目录
1、为什么要使用链表
我们在使用数组的时候,我们可以发现因为数组的长度是固定的,所以当我们想添加一个值或减少一个值的时候会很困难,而碰到这种情况的时候我们使用链表就可以很轻松的解决。
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。如图
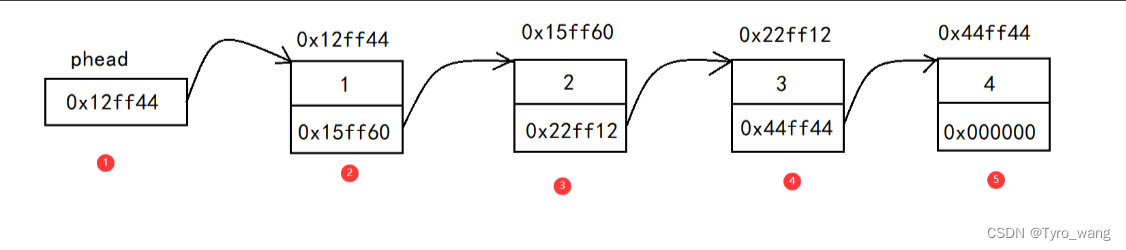
从图中我们可以发现结构体1中保留的是2的地址而2中保留的是3的地址以此类推n-1中保留的是n的地址,个个结构体由结构体中的指针变量保留的地址而链接
下面我们初始化一个链表
#include <stdio.h>
struct Test{
int demt;
struct Test *p;
};
int main(){
struct Test demo1={1,NULL};
struct Test demo2={2,NULL};
struct Test demo3={3,NULL};
demo1.p=&demo2;
demo2.p=&demo3;
printf("%d %d %d\n",demo1.demt,demo1.p->demt,demo1.p->p->demt);
return 0;
}输出结果
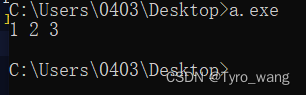
由此可证上面的结论是正确的
链表的增删改查
1、打印链表
链表在访问到本结点的数据之后,需通过该结点存放的地址找到下一个结点。
void printLink(struct Test *location){
if(location!=NULL){
while(location!=NULL){
printf("%d ",location->demt);
location=location->p;
}
}else{
printf("struct Test *location!=NULL");
}
putchar('\n');
}2、计算链表的长度
int Longlink(struct Test *location){
int len=0;
while(location!=NULL){
if(location!=NULL){
len++;
location=location->p;
}
}
return len;
}3、 查看固定的值是否存在链表中
int checkLink(struct Test *location,int count){
int cont=0;
while(location!=NULL){
if(location!=NULL && location->demt==count){
cont=1;
}
location=location->p;
}
return cont;
}4、链表的插入,在给定的值的后面插入
int rearAddLink(struct Test *location,struct Test *new,int cont){
while(location!=NULL){
if(location->demt==cont){
new->p=location->p;
location->p=new;
return 1;//插入成功
}
location=location->p;
}
return 0;//插入失败
}5、链表的插入,在给定的值的前面插入
struct Test* frontAddLink(struct Test *location,struct Test *new,int cont){
struct Test *head=location;
if(head->demt==cont){
new->p=head;
return new;
}
while(head->p!=NULL){
if(head->p->demt==cont){
new->p=head->p;//注意head->p->p时这里存放的就是cont的下一个的地址会直接跳过cont了;
head->p=new;
printf("插入成功\n");
return location;
}
head=head->p;
}
printf("插入失败\n");
return location;
}6、删除链表内固定的值
struct Test* deletLink(struct Test *location,int cont){
struct Test *head=location;
if(head->demt==cont){
head=head->p;
return head;
}
while(head->p!=NULL){
if(head->p->demt==cont){
head->p=head->p->p;
printf("删除成功\n");
return location;
}
head=head->p;
}
printf("链表内没有%d\n",cont);
return location;
}7、改,修改链表里的值
void alterLink(struct Test *location ,int a,int b){
int i=0;
while(location!=NULL){
if(location->demt==a){
location->demt=b;
i=1;
break;
}
location=location->p;
}
if(i==0){
printf("link without %d\n",a);
}
}8、链表的动态创建--头插法
struct Test* frontAddLink(struct Test *location){
struct Test *head;
while(1){
head=(struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
scanf("%d",&(head->demt));
head->p=NULL;
if(head->demt==0){
printf("exit\n");
free(head);
head=NULL;
return location;
}else{
if(location==NULL){
location=head;
}else{
head->p=location;
location=head;
}
}
}
}9、链表的动态创建--尾插法
struct Test* rearAddLink(struct Test *location){
//1、struct Test *head1=location;因为location是一个空指针,如果将head1 在这里赋值的话,下面return的值一直都是空的
struct Test *head;
struct Test *head1=location;
while(1){
head=(struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
scanf("%d",&(head->demt));
head->p=NULL;
if(head->demt==0){
printf("exit\n");
free(head);
head=NULL;
return head1;
}
if(location==NULL){
location=head;
head1=location;//2、
}else{
while(location->p!=NULL){
location=location->p;
}
location->p=head;
}
}
}




















 10万+
10万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








