14、SpringMVC执行流程
14.1、SpringMVC常用组件
- DispatcherServlet:前端控制器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:统一处理请求和响应,整个流程控制的中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求
- HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:根据请求的url、method等信息查找Handler,即控制器方法 - Handler:处理器,需要工程师开发
作用:在DispatcherServlet的控制下Handler对具体的用户请求进行处理
- HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:通过HandlerAdapter对处理器(控制器方法)进行执行
- ViewResolver:视图解析器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:进行视图解析,得到相应的视图,例如:ThymeleafView、InternalResourceView、
RedirectView
- View:视图
作用:将模型数据通过页面展示给用户
14.2、DispatcherServlet初始化过程
DispatcherServlet 本质上是一个 Servlet,所以天然的遵循 Servlet 的生命周期。所以宏观上是 Servlet
生命周期来进行调度。
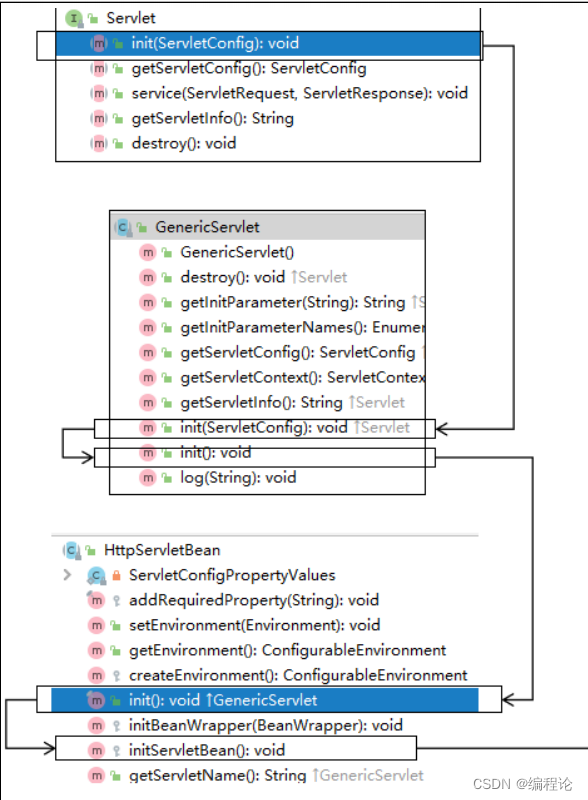
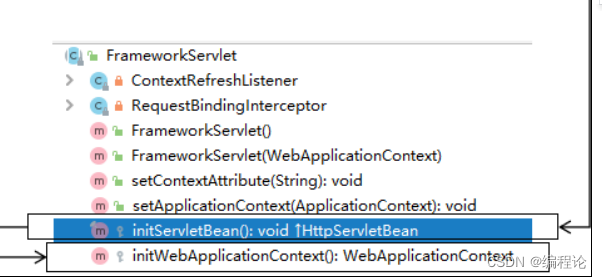
①初始化WebApplicationContext
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services
such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context
id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit
parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the
parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is
assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
// 创建WebApplicationContext
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with
refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 刷新WebApplicationContext
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
// 将IOC容器在应用域共享
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
②创建WebApplicationContext
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable
ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass))
{
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" +
getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 通过反射创建 IOC 容器对象
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 设置父容器
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
③DispatcherServlet初始化策略
FrameworkServlet创建WebApplicationContext后,刷新容器,调用onRefresh(wac),此方法在
DispatcherServlet中进行了重写,调用了initStrategies(context)方法,初始化策略,即初始化
DispatcherServlet的各个组件
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
14.3、DispatcherServlet调用组件处理请求
①processRequest()
FrameworkServlet重写HttpServlet中的service()和doXxx(),这些方法中调用了
processRequest(request, response)
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext =
LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes =
RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request,
response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(),
new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// 执行服务,doService()是一个抽象方法,在DispatcherServlet中进行了重写
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
②doService()
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude ||
attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName,
request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,
getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request,
response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath requestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath &&
!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasParsedRequestPath(request)) {
requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
// 处理请求和响应
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if
(!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (requestPath != null) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.clearParsedRequestPath(request);
}
}
}
③doDispatch()
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
/*
mappedHandler:调用链
包含handler、interceptorList、interceptorIndex
handler:浏览器发送的请求所匹配的控制器方法
interceptorList:处理控制器方法的所有拦截器集合
interceptorIndex:拦截器索引,控制拦截器afterCompletion()的执行
*/
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 通过控制器方法创建相应的处理器适配器,调用所对应的控制器方法
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request,
mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request,
response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 调用拦截器的preHandle()
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 由处理器适配器调用具体的控制器方法,最终获得ModelAndView对象
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response,
mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 调用拦截器的postHandle()
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as
well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other
scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch
failed", err);
}
// 后续处理:处理模型数据和渲染视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv,
dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing
failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
④processDispatchResult()
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws
Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered",
exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler()
: null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
// 处理模型数据和渲染视图
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
// 调用拦截器的afterCompletion()
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
14.4、SpringMVC的执行流程
- 用户向服务器发送请求,请求被SpringMVC 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet捕获。
- DispatcherServlet对请求URL进行解析,得到请求资源标识符(URI),判断请求URI对应的映射:
a) 不存在
i. 再判断是否配置了mvc:default-servlet-handler
ii. 如果没配置,则控制台报映射查找不到,客户端展示404错误
b) 存在则执行下面的流程 - 根据该URI,调用HandlerMapping获得该Handler配置的所有相关的对象(包括Handler对象以及
Handler对象对应的拦截器),最后以HandlerExecutionChain执行链对象的形式返回。 - DispatcherServlet 根据获得的Handler,选择一个合适的HandlerAdapter。
- 如果成功获得HandlerAdapter,此时将开始执行拦截器的preHandler(…)方法【正向】
- 提取Request中的模型数据,填充Handler入参,开始执行Handler(Controller)方法,处理请求。
在填充Handler的入参过程中,根据你的配置,Spring将帮你做一些额外的工作:
a) HttpMessageConveter: 将请求消息(如Json、xml等数据)转换成一个对象,将对象转换为指定
的响应信息
b) 数据转换:对请求消息进行数据转换。如String转换成Integer、Double等
c) 数据格式化:对请求消息进行数据格式化。 如将字符串转换成格式化数字或格式化日期等
d) 数据验证: 验证数据的有效性(长度、格式等),验证结果存储到BindingResult或Error中 - Handler执行完成后,向DispatcherServlet 返回一个ModelAndView对象。
- 此时将开始执行拦截器的postHandle(…)方法【逆向】。
- 根据返回的ModelAndView(此时会判断是否存在异常:如果存在异常,则执行
HandlerExceptionResolver进行异常处理)选择一个适合的ViewResolver进行视图解析,根据Model
和View,来渲染视图。 - 渲染视图完毕执行拦截器的afterCompletion(…)方法【逆向】。
- 将渲染结果返回给客户端






















 355
355











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








