkCount() <= 0)
break;
try {
Thread.sleep(550);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket.outTicket();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 剩余票数:" + ticket.checkCount());
}
3. 共享数据
临界区代码块中,多个线程共享访问的堆里面的数据
- 一般的共享数据为堆中的数据
- 加锁通常是给共享数据加锁
4. synchronized内置锁
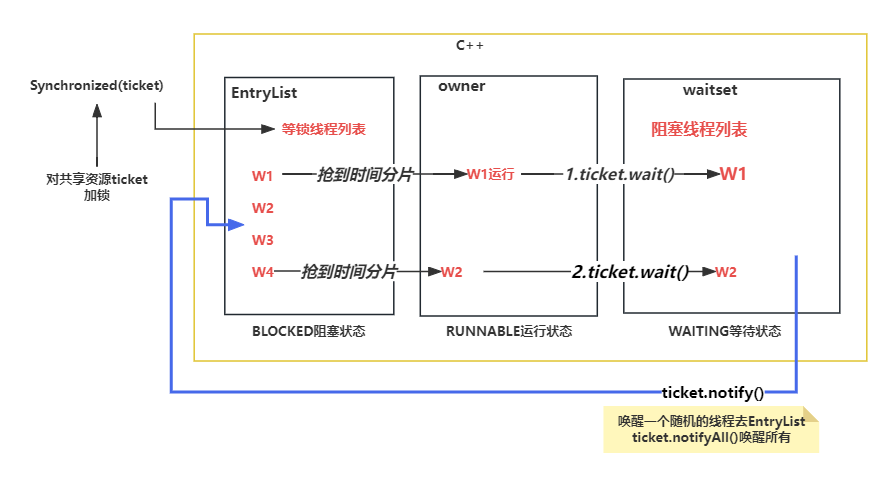
5. synchronized语法
5.1 代码块
synchronized (共享对象(plus,ticket)) {//临界区代码块
对共对象的访问(plus)(ticket)
}
比如售票买票系统
多窗口售票问题
使用synchronized上锁
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
ticket.setCount(100);
TicketTask ticketTask = new TicketTask(ticket);
Thread t1 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口3");
Thread t4 = new Thread(ticketTask,"窗口4");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
public class Ticket {
private int count;
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public int checkCount(){
return this.count;
}
public void outTicket(){
this.count--;
}
}
public class TicketTask implements Runnable {
private Ticket ticket;
public TicketTask() {
}
public TicketTask(Ticket ticket) {
this.ticket = ticket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {//对代码块进行上锁,锁为:该对象变量名
if (ticket.checkCount() <= 0)
break;
try {
Thread.sleep(550);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket.outTicket();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 剩余票数:" + ticket.checkCount());
}
}
}
}
5.2 实例方法上锁
相当于synchronized(this)
比如对汽车的保养过程
汽车的打蜡抛光(非静态)
public class SynDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car a = new Car();
Thread1 t1 = new Thread1(a);
Thread2 t2 = new Thread2(a);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class Thread1 extends Thread {
private Car a;
public Thread1(Car a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void run() {
a.fun1();
}
}
class Thread2 extends Thread {
private Car a;
public Thread2(Car a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void run() {
a.fun2();
}
}
class Car {
public void fun1() {
synchronized (this) {
System.out.println("开始打蜡");
try {
Thread.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("打蜡结束");
}
}
public void fun2() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("开始抛光");
System.out.println("抛光结束");
}
}
}
}
开始打蜡
打蜡结束
开始抛光
抛光结束
5.3 静态方法上锁
相当于synchronized(class),
public class SynDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car a = new Car();
Thread t1 = new Thread1(a);
Thread t2 = new Thread2(a);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class Thread1 extends Thread {
private Car a;
public Thread1(Car a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void run() {
a.fun1();
}
}
class Thread2 extends Thread {
private Car a;
public Thread2(Car a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void run() {
a.fun2();
}
}
class Car {
public synchronized static void fun1() {
System.out.println("开始打蜡");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("打蜡结束");
}
public static void fun2() {
synchronized (Car.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("开始抛光");
System.out.println("抛光结束");
}
}
}
6. 必须有相同的锁
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 t1 = new MyThread1();
MyThread2 t2 = new MyThread2();
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
synchronized (String.class) {
System.out.println("a");
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("b");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
synchronized (Integer.class) {
System.out.println("1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("2");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
否则无效
7. 死锁
Synchronized嵌套使用时,比如张三在A电话亭想去B电话亭,李四在B电话亭想去A电话亭,这时会发生死锁。
a线程锁定一个资源,同时想获取b线程的资源,b线程锁定一个资源,同时想获取a线程的资源。
此时会发生死锁
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (String.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
synchronized (Integer.class) {
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Integer.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
synchronized (String.class) {
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
8. CountDownLatch
juc的公共锁
- 构造函数new CountDownLatch(10)授权数量
- countDown()授权数量-1
- awit()执行后线程进入阻塞状态,直到授权数量=0;
public class Plus {
private int count;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void selfPlus(){
count++;
}
}
public class MyTask implements Runnable {
private Plus plus;
public MyTask() {
}
public MyTask(Plus plus) {
this.plus = plus;
}
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(4);
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (plus) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) {
plus.selfPlus();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Plus plus = new Plus();
MyTask myTask = new MyTask(plus);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
new Thread(myTask).start();
}
myTask.countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("真实值 = " + plus.getCount());
}
}
实际值为:400000000






















 904
904

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








