3.假设顺序列表ArrayList中存储的元素是整型数字1~5,遍历每个元素,将每个元素顺序输出。(你能想到的所有方式)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add(1);
c.add(2);
c.add(3);
c.add(4);
c.add(5);
//collection 方法1
for (int i = 0; i < c.size(); i++) {
ArrayList a = (ArrayList) c;
Object o = a.get(i);
System.out.print(o+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------");
//collection 方法2
for (Object o : c) {
System.out.print(o+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------");
//collection 方法3
Iterator iterator = c.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.print(next+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------");
//List
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
//List 方法1
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-------------");
//List 方法2
for (Object list1 : list) {
System.out.print(list1+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------");
//List 方法3
Iterator iterator1 = list.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
Object next = iterator1.next();
System.out.print(next+" ");
}
}
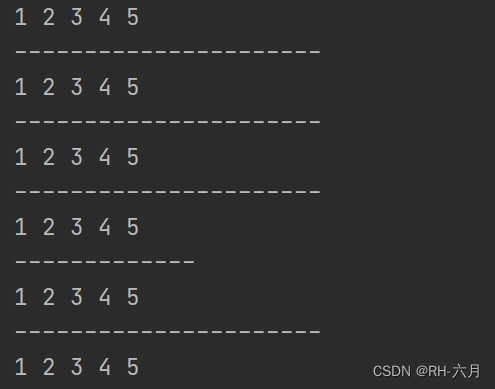
4.生成10个1到20之间的不重复的随机数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
while (set.size()<10){
int i = (int) (Math.random()*20+1);
set.add(i);
}
System.out.println(set);
}
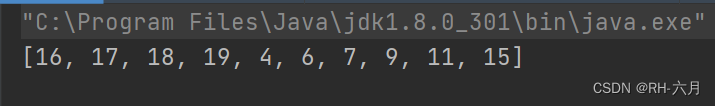
5.用一个大集合存入20个随机数字,然后筛选其中的偶数元素,放到小集合当中然后进行遍历输出
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set1 = new HashSet();
while (set1.size()<20){
Random r = new Random();
set1.add(r.nextInt(100));
}
System.out.println(set1);
Set set2 = new HashSet();
for (Object o :set1) {
Integer a = (Integer) o;
if(a%2==0){
set2.add(a);
}
}
System.out.println(set2);
}
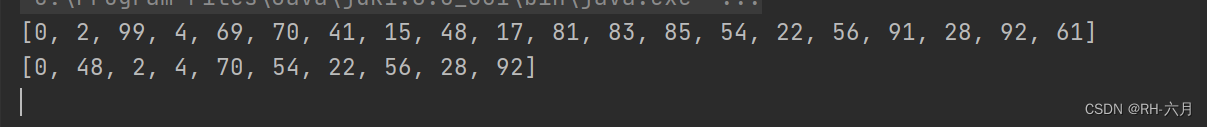
6.ArrayList去除集合中字符串的重复值(字符串的内容相同)
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add("hello");
arrayList.add("world");
arrayList.add("java");
arrayList.add("HelloWorld");
arrayList.add("hello");
System.out.println(arrayList);
ArrayList arrayList2 = new ArrayList();
for (Object o:arrayList) {
if (!arrayList2.contains(o)){
arrayList2.add(o);
}
}
System.out.println(arrayList2);
}
7.创建两个Set集合,判断这两个集合是否有交集,并打印出他们的交集
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set1 = new HashSet();
Set set2 = new HashSet();
set1.add("hello");
set2.add("hello");
set1.add("world");
set2.add("world");
set1.add("java");
set2.add("python");
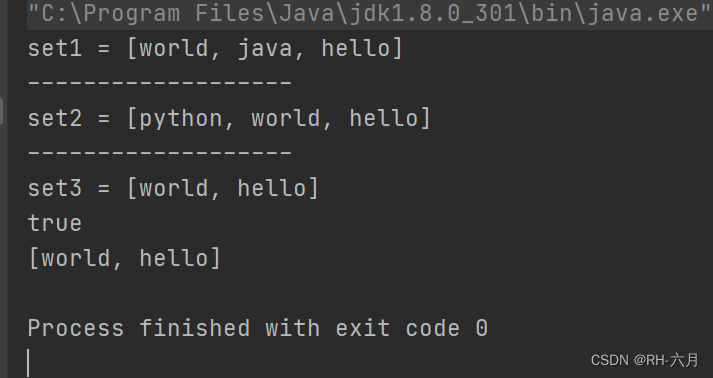
System.out.println("set1 = "+set1);
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println("set2 = "+set2);
System.out.println("-------------------");
//方法一
Set set3 = new HashSet();
for (Object o :set1) {
if (set2.contains(o)){
set3.add(o);
}
}
System.out.println("set3 = " + set3);
//方法二
System.out.println(set1.retainAll(set2));
System.out.println(set1);
}
注意逻辑
8.将1-10按照奇数在前偶数在后,奇数正序,偶数倒叙的方式保存到Set集合中(排序)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Integer a1= (Integer) o1;
Integer a2= (Integer) o2;
{
//降序
if (a1 % 2 == 0 && a2 % 2 == 0) {
return a2 - a1;
}
//升序
if (a1 % 2 == 1 && a2 % 2 == 1) {
return a1 - a2;
}
//前偶后奇 换位
if (a1 % 2 == 0 && a2 % 2 != 0) {
return 1;
}
//前奇后偶 不换
if (a1 % 2 != 0 && a2 % 2 == 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
set.add(i);
}
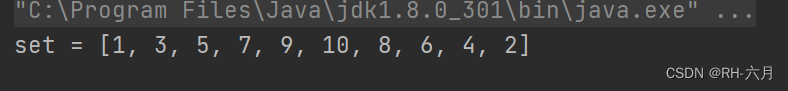
System.out.println("set = " + set);
}
9.将学生按照成绩保存到集合中,并且名字叫tom的学生不管考多少分都位于班级的第一位
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
//o1新值o2老值
Student personNew = (Student) o1;
Student personOld = (Student) o2;
{
String s = "tom";
//tom
if (personNew.getName().equals(s)&&!personOld.getName().equals(s)){
return -1;
}
if (!personNew.getName().equals(s)&&personOld.getName().equals(s)){
return 1;
}
if (!personNew.getName().equals(s)&&!personOld.getName().equals(s)){
Integer personNew_score = ((Student) o1).getScore();
Integer personOld_score = ((Student) o2).getScore();
return personOld_score-personNew_score;
}
if (personNew.getName().equals(s)&&personOld.getName().equals(s)){
Integer personNew_score = ((Student) o1).getScore();
Integer personOld_score = ((Student) o2).getScore();
return personOld_score-personNew_score;
}
}
return 0;
}
});
set.add(new Student("tom",60));
set.add(new Student("tom",70));
set.add(new Student("rh",80));
set.add(new Student("zzb",100));
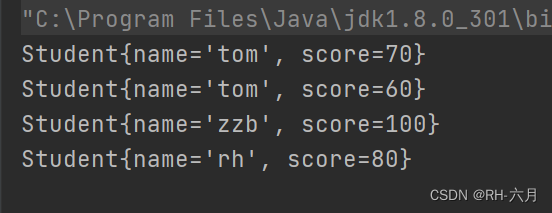
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
class Student{
private String name;
private int score;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public Student() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return score == student.score && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, score);
}
}
10.编写一个学生管理类,可以添加学生(学号要有唯一性)、删除学生、查看学生信息,使用List集合来实现
public class StudentMange {
static List list = new ArrayList();
public static void main(String[] args) {
addStudent(new Student2("tom",1));
addStudent(new Student2("tom",2));
addStudent(new Student2("zzb",3));
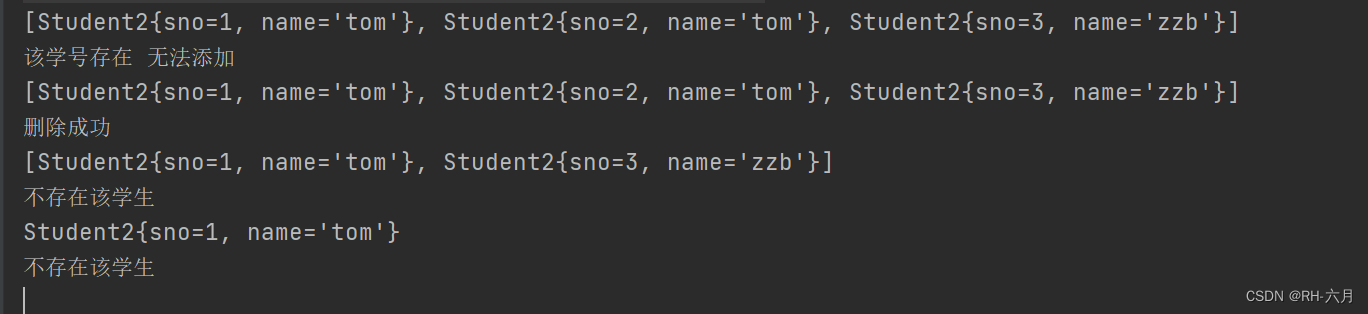
System.out.println(list);
addStudent(new Student2("jim",1));
System.out.println(list);
deleteStudent(2);
System.out.println(list);
deleteStudent(4);
showStudent(1);
showStudent(4);
}
private static void addStudent(Student2 student2) {
for (Object o : list) {
Student2 addstudent = (Student2) o;
if (student2.getSno()==addstudent.getSno()){
System.out.println("该学号存在 无法添加");
return;
}
}
list.add(student2);
}
private static void deleteStudent(int id ) {
Student2 stu = null;
for (Object o : list) {
Student2 addstudent = (Student2) o;
if (id==addstudent.getSno()){
stu=addstudent;
}else {
continue;
}
}
if (stu==null){
System.out.println("不存在该学生");
}else {
list.remove(stu);
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}
private static void showStudent(int id) {
Student2 stu = null;
for (Object o : list) {
Student2 addstudent = (Student2) o;
if (id==addstudent.getSno()){
stu=addstudent;
}else {
continue;
}
}
if (stu==null){
System.out.println("不存在该学生");
}else {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
}
class Student2{
private int sno;
private String name;
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(String name, int sno) {
this.sno=sno;
this.name=name;
}
public int getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student2{" +
"sno=" + sno +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}





















 1131
1131











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








