一、插入节点
<div class="box">
<div class="xx">111</div>
<div class="xx">22233</div>
<div class="xx">333</div>
<div class="xx">444</div>
</div>
<script>
var box=document.querySelector(".box")
var yy=document.createElement("span")
yy.innerHTML="hello"
box.insertBefore(yy,box.children[2])
</script>


2、事件语法
1、事件绑定
事件:元素在某种状态(浏览器实现的也叫事件触发)达成时 要执行的提前设定好程序 我们称之为事件句柄
三要素: 事件源 事件类型 事件处理程序(handler)
事件绑定方式:
(1)行内式:标签的属性值是执行代码
<div class="box" onclick="javaScript:console.log(9999999)">good</div>
(2)属性绑定:只能绑定一个handler(事件处理程序)
<div class="box" onclick="javaScript:myconsole.mylog()">gousd</div>
<div class="box" onclick="myconsole.mylog()">gousd</div>
<div class="box" onclick="fn()">hello</div>
<script>
var myconsole={
mylog:()=>{
console.log("你好")
}
}
function fn(){
console.log("暗号")
}
</script>
(3)给元素添加一个事件监听器 (函数处理程序)
<div class="box">well</div>
<script>
var box=document.querySelector(".box")
box.addEventListener("click",function(){
console.log("牡丹江")
}
</script>
事件的解绑方式:box.οnclick=null
2、事件类型
鼠标、滚轴:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<style>
.mouse{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
margin-left: 30px;
text-align: center;
background-color: powderblue;
cursor: alias;
overflow-y: scroll;
}
.box{
margin-left: 90px;
width: 80px;
height: 800px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
<div class="mouse">good
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<script>
var mouse=document.querySelector(".mouse")
mouse.addEventListener("click",()=>{
console.log("鼠标按下和松开时,鼠标指针在被选中的区域内")
})
mouse.addEventListener("dbclick",()=>{
console.log("鼠标第一次按下和第二次松开时,鼠标指针在被选区域内,并且时间间隔不能太长")
})
mouse.addEventListener("mousedown",()=>{
console.log("鼠标在被选区域内按下")
})
mouse.addEventListener("mouseup",()=>{
console.log("鼠标在被选区域内松开")
})
mouse.addEventListener("mouseover",()=>{
console.log("鼠标进入被选区域")
})
mouse.addEventListener("mouseout",()=>{
console.log("鼠标从被选区域内出去")
})
mouse.addEventListener("mouseleave",()=>{
console.log("鼠标从被选区域离开")
})
mouse.addEventListener("mouseenter",()=>{
console.log("鼠标从被选区域进入")
})
mouse.onwheel=function(){
console.log("鼠标滚轴滚动时,鼠标指针在被选元素内部")
}
mouse.addEventListener("scroll",function(){
console.log("元素自己的滚动条滚动,单位时间内滚动条的位置发生变化 ")
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
输入框:
<input type="text" name="" id="btn" autofocus>
<script>
var btn=document.querySelector("#btn")
btn.addEventListener("keydown",()=>{
console.log("输入框的键盘按下")
})
btn.addEventListener("keyup",()=>{
console.log("输入框的键盘被松开")
})
btn.addEventListener("keypress",()=>{
console.log("输入框的键盘被按住 ")
})
btn.addEventListener("input",()=>{
console.log("输入框在输入就触发")
})
btn.addEventListener("change",()=>{
console.log("输入框失焦value值改变时触发")
})
btn.addEventListener("focus",()=>{
console.log("输入框获取焦时触发")
})
btn.addEventListener("blur",()=>{
console.log("输入框失焦时触发")
})
</script>
3、事件对象
事件对象上存储着事件发生时的相关信息
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<style>
.box{
width: 300px;
height: 500px;
background-color: lightgreen;
cursor: cell;
margin: 30px 0 0 30px;
}
</style>
<div class="box">你好</div>
<script>
var box=document.querySelector(".box")
box.addEventListener("click",(x)=>{
console.log(x.pageX,x.pageY)
})
//pageX,pageY:鼠标点击的X,Y的坐标,包括body隐藏的
box.addEventListener("click",(x)=>{
console.log(x.clientX,x.clientY)
})
//clientX,clientY:返回鼠标位置相对于浏览器窗口左上角的坐标,单位为像素,不包括body隐藏的
box.addEventListener("click",(x)=>{
console.log(x.offsetX,x.offsetY)
})
//offsetX,offsetY:相对于元素自己的x/y,跟它是否是定位的元素无关
box.addEventListener("click",(x)=>{
console.log(x.shiftKey)
console.log(x.altKey)
console.log(x.ctrlKey)
console.log(x.metaKey)
})
//shiftKey,altKey,ctrlKey,metaKey:鼠标事件发生时,是否按下shift键,返回一个布尔值
box.addEventListener("click",(x)=>{
console.log(x.screenX,x.screenY)
})
//screenX,screenY:返回鼠标位置相对于屏幕左上角的坐标,单位为像素
box.onmousemove=function(x){
console.log(x.movementX,x.movementY)
}
//movementX,movementY:返回一个位移值,单位为像素,表示当前位置与上一个mousemove事件之间的距离
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、元素盒子模型(重点背加黑字体)
el.offsetWidth:本身宽度+边框线+左右内边距;
el.offsetHeight:本身高度+边框线+上下内边距;
el.offsetTop:相对第一个父级节点有定位属性的上偏移量;
el.offsetLeft:相对有定位属性的父节点左偏移量;
el.clientWidth:本身的宽度+左右内边距;
el.clientHeight:本身的高度+上下内边距;
el.clientTop:上边框线的宽度
el.clientLeft:左边框线的宽度
el.scrollWidth:盒子的实际宽度(包括滚动条不可见部分,不包括边线)
el.scrollHeight:盒子的实际高度(包括滚动条不可见部分,不包括边线)
el.scrollTop:滚动条向下滚动的距离;
el.scrollLeft:滚动条向右滚动的距离;
window.innerHeight:浏览器窗口可见区域高度;
window.innerWidth:浏览器窗口可见区域宽度;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<style>
body{
margin: 0px;
}
.box{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: aquamarine;
}
.box1{
width: 380px;
height: 380px;
background-color: deepskyblue;
position:absolute;
margin: 50px;
border: 3px green solid;
}
.box2{
width: 240px;
height: 240px;
background-color: red;
margin: 60px;
border: 4px blue solid;
}
</style>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var box=document.querySelector(".box")
var box1=document.querySelector(".box1")
var box2=document.querySelector(".box2")
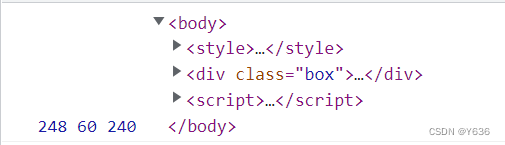
console.log(box2.offsetWidth,box2.offsetTop,box2.clientWidth,box2.offsetParent.offsetParent)
let toptotal=0;
Object.prototype.myoffsetTop=function() {
let father=this.offsetParent
toptotal+=this.offsetTop
if(father){
father.myoffsetTop()
}
return toptotal
}
var re=box2.myoffsetTop()
console.log(re) //50px+60px
</script>
</body>
</html>
 DOM操作:插入节点与事件绑定详解
DOM操作:插入节点与事件绑定详解




 本文主要介绍了DOM中的节点插入方法和事件绑定。详细讲解了事件的三要素,包括事件源、事件类型和事件处理程序。讨论了事件绑定的三种方式,以及事件解绑的方法。此外,还提到了事件对象的重要属性,如offsetWidth和offsetHeight等,用于获取元素的位置和大小信息。最后,文章提及了元素的盒子模型及其相关属性。
本文主要介绍了DOM中的节点插入方法和事件绑定。详细讲解了事件的三要素,包括事件源、事件类型和事件处理程序。讨论了事件绑定的三种方式,以及事件解绑的方法。此外,还提到了事件对象的重要属性,如offsetWidth和offsetHeight等,用于获取元素的位置和大小信息。最后,文章提及了元素的盒子模型及其相关属性。
















 756
756

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








