位运算
具有交换律,结合律.
a^a = 0 a^0 = a
如何把一个int型的数据提取最右的1来: a&(-a)
题目一
不用额外变量交换两个数
a = a^b; b = a^b; a = a^b; //如果两个变量指向同一个内存空间,结果会出错 //a=a^b=0 b=a^b=0^0=0 a=a^b=0^0=0
题目二
一个数组中一种数出现奇数次,其他数出现偶数次,怎么找到并打印这种数?
//所有数异或一遍,剩下最后的数为答案
题目三
//把int数最右边的一提取出来 a&(-a); //把int数最左边的1提取出来 a |= a >> 1; a |= a >> 2; a |= a >> 4; a |= a >> 8; a |= a >> 16; //此时a从最高位往下都是1 return (a+1) >> 1; //找到比一个数大的最小2的k次方数 a-1; a |= a >> 1; a |= a >> 2; a |= a >> 4; a |= a >> 8; a |= a >> 16; return a+1; //判断两个数奇偶是否一致 (a & 1) ^ (b & 1) == 0 ? 1 : 0; //相同返回1, 不同返回0
题目四
一个数组中有两种数出现了奇数次,其他数都出现了偶数次,怎么找出这两种数.
//
public void findTwo(int[] arr){
int len = arr.length;
int xor = 0;
int res1 = 0, res2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
xor ^= arr[i]; //全部异或,结果为res1和res2异或的结果
}
int rightone = xor&(-xor);//res1!=res2,因此必有一位res1为1,res2为0
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if((arr[i] & rightone) != 0){
res1 ^= arr[i];//将那一位为1的数异或,得到res1
}
}
res2 = xor^res1;//异或结果再异或res1得到res2
System.out.println(res1 + ", " + res2);
}
题目五
一个数组中有一种数出现k次,其他数都出现m次,m>1,k<m.找到出现了k次的数,要求空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(N)
public void onlyKTimes(int[]arr, int k,int m){
int ans = 0;
int[] t = new int[32];
for (int num : arr) {
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++){
if((num >> i & 1) == 1){
t[i] += 1;//arr中每个数哪一位是一,数组t对应位就加一
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
if(t[i] % m != 0){//第i位是一的出现了t[i]次,如果不是m倍数,说明要找的那个出现k次的数第i位为1
ans |= (1<<i);
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
基础数据结构
单向链表双向链表
public class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data){
value = date
}
}
public class DoubleNode{
public int value;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
DoubleNode(int data){
value = data;
}
}
初始化
public static Node initList(int[] arr) {
Node head = new Node(arr[0]);
Node pre = head;
Node next = null;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
next = new Node(arr[i]);
pre.next = next;
pre = next;
}
next.next = null;
return head;
}
输出
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.println(head.value);
head = head.next;
}
}
反转单链表
public Node reverseLinkedList(Node head){
Node pre = null;
Node next = head;
while(next != null){
pre = next;
next = next.next;
next.next = pre;
}
head.next = null;
return pre;
}
队列
双向链表实现
数组实现
public class MyQueue {
private int[] arr;
private int end; //插入位置
private int begin; //出队位置
private int size; //当前元素个数
private final int limit; //限制
@Override
public String toString() { //没写完,想不出好方法把MyQueue的元素全部输出
int[] ans;
if(begin <= end){
ans = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, begin, end);
}
else ans = Arrays.copyOfRange()
return "MyQueue{" +
"arr=" + Arrays.toString(arr) +
'}';
}
public MyQueue(int limit) {
arr = new int[limit];
end = 0;
begin = 0;
size = 0;
this.limit = limit;
}
public void push(int value) {
if (size == limit) {
throw new RuntimeException("队满");
}
size++;
arr[end] = value;
end = nextIndex(end);
}
public int pop() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("队空");
}
size--;
int ans = arr[begin];
begin = nextIndex(begin);
return ans;
}
private int nextIndex(int i) {
return i < limit - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
myQueue.push(i);
if(i == 2 || i == 4) myQueue.pop();
}
System.out.println(myQueue);
}
}
用栈实现队列
栈
java用vector实现,push,pop直接调用vector中的addElement(item),removeElementAt(len - 1);
数组实现
队列实现
哈希表
递归
Master公式
计算递归的时间复杂度

二分查找
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int left, int right, int tar){
int mid = 0;
while(left < right){
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(tar <= arr[mid]) right = mid;
else left = mid+1;
}
return left;
}
归并排序
public static void devide(int[] arr, int L, int R){
if(L >= R) return;
int mid = L + ((R-L) >> 1);
devide(arr, L, mid);
devide(arr, mid+1, R);
Merge(arr, L, mid, R);
}
public static void Merge(int[] arr, int L, int M, int R) {
int[] help = new int[R - L + 1];
int helpIndex = 0, p1 = L, p2 = M + 1;
while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) {
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++];
}
while(p1 <= M){
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p1++];
}
while(p2 <= R){
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p2++];
}
for (int i = 0; i < helpIndex; i++) {
arr[L+i] = help[i];
}
}
//迭代实现
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
int mergeSize = 1; //长度小于等于1的视为一组
while (mergeSize < N) {
int L = 0; //左组的最左坐标
while (L < N) {
int M = L + mergeSize - 1;//左组的最右坐标
if (M >= N) break;
int R = Math.min(M + mergeSize, N - 1);//右组最左坐标
Merge(arr, L, M, R);
L = R + 1;
}
//防溢出,如果数组长度无限接近int型最大值,可能会溢出
if(mergeSize > N/2) break;
mergeSize <<= 1;//每次翻倍
}
}
小和问题
在一个数组中,一个数左边比它小的数的总和,叫该数的小和 所有数的小和累加起来,叫数组小和 例子: [1,3,4,2,5] 1左边比1小的数:没有 3左边比3小的数:1 4左边比4小的数:1、3 2左边比2小的数:1 5左边比5小的数:1、3、4、 2 所以数组的小和为1+1+3+1+1+3+4+2=16 给定一个数组arr,求数组小和
//如果直接求O(n2),利用归并O(nlogn),当左右两边有序,arr[p1] < arr[p2],则arr[p1]比p2位置右边的都小
int res = 0;//Merge函数中,合并时如果左边小,res需要变化
while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) {
if(arr[p1] < arr[p2]){
res += arr[p1] * (R-p2+1); //res+=arr[p1]*右边比他大的个数
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p1++];
}
else help[helpIndex++] = arr[p2++];
}
逆序对
在一个数组中,任何一个前面的数a,和任何一个后面的数b,如果(a,b)是降序的,就称为降序对 给定一个数组arr,求数组的降序对总数量
while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) {
if(arr[p1] <= arr[p2]){
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p1++];
}
else {
res += (M-p1+1); //当右组数比左组数小,产生逆序
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p2++];
}
}
双倍逆序对
在一个数组中,对于任何一个数num,求有多少个(后面的数*2)依然<num,返回总个数 比如:[3,1,7,0,2] 3的后面有:1,0 1的后面有:0 7的后面有:0,2 0的后面没有 2的后面没有 所以总共有5个
int Process(int[] arr, int L, int R){
if(L >= R) return 0; //递归边界: R至少=L+1
int M = (L+R) >> 1;
return Process(arr, L, M) + Process(arr, M+1, R)
+ Merge(arr, L, M, R);
}
public int Merge(int[] arr, int L, int M, int R){
//[L...M] [M+1...R]合并 [1,3,7] [0,2] 边排序边计算,因此左右集合有序
int res = 0;
int WindowLen = M+1; //目前囊括进来了[M+1,WindowLen)中的数
for(int i = L; i <= M; i++){//遍历左集合
while(WindowLen <= R && arr[i] > arr[WindowLen] << 1){
WindowLen++;
}
res += WindowLen;
}
//已经计算出现在的双倍逆序对个数,继续排序为后面做准备
int p1 = L, p2 = M+1;
int[] help = new int[R-L+1];
int helpIndex = 0;
while(p1 <= M && p2 <= R){
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++];
}
while(p1 <= M){
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p1++];
}
while(p2 <= R){
help[helpIndex++] = arr[p2++];
}
for(int i = 0; i < helpIndex; i++){
arr[L+i] = help[i];
}
return res;
}
区间和的个数
给定一个数组arr,两个整数lower和upper,
返回arr中有多少个子数组的累加和在[lower,upper]范围上
Leetcode题目:https://leetcode.com/problems/count-of-range-sum/
public int countRangeSum(int[] nums, int lower, int upper) {
long psum[] = new long[nums.length];//前缀和数组,用long型是怕元素超界
psum[0] = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
psum[i] = psum[i-1] + nums[i];
}
return process(psum, lower, upper, 0, nums.length-1);
}
private int process(long[] psum, int lower, int upper, int L, int R) {
if(L == R){
if(psum[L] >= lower && psum[L] <= upper) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int mid = (L+R) >> 1;
return process(psum, lower, upper, L, mid) + process(psum, lower, upper, mid+1, R)
+ Merge(psum, lower, upper, L, mid, R);
}
private int Merge(long[] psum, int lower, int upper, int L, int mid, int R) {
//[L...mid] [mid+1...R]
//先计算满足条件的个数
int res = 0;
int windowL = L, windowR = L; //满足的个数在[windowL,windowR)之间
for(int i = mid+1; i <= R; i++){
long expect_lower = psum[i] - upper;
long expect_upper = psum[i] - lower;
while(windowL <= mid && psum[windowL] < expect_lower){
windowL++;
}
while (windowR <= mid && psum[windowR] <= expect_upper){
windowR++;
}
res += (windowR - windowL);
}
//进行合并排序
int p1 = L, p2 = mid+1;
long[] help = new long[R-L+1];
int helpIndex = 0;
while(p1 <= mid && p2 <= R){
help[helpIndex++] = (psum[p1] <= psum[p2]) ? psum[p1++] : psum[p2++];
}
while(p1 <= mid){
help[helpIndex++] = psum[p1++];
}
while(p2 <= R){
help[helpIndex++] = psum[p2++];
}
for(int i = 0; i < helpIndex; i++){ //注意别忘写回
psum[L+i] = help[i];
}
return res;
}
快速排序
荷兰国旗问题
给定数组arr,和一个值target,要求将数组划分为[<target, target, >target]三部分. 各部分不要求有序.
O(n)方法: 设定windowL左边界-1,windowR右边界arr.len
for(int i = 0; i < windowR; i++){
if(arr[i] < target) {
arr[i]和arr[windowL+1]交换;
windowL++;
}
else if(arr[i] > target){
arr[i]和arr[windowR-1]交换;
windowR--;
}
else if(arr[i] == target){
什么都不做
}
}
快排
//1.0 在荷兰国旗问题基础上,将target设为数组最后一个,让windowR初始为arr.len-1,最后数组分成[<t, =t, >t],再swap(arr[arr.len-1], arr[windowR]),target这个数左边必然比他小,右边必然比他大.接着处理[0, windowR-1][windowR+1, arr.len] //2.0 最后返回等于target的区间,下次操作从[0, windowL]和[windowR+1, arr.len-1]入手 //3.0 当数组本来就有序,target每次都是最大的相当于对[0,len-1][0,len-2]....[0,1] O(n2) 因此多添一行代码,每次将R位置的数和数组中随机一个数交换,确保target随机 swap(arr, R, L+(int)(Math.Random()*(R-L+1))
//1.0
public static void swap(int[] arr, int left, int right){
int temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
}
public static int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right, int tar){
int i = left; // index of smaller element
for (int j = left; j < right; j++) {
if (arr[j] < tar) {
swap(arr, i++, j);
}
}
swap(arr, i, right); // place pivot in correct position
return i;
}
public static void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right){
if(left >= right) return;
int tar = arr[right];
int index = testAPI.partition(arr,left, right, tar);
sort(arr,left,index-1);
sort(arr,index+1,right);
}
堆和堆排序
堆:完全二叉树. 可以用数组表示.
大根堆: 每个子树中最大值都在头节点的完全二叉树
// 大根堆
public static class MyMaxHeap{
private int[] heap;
private int heapSize;//当前大小
private int limit;//数组长度,可以额外写扩容函数
public MyMaxHeap(int limit) {
heap = new int[limit];
this.limit = limit;
heapSize = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return heapSize == 0;
}
public boolean isFull(){ return heapSize == limit; }
public void print(){
int[] res = Arrays.copyOf(heap, heapSize);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(res));
}
public void add(int value){
if(heapSize >= limit) {
throw new RuntimeException(" 超界限了");
}
heap[heapSize] = value;
siftUp(heapSize);
heapSize++;
}
public int poll(){
if(heapSize == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("堆空");
}
int res = heap[0];
swap(0, --heapSize);
siftDown(0);
return res;
}
//将index位置上的数往上移到恰当的位置
void siftUp(int index){
while(heap[index] > heap[(index-1)/2]){ //包含了index >= 0的考虑,(int)(-1)/2=0
swap(index, (index-1) >> 1);
index = (index-1) >> 1;
}
}
//把index位置上的数往下移到恰当的位置
void siftDown(int index){
int leftChild = 2*index+1;
//和上移不同的是考虑边界问题不同
while(leftChild < heapSize){
//找到最大位置
int largest = leftChild+1 < heapSize && heap[leftChild+1] > heap[leftChild]
? leftChild+1 : leftChild;
largest = heap[largest] > heap[index] ? largest : index;
//确定是否需要交换
if(largest == index) break;
else {
swap(largest, index);
index = largest;
leftChild = 2*index+1;
}
}
}
建堆正常时间复杂度: O(n*logn) 每次logn,一共n次
排序复杂度: O(n*logn)
建堆优化: O(n)
//前提,数组提前知道,而不是一个一个给
for(int i = arr.length; i >= 0; i--){
siftDown(i);
}
//原理: 整个树最底下的节点最多,用siftDown下沉而不是diftUp上浮会省很多时间
堆排序
MyHeap.MyMaxHeap myMaxHeap = new MyHeap.MyMaxHeap(arr.length);
for(Integer i : arr){
myMaxHeap.add(i);
}
for(int MaxIndex = arr.length-1; MaxIndex >= 0; MaxIndex--){
arr[MaxIndex] = myMaxHeap.poll();
}
近乎有序数组排序
已知一个几乎有序的数组. 排好序,每个元素移动距离不超过k. 请选择合适排序策略进行排序.
解: 0位置上的数必定是,0-k的数最小值. 因此建一个小根堆,放入0-k. poll()出来的数放到0, 然后add(k+1). 最后O(n*logk)
线段最大重合问题
给定很多线段,每个线段都有两个数[start, end],表示线段开始位置和结束位置,左右都是闭区间
规定:1)线段的开始和结束位置一定都是整数值
2)线段重合区域的长度必须>=1
返回线段最多重合区域中,包含了几条线段
public static int maxCover(int[][] segment){
//按线段初始位置排序
Arrays.sort(segment, (o1, o2) -> {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
});
//按顺序遍历
int MaxCover = -1;
int len = segment.length;
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//把线段右边<=当前线段左边的poll出小根堆
while(!heap.isEmpty() && segment[i][0] >= heap.peek()){
heap.poll();
}
heap.add(segment[i][1]); //把当前线段最右边加入小根堆
//小根堆有多少数说明重合了多少
MaxCover = Math.max(MaxCover, heap.size());
}
return MaxCover;
}
加强堆
java实现的PriorityQueue对于找到指定位置的时间复杂度是O(n). 并且如果修改了堆中数据的值,堆就失效了.
存在问题: 如果堆存储基础类型, 向索引表中添加相同数据会覆盖. 解决策略: 自定义一个类封装起来或利用下标
public class IndexHeap<T> { //加强堆(泛型+自定义比较器+反向索引表)
private ArrayList<T> heap;
private Comparator<? super T> comp;//泛型的下限是T,比如IndexHeap(Student)可以用Person的比较器
public HashMap<T, Integer> indexMap;//反向索引表,根据对象获得数组索引
private int heapSize;
public IndexHeap(Comparator com){
this();
comp = com;
}
public IndexHeap() {
indexMap = new HashMap<>();
heap = new ArrayList<>();
heapSize = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return heapSize == 0;
}
public int size() { return heap.size(); }
public boolean contains(T obj){
return indexMap.containsKey(obj);
}
public T peek(){
assert heapSize==0 : ("堆空了");
return heap.get(0);
}
public void print(){
for(T i : heap){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
void add(T object){
heap.add(object);
indexMap.put(object, heapSize);
siftUp(heapSize++);
}
T poll(){
assert heapSize==0 : ("堆空了");
T res = heap.get(0);
indexMap.remove(res);
T replace = heap.get(--heapSize);
heap.set(0, replace);
siftDown(0);
return res;
}
/**把index位置的数,向上移到合适的位置*/
private void siftUp(int index) {//返回负数,第一个参数应该排前面
while(comp.compare(heap.get(index), heap.get((index-1)>>1)) < 0){
swap(index, (index-1)>>1);
index = (index-1)/2;
}
}
/**通过坐标交换*/
private void swap(int i, int j) {
T o1 = heap.get(i);
T o2 = heap.get(j);
heap.set(i, o2);
heap.set(j, o1);
indexMap.put(o1, j); //旧值更新
indexMap.put(o2, i);
}
//将指定对象移除 先得到最后面, 交换, 去掉最后面, 去掉索引, 更改索引, resign
void remove(T obj){
T replace = heap.get(heapSize-1);
int index = indexMap.get(obj);
swap(index, heapSize-1);
heap.remove(heapSize);
indexMap.remove(obj);
indexMap.put(replace, index);
resign(obj);
}
private void resign(T obj) {
siftUp(indexMap.get(obj));
siftDown(indexMap.get(obj));
}
/**把index位置的数向下移到合适的位置*/
private void siftDown(int index) {
int leftChild = index*2+1;
while(leftChild < heapSize){
int resIndex = comp.compare(heap.get(index), heap.get(leftChild)) < 0 ?
index : leftChild;
if(leftChild+1 < heapSize){
resIndex = comp.compare(heap.get(resIndex), heap.get(leftChild+1)) < 0 ?
resIndex : (leftChild+1);
}
if(resIndex == index) return;
else{
swap(resIndex, index);
index = resIndex;
leftChild = index*2+1;
}
}
}
}
例题
做一个加强堆的题目,给定一个整型数组,int[] arr;和一个布尔类型数组,boolean[] op 两个数组一定等长,假设长度为N,arr[i]表示客户编号,op[i]表示客户操作
arr= [3,3,1,2,1,2,5…
op = [T,T,T,T,F,T,F…
依次表示:
3用户购买了一件商品,3用户购买了一件商品,1用户购买了一件商品,2用户购买了一件商品,1用户退货了一件商品,2用户购买了一件商品,5用户退货了一件商品…
现在你作为电商平台负责人,你想在每一个事件到来的时候,都给购买次数最多的前K名用户颁奖。
所以每个事件发生后,你都需要一个得奖名单(得奖区)。
得奖系统的规则:
1,如果某个用户购买商品数为0,但是又发生了退货事件, 则认为该事件无效,得奖名单和上一个事件发生后一致,例子中的5用户
2,某用户发生购买商品事件,购买商品数+1,发生退货事件,购买商品数-1
3,每次都是最多K个用户得奖,K也为传入的参数如果根据全部规则,得奖人数确实不够K个,那就以不够的情况输出结果
4,得奖系统分为得奖区和候选区,任何用户只要购买数>0,一定在这两个区域中的一个
5,购买数最大的前K名用户进入得奖区,在最初时如果得奖区没有到达K个用户,那么新来的用户直接进入得奖区
6,如果购买数不足以进入得奖区的用户,进入候选区
7,如果候选区购买数最多的用户,已经足以进入得奖区,该用户就会替换得奖区中购买数最少的用户(大于才能替换),如果得奖区中购买数最少的用户有多个,就替换最早进入得奖区的用户如果候选区中购买数最多的用户有多个,机会会给最早进入候选区的用户
8,候选区和得奖区是两套时间, 因用户只会在其中一个区域,所以只会有一个区域的时间,另一个没有从得奖区出来进入候选区的用户,得奖区时间删除,进入候选区的时间就是当前事件的时间(可以理解为arr[i]和op[i]中的i)从候选区出来进入得奖区的用户,候选区时间删除,进入得奖区的时间就是当前事件的时间(可以理解为arr[i]和op[i]中的i)
9,如果某用户购买数==0,不管在哪个区域都离开,区域时间删除,离开是指彻底离开,哪个区域也不会找到该用户如果下次该用户又发生购买行为,产生>0的购买数,会再次根据之前规则回到某个区域中,进入区域的时间重记.
请遍历arr数组和op数组,遍历每一步输出一个得奖名单
前缀树
前缀树——trie /ˈtraɪ//树,也叫作“单词查找树”、“字典树”。
它属于多叉树结构,典型应用场景是统计、保存大量的字符串,经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查找时间,最大限度的减少无谓字符串的比较和存储空间。(用哈希表只能查询每个字符串出现的次数,公共前缀出现次数查不到)
例: 记录了"abc"、"abd"、"bcf"、"abcd" 这四个字符串的前缀树如下图所示:
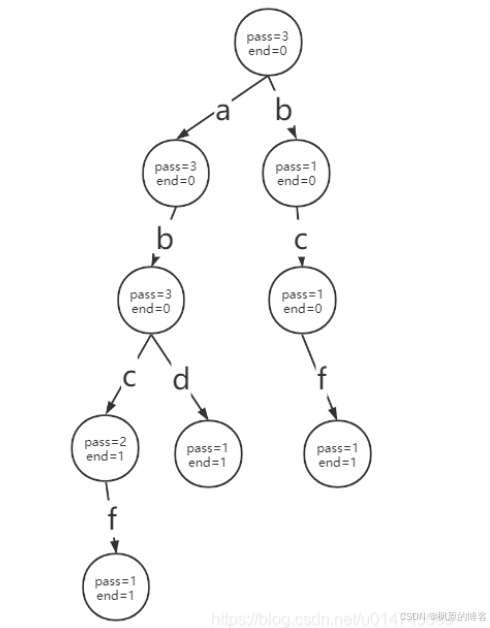
/**前缀树*/
public class Trie {
private static class Node{
int pass; //通过此节点次数
int end; //以此节点结束次数
HashMap<Integer, Node> next; //字符对应的下一个节点
//注:如果字符串由26个字母组成,用Node[] = new Node[26]也行
public void Node(){
pass = 0;
end = 0;
next = new HashMap<>();
}
}
Node root;
public void Trie(){
root = new Node();
}
/**添加字符串*/
void add(String str){
if(str == null) return;
Node node = root;
node.pass++;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int tar;
for(char c : chars){
tar = (int) c;
if(!node.next.containsKey(tar)){
Node n = new Node();
node.next.put(tar,n);
}
node = node.next.get(tar);
node.pass++;
}
node.end++;
}
/**删除字符串*/
void remove(String str){
if(str == null || !exist(str)) return;
Node node = root;
node.pass--;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int tar;
for(char c : chars){
tar = (int) c;
if(node.next.get(tar).pass-1 == 0){ //经过次数减为零,后面都不用管了
node.next.remove(tar);
return;
}
node = node.next.get(tar);
node.pass--;
}
node.end--;
}
/**返回字符串前缀出现次数*/
public int countWordsStartingWith(String str){
if(str == null) return 0;
Node node = root;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int tar;
for(char c : chars){
tar = (int) c;
if(!node.next.containsKey(tar)){
return 0;
} else{
node = node.next.get(tar);
}
}
return node.pass;
}
/**返回字符串匹配的次数*/
public int countWordsEqualTo(String str) {
if(str == null) return 0;
Node node = root;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int tar;
for(char c : chars){
tar = (int) c;
if(!node.next.containsKey(tar)){
return 0;
} else{
node = node.next.get(tar);
}
}
return node.end;
}
/**添判断是否存在字符串*/
public boolean exist(String str){
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
Node node = root;
int tar;
for(char c : chars){
tar = (int) c;
if(!node.next.containsKey(tar)){
return false;
} else{
node = node.next.get(tar);
}
}
return true;
}
}
基数排序
动态图演示: https://pic1.zhimg.com/v2-6690b1054909755ffcca96feb7a4d3ec_b.webp 先排个位,先进先出的取出, 再排十位...
// 120 20 11 21 38 44
//第一遍: 120 20 11 21 44 38
//第二遍: 11 120 20 21 38 44
//第三遍: 11 20 21 38 44 120
public static void radixSort(int[] arr){
int len = arr.length;
int[] help = new int[len]; //每按位排一次,用help存,排完写回arr
int maxDigit = maxdigit(arr);
int p = 0;//先按数的第0位即个位排序
for(int i = 0; i < maxDigit; i++){
//初始化count,并求前缀和
int[] count = new int[10];
for(int s = 0; s < len; s++){
int k = getDigit(arr[s],p);
count[k]++;
}
for(int j = 1; j < 10; j++){
count[j] += count[j-1];
}
//从右往左找的数应该的位置
for(int m = len-1; m >= 0; m--){
int location = --count[getDigit(arr[m],p)];
help[location] = arr[m];
}
arr = Arrays.copyOf(help, len);
p++;
}
}
private static int getDigit(int i, int p) { //求第p位的数
return (int)(i/(int)Math.pow(10,p))%10;
}
/**求出数组中最大数的位数*/
private static int maxdigit(int[] arr) {
int len = arr.length;
int maxm = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
maxm = Math.max(maxm, arr[i]);
}
int res = 0;
while(maxm > 0){
maxm /= 10;
res++;
}
return res;
}
排序算法稳定性
同等的数,在排序后仍然保持排序前的相对顺序.
对于基本类型无意义,对于非基本类型有意义.
例如: 根据年龄排序,再根据班级排序. 如果之后每个班里的学生年龄有序,就说明排序具有稳定性.
插入排序: 2222122 直接把1和第一个2交换位置,没有稳定性
冒泡排序: 相邻的数如果相等就不交换. 有稳定性
插入排序: 第i个数,往前交换,如果相等就停止. 有稳定性
归并排序: 合并的时候, arr[l] == arr[r] 先拷贝arr[l], l++; 有稳定性
快速排序: partition过程小于tar放左边,大于tar放右边 不稳定
例: 4444412 tar=2 从左向右遍历,遇到1,1和第一个4交换.
堆排序: 不稳定
排序算法总结


相比之下,同样是N*logN,快排的常数项更小,因此更快. 工程上对排序的改进一般从1)稳定性考虑 2) 利用O(N^2)插入排序常数项小,在数据量小时候的优势.
链表
链表中点
返回链表中点偏前,中点偏后,中点偏前前一个,中点偏后前一个. (利用快慢指针以及快慢指针的初始位置实现)
复制带随机指针的链表
138. 复制带随机指针的链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
法一: 用HashMap<Node,Node>记录源Node和新的Node,注意不能用<Integer,Node>因为不同节点value会重复
法二: 第一步把复制的节点插入: N1->N1'->N2->N2'->.....
第二步把把新节点的random赋值 第三步把链表拆开
判断链表是否回文
//方法一: 利用stack先进后出,判断是否是回文串
//方法二: 找到链表中点,将链表后面反转.判断后再恢复.
public static boolean ispalindromeList(Node head) {
boolean res = true;
//边界
if (head == null || head.next == null) return res;
//找到中点
Node mid;
Node quick = head;
Node slow = head;
while (quick.next != null && quick.next.next != null) {
quick = quick.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
mid = slow;
//反转
Node pre = mid;
Node left;
Node right;
//顺序是pre left right....null
if (pre.next.next != null) {
left = pre.next;
right = pre.next.next;
while (right.next != null) { //边界条件设的是right.next不为空,left!=null更直观,且不用判断pre.next.next != null
left.next = pre;
pre = left;
left = right;
right = right.next;
}
left.next = pre;
right.next = left;
} else {
right = pre.next;
right.next = pre;
}
//判断
pre = right;
left = head;
while (right != mid) {
if (left.value != mid.value) {
res = false;
break;
}
left = left.next;
right = right.next;
}
//恢复
//顺序是....left right pre null
right = pre.next;
pre.next = null;
while(right != mid){//受上面的边界启发,
left = right.next;
right.next = pre;
right = left;
pre = right;
}
return res;
}
划分链表
给定一个单链表的头节点head,给定一个整数n,将链表按n划分成左边<n、中间==n、右边>n
单链表相交节点问题
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2. 请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点。如果不相交返回null
要求如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)
// public static class Node {
// public int value;
// public Node next;
//
// public Node(int data) {
// this.value = data;
// }
// }
/**返回相交节点*/
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2){
if(head1 == null || head2 == null) return null;
//根据两个单链表是否有环分情况
Node n1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node n2 = getLoopNode(head2);
//都无环
if(n1 == null && n2 == null) return noLoop(head1,head2);
//都有环
else if(n1 != null && n2 != null) {
return bothLoop(head1, n1, head2, n2);
}
//一个有环一个没有不可能相交
else return null;
}
/**返回链表入环节点,如果没有返回null*/
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head){
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return null;
}
Node fast = head.next.next;
Node slow = head.next;
//边界
if(head == null) return null;
//快慢指针往前走知道相遇
while(fast != slow){
if(fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null){
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//慢指针移到头节点,同时移动直到相遇,必在入环节点相遇
slow = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
// 如果两个链表都无环,返回第一个相交节点,如果不相交,返回null
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2){
//判断是否连接,看最后一个节点地址相同
Node n1 = head1, n2 = head2;
int len1 = 1, len2 = 1;
while(n1.next != null){
n1 = n1.next;
len1++;
}
while(n2.next != null){
n2 = n2.next;
len2++;
}
if(n1 != n2) { //不相交
return null;
}
//相交,求第一个交点.倒着走相同的长度(长的先走出多于短链表的距离,再一块走)
int len = len1 >= len2 ? len1-len2 : len2-len1;
if(len1 >= len2){
while(len > 0){
head1 = head1.next;
len--;
}
} else {
while(len > 0){
head2 = head2.next;
len--;
}
}
while(head1 != head2){
head1 = head1.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
return head1;
}
// 两个有环链表,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交返回null
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2){
Node cur1;
Node cur2;
//情况一: 相交且入环节点相同
if(loop1 == loop2){//可以看成两无环链表最后节点为loop1/loop2
//相当于noLoop()的结尾是loop1和loop2情况
int n = 0;
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
while(cur1 != loop1){
cur1 = cur1.next;
n++;
}
while(cur2 != loop2){
cur2 = cur2.next;
n--;
}
// 长的是cur1,短的是cur2
cur1 = n >= 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while(n > 0){
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur1 != cur2){
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
} else {
//情况二: 相交且入环节点不同
//情况三: 不相交
cur1 = loop1.next;
cur2 = loop2;
if(cur1 == null) System.out.println("hhh");
while(cur1 != loop1){
cur1 = cur1.next;
if(cur1 == cur2) return loop1;
}
return null;
}
}
二叉树 class10
先序遍历: 头左右; 中序遍历: 左头又; 后序遍历: 左右头
递归遍历

递归的看: F C A A A C D B B B D D C F E H H H G M M M G G E F
都是由递归加工而来,每个节点都相当于遍历三次,先序,中序,后序就是分别在第一次,第二次.第三次遇到节点打印
void TreeNode(TreeNode head){
if(head == null) return;
//----1
TreeNode(head.left);
//----2
TreeNode(head.right);
//----3
}
非递归遍历
/**头左右*/
public static void pre(Node head) {
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if (head.right != null) {
stack.push(head.right);
}
if (head.left != null) {
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**中序遍历:左中右(用左子树拆分整个树)*/
public static void in(Node cur) {
System.out.print("in-order: ");
if (cur != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**两个栈后序遍历:左右头(把头右左逆序打印)*/
public static void pos1(Node head) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>();
s1.push(head);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
head = s1.pop(); // 头 右 左
s2.push(head);
if (head.left != null) {
s1.push(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
// 左 右 头
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**一个栈后序遍历*/
public static void pos2(Node h) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (h != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(h);
Node c = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
c = stack.peek();
if (c.left != null && h != c.left && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.left);
} else if (c.right != null && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.right);
} else {
System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " ");
h = c;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
按层遍历
相当于图的宽度优先遍历(利用queue队列)
public static void level(Node head) {
if(head == null) return;
Node cur;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(head);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
cur = q.poll();
System.out.println(cur.value);
if(cur.left!=null) q.add(cur.left);
if(cur.right!=null) q.add(cur.right);
}
}
二叉树序列化反序列化
class11
/**树的序列化和反序列化
* 只有先序,后序和层序可以序列化与反序列化,中序有歧义
* */
public class SerializeAndReconstructTree {
/**
* 序列化: 将树的节点按一定顺序翻译成字符串存储,这里利用队列存储
*/
//先序序列化
public static Queue<String> preSerial(Node head){
Queue<String> ans = new LinkedList<>();
if(ans == null) System.out.println("hhh");
pres(head, ans);
return ans;
}
public static void pres(Node head, Queue<String> ans){
if(head == null) ans.add(null);
else{
ans.add(String.valueOf(head.value));
pres(head.left,ans);
pres(head.right,ans);
}
}
//先序反序列化
public static Node buildByPreQueue(Queue<String> prelist){
if(prelist.isEmpty()) return null;
String val = prelist.poll();
if(val == null){
return null;
} else{
Node cur = new Node(Integer.parseInt(val));
cur.left = buildByPreQueue(prelist);
cur.right = buildByPreQueue(prelist);
return cur;
}
}
//层序序列化
public static Queue<String> levelSerial(Node head){
Queue<Node> nextNode = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<String> ans = new LinkedList<>();
if(head == null){
ans.add(null);
return ans;
}
nextNode.add(head);
ans.add(String.valueOf(head.value));
while(nextNode != null){
Node cur = nextNode.poll();
if(cur.left != null){
nextNode.add(cur.left);
ans.add(String.valueOf(cur.left.value));
} else{
ans.add(null);
}
if(cur.right != null){
nextNode.add(cur.right);
ans.add(String.valueOf(cur.right.value));
} else {
ans.add(null);
}
}
return ans;
}
//层序反序列化
public static Node buildByLevelQueue(Queue<String> levelList){
Node res = null;
Node cur = null;
// if(levelList.isEmpty()) return null;
while(!levelList.isEmpty()){
String val = levelList.poll();
if(val == null) res = null;
else{
cur = new Node(Integer.valueOf(val));
// cur =
}
}
return res;
}
}
n叉树转为二叉树(并反转)
将子节点放到父节点左孩子的右边界上
public static class Node {//多叉树
public int val;
public List<Node> children;//孩子节点
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
//把多叉树转为二叉树
public TreeNode encode(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(root.val);
head.left = en(root.children);
return head;
}
private TreeNode en(List<Node> children) {
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode cur = null;
for (Node child : children) {
TreeNode tNode = new TreeNode(child.val);
if (head == null) {
head = tNode;
} else {
cur.right = tNode;
}
cur = tNode;
cur.left = en(child.children);
}
return head;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
public Node decode(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return new Node(root.val, de(root.left));
}
public List<Node> de(TreeNode root) {
List<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
while (root != null) {
Node cur = new Node(root.val, de(root.left));
children.add(cur);
root = root.right;
}
return children;
}
求树的最大宽度
记录二叉树每一层的最后一个节点curEnd并随时更新下一层最后节点nextEnd
层序遍历
public static int maxWidthNoMap(Node head) {
if(head == null) return 0;
int res = -1;
int now = 0;
Queue<Node> st = new LinkedList<>();
Node curEnd = head;
Node nextEnd = head;
st.add(curEnd);
Node curNode = null;
while(!st.isEmpty()){
curNode = st.poll();
now++;
if(curNode.left != null){
st.add(curNode.left);
nextEnd = curNode.left;
}
if(curNode.right != null){
st.add(curNode.right);
nextEnd = curNode.right;
}
if(curNode == curEnd){
curEnd = nextEnd;
res = Math.max(res,now);
now = 0;
}
}
return res;
}
判断是否是平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树:任意节点为头的子树,都满足左树和右树高度相差小于等于1
因此判断是平衡二叉树: 1) 左树平衡 2) 右树平衡 3) |左树高-右树高| < 2 (感受递归思想)
public static Info process(GernerateTree.Node x){
if(x == null){
return new Info(true, 0);
}
Info left = process(x.left);
Info right = process(x.right);
boolean isBalenced = true;
if(left.isBalanced == false || right.isBalanced == false){
isBalenced = false;
}
if(Math.abs(left.height-right.height) > 1) {
isBalenced = false;
}
return new Info(isBalenced, Math.max(left.height, right.height)+1);
}
判断是否为搜索二叉树
搜索二叉树:任意节点为头的子树,左树节点值都比右树小
因此判断是搜索二叉树: 1) 左树是 2) 右树是 3) 节点值大于左树最大值 4) 节点值小于右树最小值
为了使用递归解题, 需要抽取出公共子问题, 既然左树和右树不同, 那么就同时求最大值和最小值
//边界:左孩子为空,右孩子为空,孩子都为空
//若为空,isBST=true, minNum = MAXINT, maxNum = MININT;
public static Info process(Node node){
//如果当节点为空返回null,之后每一步都需要判断是否为空,很麻烦,若为空将最大值设为Integer的最小值,最小值设为Integer的最大值.不影响后面判断isBST,
if(node == null){
return new Info(true, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
Info left = null;
Info right = null;
left = process(node.left);
right = process(node.right);
boolean isBST = true;
if((!left.isBST || !right.isBST || node.value <= left.maxNum || node.value >= right.minNum)){
isBST = false;
}
int minNum = Math.min(node.value, left.minNum);
int maxNum = Math.max(node.value, right.maxNum);
return new Info(isBST, maxNum, minNum);
}
求整颗二叉树最大距离
可能性: 1) 左子树中产生 2) 右子树中产生 3) 左树高度+右树高度+1
所以class Info{ int maxDistance, int height}
判断是否是满二叉树
法一.可能性: 1) 左子树是满的 2) 右子树是满的 3) 两个子树高度相等
法二.1) 节点数 2) 高度 当 节点数 = 1 << 高度 - 1 时, 为满二叉树
求二叉树中最大的二叉搜索子树的大小
可能性: 1) isBST 2) 树节点个数 3) 节点max值 4) 节点min值 5) 当前最大二叉搜索子树大小
isBST可以通过 2) == 5) 判断
public static int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode head) {
if(head == null) return 0;
return process(head).maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
public static Info process(TreeNode head){
//head为空
if(head == null){
return new Info(0,0, Integer.MIN_VALUE,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//左树,右树信息
Info left = process(head.left);
Info right = process(head.right);
//是否是BST
boolean isBST = true;
if(left.maxBSTSubtreeSize != left.allSize || right.maxBSTSubtreeSize != right.allSize){
isBST = false;
}
if(head.val <= left.max || head.val >= right.min){
isBST = false;
}
//max,min
int max = Math.max(head.val, right.max);
int min = Math.min(head.val, left.min);
//allSize
int allSize = left.allSize + right.allSize + 1;
//maxBSTSubtreeSize
int maxBSTSubtreeSize = Math.max(left.maxBSTSubtreeSize, right.maxBSTSubtreeSize);;
if(isBST){
maxBSTSubtreeSize = allSize;
}
//返回
return new Info(maxBSTSubtreeSize, allSize, max, min);
}
判断是否是完全二叉树
法一. 层序遍历每个节点: 当有节点有右无左,或者之前节点左右孩子不满,后面的节点都没有子孩子
法二.递归. 1) 左满二叉树,右满二叉树且高度相等 2) 左完全二叉树, 右满且左高=右高+1 3) 左满,右完全且,高度相等 4) 左满,右满且, 左高=右高+1
所以class Info{boolean isFull; int height; boolean isCBT};
找出两个节点的最低公共祖先
可能性1) 子树已经找到答案 2) 子树只找到a或b 3) 都没找到 4)
之要列出Info就很简单了
//返回以x为头节点的树中节点a和节点b的公共最小祖先
public static Info process(Node x, Node a, Node b) {
if(x == null){
return new Info(false, false, null);
}
Info left = process(x.left, a, b);
Info right = process(x.right, a, b);
boolean findA = (left.findA || right.findA || x == a);
boolean findB = (left.findB || right.findB || x == b);
Node ans = null;
if(left.ans != null){
ans = left.ans;
}
else if(right.ans != null){
ans = right.ans;
}
else if(findA && findB){
ans = x;
}
return new Info(findA, findB, ans);
}
满足节点间没有直接父子关系,找出多叉树中最大的节点和
Info需要包括: 1) 选择当前节点的最大节点和 2) 不选择当前节点的最大节点和
public static Info process(Employee em){
if(em == null){
return new Info(0,0);
}
int yes = em.happy, no = 0;
for(Employee e : em.nexts){
Info info = process(e);
yes += info.no;
no += Math.max(info.yes, info.no);//注意!!!
}
return new Info(no, yes);
}
贪心class14
给定字符串数组,返回所有字符串拼接结果中字典序最小的
将字符串数组自定义排序,再拼接
public static class MyComparator implements Comparator<String> {
@Override
public int compare(String a, String b) {
return (a + b).compareTo(b + a);
}
}
会场场次最大
一些项目需要占用会议室宣讲,会议室同时只容纳一个项目.给出每个项目开始和结束时间,安排日程保证宣讲场次最大.
贪心: 每次都选结束时间最早的
划分金条
一块金条切成两半,是需要花费和长度数值一样的铜板。比如长度为20的金条,不管怎么切都要花费20个铜板,一群人想整分整块金条,怎么分最省铜板?
例如,给定数组{10,20,30},代表一共三个人,整块金条长度为60,金条要分成10,20,30三个部分。如果先把长度60的金条分成10和50,花费60;再把长度50的金条分成20和30,花费50;一共花费110铜板。但如果先把长度60的金条分成30和30,花费60;再把长度30金条分成10和20,花费30;一共花费90铜板。
public static int lessMoney(int[] arr){
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int num : arr){
pq.add(num);
}
int sum = 0;
int cur = 0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
cur = pq.poll()+pq.poll();
sum += cur;
pq.add(cur);
}
return sum
}
最大收益
输入正数数组costs、正数数组profits、正数K和正数M
costs[i]表示i号项目的花费,profits[i]表示i号项目在扣除花费之后还能挣到的钱(利润),K表示你只能串行的最多做k个项目,M表示你初始的资金
说明:每做完一个项目,马上获得的收益,可以支持你去做下一个项目,不能并行的做项目。输出:最后获得的最大钱数
// 最多K个项目
// W是初始资金
// Profits[] Capital[] 一定等长
// 返回最终最大的资金
public static int findMaximizedCapital(int K, int W, int[] Profits, int[] Capital) {
int ans = 0;
PriorityQueue<program> profit = new PriorityQueue<>(new profitCom());
PriorityQueue<program> capital = new PriorityQueue<>(new capitalCom());
for(int i = 0; i < Profits.length; i++){
capital.add(new program(Capital[i], Profits[i]));
}
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++){
while(capital.peek().capital <= W && !capital.isEmpty()){
profit.add(capital.poll());
}
if(profit.isEmpty()) return W;
program p = profit.poll();
W += p.profit;
}
return W;
}
点灯问题
给定一个字符串,只由'X'和'.'两种字符构成。'X'表示墙,不能放灯,也不需要点亮;'.'表示居民点,可以放灯,需要点亮。如果灯放在i位置,可以让i-1,i和i+1三个位置被点亮。返回如果点亮str中所有需要点亮的位置,至少需要几盏灯
并查集class14
并查集是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不相交集合(disjoint sets)的合并及查询问题.
利用多叉树形结构, 合并两个节点所在集合就相当于将节点的根,相连.
优化策略: 1. 小的树挂在大树下面 2. 每次查找父节点, 利用路径压缩将树变得扁平
实现
数组实现
//查找和合并,经过路径压缩时间复杂度近乎O(1)
public class UnionFind { //patent数组中保存各元素的父节点,初始为自己本身
//若连元素相连,则将他们的父节点相连
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank; //rank[i]表示以i为根的集合所表示的树的层数
private int count; //集合个数
//默认从0-count-1,一共count个集合
public UnionFind(int count) {
parent = new int [count];
rank = new int[count];
this.count = count;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//!默认的元素为0到count-1!
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1; //初始树只有一层
}
}
//写法一: 每次压缩,但压缩不完全
public int find(int p) {
while(p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];//路径压缩
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
//写法二: 每次压缩,把路径上所有节点指向根节点
public int find(int p){
if(p == parent[p]) return p;
parent[p] = find(parent[p]);
return parent[p];
}
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
int proot = find(p);
int qroot = find(q);
return qroot == proot;
}
public void unionElements(int p, int q) {
int proot = find(p);
int qroot = find(q);
if(proot == qroot){
return;
}
if( rank[proot] < rank[qroot]) {
parent[proot] = qroot;
}
else if(rank[proot] > rank[qroot]){
parent[qroot] = proot;
}
else if(rank[proot] == rank[qroot]) {
parent[proot] = qroot;
rank[qroot]++;
}
count--;
}
};
hashmap实现:
public static class Node<T>{
T val;
public Node(){}
public Node(T value){
val = value;
}
}
public HashMap<T,Node> map;
public HashMap<Node,Node> father;
public HashMap<Node,Integer> size;
public UnionFind(List<T> values) {
map = new HashMap<>();
father = new HashMap<>();
size = new HashMap<>();
for (T cur : values) {
Node<T> node = new Node<>(cur);
map.put(cur, node);
father.put(node, node);
size.put(node, 1);
}
}
public void union(T a, T b){
Node n1 = map.get(a);
Node n2 = map.get(b);
Node f1 = getFather(n1);
Node f2 = getFather(n2);
if(f1 != f2){
Node<T> bigger = size.get(f1) > size.get(f2) ? f1 : f2;
Node<T> smaller = bigger == f1 ? f2 : f1;
// father.remove(smaller);
father.put(smaller, bigger);
size.remove(smaller);
size.put(bigger, size.get(f1) + size.get(f2));
}
}
public boolean inSameSet(T a, T b){
return getFather(map.get(a)) == getFather(map.get(b));
}
// private Node<T> getFather(Node<T> node) {
// while(father.get(node) != node){
// node = father.get(node);
// }
// return node;
// }
//路径压缩优化
private Node<T> getFather(Node<T> node){
Stack<Node<T>> st = new Stack<>();
while(father.get(node) != node){
st.push(node);
node = father.get(node);
}
while(!st.isEmpty()){
father.put(st.pop(), node);
}
return node;
}
岛屿数量
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
法一. 感染, 遍历二位数组,每当遇到岛屿, 将附近岛屿全部感染. num++;
法二. 并查集
图class16
图的表示方法有很多, 邻接表, 邻接矩阵, 用一个数组(下标代表入读节点,值代表出度节点)也可以.
为了保证算法一致性, 自定义一个图, 每次将给定数据转化为自己的图
宽度优先遍历
HashSet+PriorityQueue
深度优先遍历
递归 或 栈模拟
拓扑排序
对一个有向无环图 ( Directed Acyclic Graph 简称 DAG ) G 进行拓扑排序,是将 G 中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点 u 和 v ,若边 < u , v > ∈ E ( G ),则 u 在线性序列中出现在 v 之前。
/**
* Definition for Directed graph.
* class DirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* List<DirectedGraphNode> neighbors;//指向的相邻节点
* DirectedGraphNode(int x) {
* label = x;
* neighbors = new ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode>();
* }
* }
*/
法一: 记录每个节点的入度. 先将入度为零的输出, 剩下的节点入度减一. 循环
/**给出所有的点,返回拓扑排序结果*/
public ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> topSort(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph) {
// write your code here
ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> ans = new ArrayList<>();
//记录每个点的入度map(node,num)
HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(DirectedGraphNode node: graph){
map.put(node, 0);
}
for(DirectedGraphNode node : graph){
for(DirectedGraphNode next : node.neighbors){
map.put(next, map.get(next)+1);
}
}
//入度为零的保存
Queue<DirectedGraphNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for(DirectedGraphNode node : graph){
if(map.get(node) == 0){
queue.add(node);
}
}
//输出入度为零的,减去入度为零节点相邻节点的入度
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
DirectedGraphNode node = queue.poll();
ans.add(node);
for(DirectedGraphNode next : node.neighbors){
int now = map.get(next)-1; //当前入度
map.put(next, now);
if(now == 0){
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
法二: 以每个节点为头遍历,节点个数多的一定排的靠前.
法三: 以每个节点为头遍历,深度大的一定靠前.
最小生成树
一个有 n 个结点的连通图的生成树是原图的极小连通子图,且包含原图中的所有 n 个结点,并且有保持图连通的最少的边。最小生成树可以用kruskal算法或prim算法求出。
Kruskal算法: 每次选择权值最小的边相连的两个节点合并(保证合并后没环) 因此利用并查集, 当两个节点不在同一个集合,就可以合并.

Prim算法: 随便选一个点, 找到它所有边中权值最小的点, 解锁新的点, 多考虑新的点的所有边的权值...

Dijkstra
解决有权图中的最短路径问题
public HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra(Node node){
HashMap<Node, Integer> ans = new HashMap<>();
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>();//记录走过的点,做过的就不再判断
//以node为起始点,遍历到其他点的边.更新从node到其他点的距离,每次选取到其他点最短距离
// 的点(且没被选过). 再从新的点继续遍历.
set.add(node);
ans.put(node, 0);//node初始到自己距离为0
Node minNode = node;//每轮选取的点,初始选node,因为distance(node->node)=0最小
while(minNode != null) {
int Distance = ans.get(node);
int curDistance = 0;
for (Edge edge : node.edges) {
if(!ans.containsKey(edge.to)){
curDistance = Distance + edge.weight;
} else {
curDistance = Math.min(Distance + edge.weight, ans.get(edge.to));
}
ans.put(edge.to, curDistance);
}
//找到新的minNode
minNode = getMinNode(ans, set);
set.add(minNode);
}
return ans;
}
//遍历ans,找到最近的且没被选过的节点,返回
public Node getMinNode(HashMap<Node, Integer> ans, HashSet<Node> set){
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Node minNode = null;
for (Map.Entry<Node, Integer> entry : ans.entrySet()) {
Node n = entry.getKey();
int val = entry.getValue();
if(!set.contains(n)){
if(val < minDistance){
minDistance = val;
minNode = n;
}
}
}
return minNode;
}
优化: 每次getMinNode都需要遍历所有ans中的节点,找到路径最短的. 如果利用加强堆, 实现自动排序, 就能快很多.
递归
在计算机科学中是指一种通过重复将问题分解为同类的子问题而解决问题的方法。
递归的特点
汉诺塔问题
整个过程可以总结成LeftToRight, LeftToMiddile, MiddleToRight, MiddleToLeft, RightToLeft, RightToMiddle.
因此只用写这六个函数即可, 参数为当前第几个节点
public void LeftToRight(int n){
if(n == 1)
System.out.println("Move 1 From Left To Right")
return;
}
LeftToMiddle(n-1);
System.out.println("Move" + n + "From Left To Right");
MiddleToRight(n-1);
}
如果过程进一步精简: 发现参数越多包含情况更多
public void FromTo(int n, String from, String to, String other){
if(n == 1){
System.out.println("Move 1 From" + from + to);
return;
}
FromTo(n-1, from, other, to);
System.out.println("Move" + n + "From" + from + "To" + to)
FromTo(n-1, other, to, from);
}
打印字符串全排列
法一. 记录当前字符串now以及剩余字符串rest, 选一个放入当前字符串now, rest排除选中字符. 递归结束再恢复
//当前字符串为now, 对剩余字符串rest进行全排列
public static void process(List<String> ans, ArrayList<Character> rest, String now){
//边界条件
if(rest.size() == 0){
ans.add(now);
return;
}
int index = now.length();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[256];
for(int i = 0; i < rest.size(); i++){
char c = now.charAt(i);
if(!visited[c]){
visited[c] = true;
rest.remove(i);
process(ans, rest, now+i);
rest.add(i,c);
}
}
}
法二: 选中一个与当前字符交换, 轮流当第一个字符, 轮流当第二个字符... 递归后再交换回来
public static void process2(List<String> ans, char[] now, int index){
//边界条件
if(index == now.length){
ans.add(String.valueOf(now));
return;
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[256];
for(int i = index; i < now.length; i++){
if(!visited[now[i]]){
visited[now[i]] = true;
swap(now, index, i);
process2(ans, now, index+1);
swap(now, index, i);
}
}
}
将栈逆序
不使用额外结构, 用递归实现
//将当前栈栈反转
public static void reverseStack(Stack<Integer> stack){
if(stack.isEmpty()) return;
Integer down = getDown(stack);
reverseStack(stack);
stack.push(down);
}
//取出并返回栈的最底层元素
public static Integer getDown(Stack<Integer> stack){
Integer up = stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()) return up;
Integer result = getDown(stack);
stack.push(up);
return result;
}
动态规划
与分治思想类似, 也是将问题化为更小的子问题, 当子问题不是相互独立, 有些子问题被重复计算了多次, 保存子问题的答案, 简化后续问题的计算
所有的 递归+记忆化 都能转化为动态规划, 因此可以说动态规划是结果, 直接推状态转移方程很难, 但是如果先从递归入手就简单许多
-
从左往右尝试模型
-
范围尝试模型
-
样本对应模型
-
业务限制模型
优化技巧: 1. 空间压缩 2. 状态化简 (如果状态转移不是O(1)而是O(n),化简) 3. 四边形不等式
暴力递归转动态规划
1.如果一个递归问题,有重复的子问题,就相当于一棵树往下分叉,有节点一样,那么就说明改为动态规划有利可图
2.动态规划都对应暴力递归, 但是暴力递归不一定对应动态规划
机器人问题class18
假设有排成一行的N个位置记为1~N,N一定大于或等于2, 开始时机器人在其中的M位置上(M一定是1~N中的一个)
如果机器人来到1位置,那么下一步只能往右来到2位置;如果机器人来到N位置,那么下一步只能往左来到N-1位置;如果机器人来到中间位置,那么下一步可以往左走或者往右走;
规定机器人必须走K步,最终能来到P位置(P也是1~N中的一个)的方法有多少种; 给定四个参数 N、M、K、P,返回方法数
/**递归*/
public static int process1(int N, int now, int rest, int to){
if(rest == 0){
if(now == to) return 1;
else return 0;
}
if(now == 1){
return process1(N, 2, rest-1, to);
}
if(now == N){
return process1(N, N-1, rest-1, to);
}
return process1(N, now-1, rest-1, to) + process1(N, now+1, rest-1, to);
}
/**递归+记忆化*/
public static int process2(int N, int now, int rest, int to, int[][] dp){
if(dp[now][rest] != -1) return dp[now][rest];
if(rest == 0){
if(now == to) {
dp[now][0] = 1;
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
if(now == 1){
int ans = process1(N, 2, rest-1, to);
dp[2][rest-1] = ans;
return ans;
}
if(now == N){
int ans = process1(N, N-1, rest-1, to);
dp[N-1][rest-1] = ans;
return ans;
}
else{
int ans1 = process1(N, now-1, rest-1, to);
int ans2 = process1(N, now+1, rest-1, to);
dp[now-1][rest-1] = ans1;
dp[now+1][rest-1] = ans2;
return ans1+ans2;
}
}
//动态规划dp[i][j]表示从i到终点走j步可能的情况
public static int process3(int N, int now, int rest, int to, int[][] dp){
dp[to][0] = 1;//默认数组其他位置都是0
//一列一列遍历
for(int j = 1; j <= rest; j++){
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
if(i == 1){
dp[i][j] = dp[2][j-1];
} else if(i == N){
dp[i][j] = dp[N-1][j-1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i+1][j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[now][rest];
}
纸牌问题
给定一个整型数组arr,代表数值不同的纸牌排成一条线, 玩家A和玩家B依次拿走每张纸牌. 规定玩家A先拿,玩家B后拿, 但是每个玩家每次只能拿走最左或最右的纸牌. 玩家A和玩家B都绝顶聪明. 请返回最后获胜者的分数
例: 50 100 20 10 四张指派, A先拿10, B拿50, A拿100 B拿20 , res = 110;
//先手能拿到的最好分数
public static int process2A(int[] arr, int from, int to){
if(from == to){
return arr[from];
}
int ans1 = arr[from] + process2B(arr, from+1, to);
int ans2 = arr[to] + process2B(arr, from, to-1);
return Math.max(ans1, ans2);
}
//后手能拿到的最好分数
public static int process2B(int[] arr, int from, int to){
if(from == to){
return 0;
}
//假设arr[from]被先手拿走,后手尽全力拿[from+1,to];arr[to]被先手拿走,后手尽全力拿[from,to-1]
int ans1 = process2A(arr, from+1, to);
int ans2 = process2A(arr, from, to-1);
//注意: 先手很聪明,后手只能拿更小的
return Math.min(ans1, ans2);
}
数字字符串转换class19
规定1和A对应、2和B对应、3和C对应...26和Z对应, 那么一个数字字符串比如"111”就可以转化为: "AAA"、"KA"和"AK" 给定一个只有数字字符组成的字符串str,返回有多少种转化结果.
//返回从index开始的可能情况
public static int process1(String str, int index){
if(index == str.length()) return 1;
if(str.charAt(index) == '0') return 0;
if(index+1 < str.length() && Integer.valueOf(str.substring(index, index+2)) <= 26){
return process1(str, index+1) + process1(str,index+2);
} else {
return process1(str,index+1);
}
}
public static int dp(String str) {
int len = str.length();
int[] dp = new int[len+1];
dp[len] = 1;
for(int i = str.length()-1; i >= 0; i--){
if(str.charAt(i) == '0'){
dp[i] = 0;
}
else if(i+1 < len && Integer.valueOf(str.substring(i, i+2)) <= 26){
dp[i] = dp[i+1] + dp[i+2];
}
else dp[i] = dp[i+1];
}
return dp[0];
}
字符串贴纸
给定一个字符串str,给定一个字符串类型的数组arr,出现的字符都是小写英文. arr每一个字符串,代表一张贴纸,你可以把单个字符剪开使用,目的是拼出str来. 返回需要至少多少张贴纸可以完成这个任务
例子:str= "babac",arr = {"ba","c","abcd"} ba + ba + c 3 abcd + abcd 2 abcd+ba 2 所以返回2
https://leetcode.com/problems/stickers-to-spell-word
法一: 对于目标,可以多次选择
public int process1(String[] stickers, String target){
if(target.length() == 0) return 0;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(String str : stickers){
String now = minus(target, str);
if(now.length() != target.length()){
min = Math.min(min, process1(stickers, now));
}
}
if(min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return min;
else return min+1;
}
private String minus(String target, String str) {
char[] chars1 = target.toCharArray();
char[] chars2 = str.toCharArray();
int[] count = new int[26];
for(char c : chars1){
count[c-'a']++;
}
for(char c : chars2){
count[c-'a']--;
}
StringBuilder string = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++){
if(count[i] != 0){
for(int j = 0; j < count[i]; j++){
string.append((char)(i+'a'));
}
}
}
return string.toString();
}
法二: 剪枝 + 记忆化
//sticker[i][k]存储第i个字符串贴纸中第k个字符的数目
public int process2(int[][] stickers, String target, HashMap<String, Integer> map ){
if(target.length() == 0) return 0;
//记忆化
if(map.containsKey(target)){
return map.get(target);
}
char[] tar = target.toCharArray();
int[] tcounts = new int[26];
for (char cha : tar) {
tcounts[cha - 'a']++;
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < stickers.length; i++){
//必须保证此刻选的贴纸包含target的第一个字符,这既保证个贴纸有效,又避免需要A,B,C三个贴纸,但找了ABC,BAC,BCA,CBA,CAB这么多次. (剪枝)
if(stickers[i][target.charAt(0)-'a'] > 0){
StringBuilder stringbuilder = new StringBuilder();
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++){
int k = tcounts[j] - stickers[i][j];
while(k > 0){
stringbuilder.append((char)('a'+j));
k--;
}
}
String rest = stringbuilder.toString();
min = Math.min(min, process2(stickers, rest, map));
}
}
int ans = min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? min : min+1;
map.put(target, ans);
return ans;
}
最长公共子序列
给定两个字符串str1和str2,返回这两个字符串的最长公共子序列长度
比如 : str1 = “a12b3c456d”,str2 = “1ef23ghi4j56k” 最长公共子序列是“123456”,所以返回长度6
递归尝试:
//求str1[0-i]和str2[0-j]位置的最长公共子序列
public static int process1(char[] str1, char[] str2, int i, int j){
//边界条件
if(i == -1 || j == -1) return 0;
char k = str1[i];
char p = str2[j];
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(str1[i] == str2[j]){
//以i,j结尾
res = Math.max(res, process1(str1, str2, i-1, j-1)+1);
} else{
//不以i,j结尾
res = Math.max(res, process1(str1, str2, i-1, j-1));
}
//最长公共子序列以i结尾
res = Math.max(res, process1(str1, str2, i, j-1));
//最长公共子序列以j结尾
res = Math.max(res, process1(str1, str2, i-1, j));
return res;
}
改成动态规划:
public static int process2(char[] str1, char[] str2){
int M = str1.length, N = str2.length;
int[][] dp = new int[M+1][N+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= M; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
if(str1[i-1] == str2[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j-1]+1, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[M][N];
}
最长回文序列class20
给定一个字符串str,返回这个字符串的最长回文子序列长度
比如 : str = “a12b3c43def2ghi1kpm” 最长回文子序列是“1234321”或者“123c321”,返回长度7
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/
法一: 将str逆序为str1, 求str和str1的最长公共子序列
法二: 递归
//返回s[l,r]的最长回文子序列
public static int process1(char[] s, int l, int r){
if(l > r) return 0;
if(l == r) return 1;
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(s[l] == s[r]) {
res = Math.max(res, process1(s, l+1, r-1)+2);
} else {
int tmp = Math.max(process1(s, l+1, r), process1(s, l, r-1));
res = Math.max(tmp, res);
}
return res;
}
法三: 动态规划
/*
1 0 0 0 tar
x 1 0 0 0
x x 1 0 0
x x x 1 0
x x x x 1
*/
public static int process2(char[] s){
int N = s.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N+1][N+1]; //dp[i][j]代表从
for(int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = i; j <= N-1; j++){
if(i == j) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
continue;
}
int max = Math.max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
if(s[i] == s[j]) max = Math.max(max, dp[i+1][j-1]+2);
dp[i][j] = max;
}
}
return dp[0][N-1];
}
棋盘问题
请同学们自行搜索或者想象一个象棋的棋盘,
然后把整个棋盘放入第一象限,棋盘的最左下角是(0,0)位置 那么整个棋盘就是横坐标上9条线、纵坐标上10条线的区域. 给你三个 参数 x,y,k 返回“马”从(0,0)位置出发,必须走k步
最后落在(x,y)上的方法数有多少种?
//返回从(x,y)到(a,b)马走step步可能性 注: 棋盘大小9*10
public static int process1(int x, int y, int step, int a, int b){
if(x >= 9 || x < 0 || y < 0 || y >= 10) return 0; //出界
if(step == 0) {
if(x == a && y == b) return 1; //到达
else return 0; //到不了
}
//四种可能左上,右上,左下,右下
int leftUp = process1(x-2, y+1, step-1, a, b) +
process1(x-1, y+2, step-1, a, b);
int rightUp = process1(x+2, y+1, step-1, a, b) +
process1(x+1, y+2, step-1, a, b);
int leftDown = process1(x-2, y-1, step-1, a, b) +
process1(x-1, y-2, step-1, a, b);
int rightDown = process1(x+2, y-1, step-1, a, b) +
process1(x+1, y-2, step-1, a, b);
return leftUp+leftDown+rightUp+rightDown;
}
public static void jump(int a, int b, int k) {
System.out.println(process1(0, 0, k, a, b));
}
动态规划
public static int process2(int step, int a, int b){
//递归依赖x,y,step,所以需要三维数组,但因为第step层只依赖于第step-1层,用两层即可
int[][][] dp = new int[9][10][2];
//边界,当step等于0
dp[a][b][0] = 1;
//状态转移
int now = 0;
while(step > 0){
step--;
for(int x = 0; x < 9; x++){
for(int y = 0; y < 10; y++){
int res = plus(dp, x-2, y+1, now) + plus(dp, x-1, y+2, now)
+ plus(dp, x+2, y+1, now) + plus(dp, x+1, y+2, now)
+ plus(dp, x-2, y-1, now) + plus(dp, x-1, y-2, now)
+ plus(dp, x+2, y-1, now) + plus(dp, x+1, y-2, now);
dp[x][y][(now+1)%2] = res;
}
}
now = (now+1)%2;
}
return dp[0][0][now]; // 对应System.out.println(process1(0, 0, k, a, b));
}
}
喝咖啡杯问题
给定一个数组arr,arr[i]代表第i号咖啡机泡一杯咖啡的时间. 给定一个正数N,表示N个人等着咖啡机泡咖啡,每台咖啡机只能轮流泡咖啡. 只有一台咖啡机,一次只能洗一个杯子,时间耗费a,洗完才能洗下一杯.每个咖啡杯也可以自己挥发干净,时间耗费b,咖啡杯可以并行挥发
假设所有人拿到咖啡之后立刻喝干净,返回从开始等到所有咖啡机变干净的最短时间
三个参数:int[] arr、int N,int a、int b
货币问题1
arr是货币数组,其中的值都是正数。再给定一个正数aim。每个值都认为是一张货币,即便是值相同的货币也认为每一张都是不同的,返回组成aim的方法数
例如:arr = {1,1,1},aim = 2 第0个和第1个能组成2,第1个和第2个能组成2,第0个和第2个能组成2 一共就3种方法,所以返回3
法一: 对于目标,index位置只能选一次(字符串贴纸,可以选择多次)
//感觉:当前货币值是一个状态
public static int process1(int[] arr, int aim, int index){
if(aim == 0) return 1;
if(index > arr.length-1) return 0;
if(aim < 0) return 0;
return process1(arr, aim-arr[index], index+1) + process1(arr, aim, index+1);
}
法二: 注意边界当index = N, aim = 0 依然返回1
//dp[0~aim][index~0]
public static int process2(int[] arr, int aim){
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[aim+1][N+1];
for(int j = N; j >= 0; j-- ){
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= aim; i++){
for(int j = N-1; j >= 0; j--){
if(i >= arr[j]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-arr[j]][j+1] + dp[i][j+1];
}
else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j+1];
}
}
}
return dp[aim][0];
}
货币问题2
arr是面值数组,其中的值都是正数且没有重复。再给定一个正数aim。每个值都认为是一种面值,且认为张数是无限的。返回组成aim的方法数
例如:arr = {1,2},aim = 4 方法如下:1+1+1+1、1+1+2、2+2 一共就3种方法,所以返回3
法一.
public static int process1(int[] arr, int index, int aim){
if(index >= arr.length){
if(aim == 0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
if(aim < 0) return 0;
if(arr[index] > aim) {
return process1(arr, index+1, aim);
}
else{
return process1(arr, index+1, aim) + process1(arr, index, aim-arr[index]);
}
}
法二
public static int process2(int[] arr, int aim){
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N+1][aim+1];
//边界
dp[N][0] = 1;
for(int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = 0; j <= aim; j++){
if(arr[i] <= j){//可以选择arr[i]
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j] + dp[i][j-arr[i]];
}
else{
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
货币问题3
arr是货币数组,其中的值都是正数。再给定一个正数aim。每个值都认为是一张货币,认为值相同的货币没有任何不同,返回组成aim的方法数
例如:arr = {1,2,1,1,2,1,2},aim = 4 方法:1+1+1+1、1+1+2、2+2一共就3种方法,所以返回3
打怪兽
给定3个参数,N,M,K 怪兽有N滴血,等着英雄来砍自己, 英雄每一次打击,都会让怪兽流失[0~M]等概率的一个值. 求K次打击之后,英雄把怪兽砍死的概率
/**
* 返回打死的概率
* @param N 怪物N滴血
* @param M 伤害0~M
* @param K 打K次
* @return */
public static double killMonster(int N, int M, int K){
if(N < 1 || M < 1 || K < 1) return 0;
//long res = process1(N,M,K);
long res = dp2(N,M,K);
double all = Math.pow(M+1,K);
return (double)((double)res/all);
}
//递归
public static long process1(int N, int M, int K){
if(K <= 0){
return N <= 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
long res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= M; i++){
res += process1(N-i, M, K-1);
}
return res;
}
//动态规划
public static long dp1(int N, int M, int K){
long[][] dp = new long[K+1][N+1];
dp[0][0] = 1;
//dp[i][j] 还剩i次,怪物还剩j血,最终能够打死怪物的可能方法数
for(int i = 1; i <= K; i++){
dp[i][0] = (long)Math.pow(M+1, i);
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++){
for(int p = 0; p <= M; p++){
//当j-p<0 要么用公式计算,要么将数组扩大扩大
if(j-p >= 0) dp[i][j] += dp[i-1][j-p];
else {
dp[i][j] += (long)Math.pow(M+1, i-1);
}
}
}
}
return dp[K][N];
}
//将化简K*N循环中的0~M循环.
public static long dp2(int N, int M, int K){
long[][] dp = new long[K+1][N+1];
dp[0][0] = 1;
//dp[i][j] 还剩i次,怪物还剩j血,最终能够打死怪物的可能方法数
for(int i = 1; i <= K; i++){
dp[i][0] = (long)Math.pow(M+1, i);
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++){
//例: M=3 dp[3][10] = dp[2][7,8,9,10] dp[3][9] = dp[2][6,7,8,9];
dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j-1] + dp[i-1][j]);
if(j-M-1 >= 0){
dp[i][j] -= dp[i-1][j-M-1];
}
else dp[i][j] -= Math.pow(M+1, i-1);
}
}
return dp[K][N];
}
货币问题4
arr是面值数组,其中的值都是正数且没有重复。再给定一个正数aim。每个值都认为是一种面值,且认为张数是无限的。返回组成aim的最少货币数
//arr[0~index-1]已经尝试过,现在尝试第index个,当前目标aim.从左往右尝试模型
public static int process1(int[] arr, int index, int aim){
if(index == arr.length){
return aim == 0 ? 0: Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int num = 0; num*arr[index] <= aim; num++){
int follow = process1(arr, index+1, aim-num*arr[index]);
if(follow != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
res = Math.min(res, follow+num);
}
}
return res;
}
public static int dp1(int[] arr, int aim){
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N+1][aim+1];
for(int k = 1; k <= aim; k++){
dp[N][k] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
for(int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = 0; j <= aim; j++){
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int num = 0; num*arr[i] <= j; num++){
if(dp[i+1][j-num*arr[i]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i+1][j-num*arr[i]] + num, dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
public static int dp2(int[] arr, int aim){
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N+1][aim+1];
for(int k = 1; k <= aim; k++){
dp[N][k] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
for(int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = 0; j <= aim; j++){
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j];
// 假设arr[5] = 3 dp[5][11] = min(dp[6][11],dp[6][8],dp[6][5],dp[6][2])
// dp[5][8] = min(dp[6][8], dp[6][5], dp[6][2])
if(j-arr[i] >= 0 && dp[i][j-arr[i]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j-arr[i]]+1,dp[i+1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
整数拆分
给定一个正数n,求n的裂开方法数,规定:后面的数不能比前面的数小
比如4的裂开方法有:1+1+1+1、1+1+2、1+3、2+2、4 5种,所以返回5
求相差最小的拆分
给定一个正数数组arr,请把arr中所有的数分成两个集合,尽量让两个集合的累加和接近.
返回最接近的情况下,较小集合的累加和
1.递归: 想了很久, 其实先定好状态再根据状态推会简单很多, 比如定义process(arr, index, sum)返回arr[index....]中小于等于sum的最大组合.
//返回arr[index-arr.length]拆分成两个组,中较小的组(保证两个组相差最小)
public static int process(int[] arr, int index, int sum){
if(index == arr.length) return 0;
//较小的组不选arr[index]
int nSelect = process(arr, index+1, sum);//index+1后较小组的和
//较小的组选arr[index]
int ySelect = 0;
if(sum >= arr[index]){
ySelect = arr[index] + process(arr, index+1, sum-arr[index]);
}
return Math.max(nSelect, ySelect);
}
2.dp: 发现递归过程会出现重复计算,因此可用dp优化
public static int dp(int[] arr, int sum){
int N = arr.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N+1][sum+1];
for(int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = 0; j <= sum; j++){
int nSelect = dp[i+1][j];
int ySelect = 0;
if(j >= arr[i]){
ySelect = arr[i] + dp[i+1][j-arr[i]];
}
dp[i][j] = Math.max(nSelect,ySelect);
}
}
return dp[0][sum];
}
求相差最小的拆分2
给定一个正数数组arr,请把arr中所有的数分成两个集合
如果arr长度为偶数,两个集合包含数的个数要一样多,如果arr长度为奇数,两个集合包含数的个数必须只差一个
请尽量让两个集合的累加和接近. 返回最接近的情况下,较小集合的累加和
//返回目标长度len的分组,保证小于等于rest同时尽可能大
public static int process1(int[] arr, int index, int rest, int len){
if(len == 0) return 0;
if(index == arr.length) {
if(len == 0) return 0;
else return -1;
}
int nFollow = process1(arr, index+1, rest, len);
int yFollow = -1;
if(rest >= arr[index]){
int p = process1(arr, index+1, rest-arr[index], len-1);
if(p != -1){
yFollow = arr[index] + p;
}
}
return Math.max(nFollow, yFollow);
}
//index层,len行,rest列其中index不可以优化掉,因为arr[index]需要变化
public static int dp(int[] arr, int sum){
int N = arr.length;
int[][][] dp = new int[N+1][N/2+2][sum+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= N/2+1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= sum; j++){
dp[N][i][j] = -1;
}
}
for(int index = N-1; index >= 0; index--){
for(int i = 0; i <= N/2+1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= sum; j++){
int not = dp[index+1][i][j];
int yes = -1;
if(i >= 1 && j >= arr[index]){
int tmp = dp[index+1][i-1][j-arr[index]];
if(tmp != -1) yes = tmp + arr[index];
}
dp[index][i][j] = Math.max(not, yes);
}
}
}
if(N % 2 == 0) return dp[0][N/2][sum];
else return Math.max(dp[0][N/2+1][sum],dp[0][N/2][sum]);
}
线段树
-
线段树是一种二叉搜索树, 因此每个节点最多两颗子树, 且左小右大. 每个节点存储一个区间. 每次操作也都是操作一个区间
-
线段树提供区间范围上的增添, 修改, 查询, 比较常用的最值线段树, 区间和线段树
-
利用ST表求区间最值, 建表O(nlogn), 查询O(1). 但是不能动态的查询
-
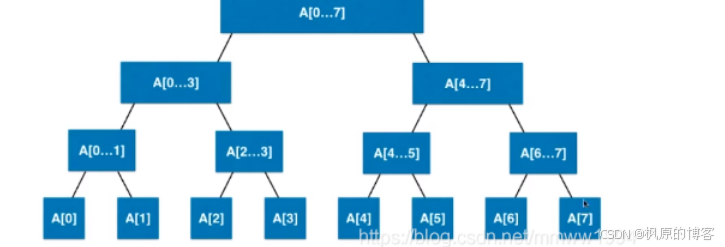
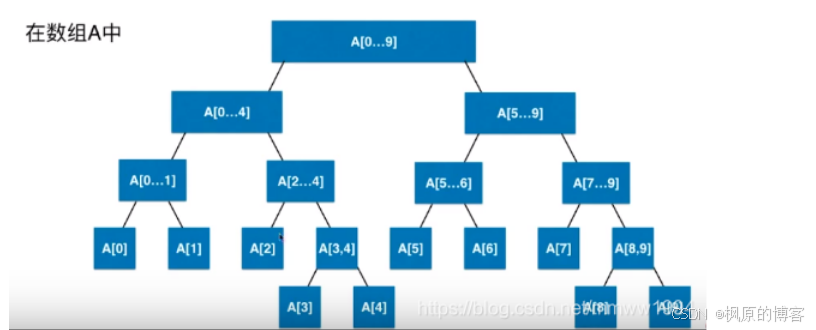
存储方式: 除最后一层, 构成满二叉树, 因此用数组存储. 如果元素个数为2^k, 构造的线段树为完全二叉树, 需要2n的空间
如果不是2的整数幂, 最多需要4n空间, 叶子节点n, 非叶子节点n, 因为叶子节点凸出来, 多了一层, 再多2n个节点
华为OD笔试D卷
1、最长子字符串的长度
题目描述
给你一个字符串 s,首尾相连成一个环形,请你在环中找出 'o' 字符出现了偶数次最长子字符串的长度。
| 输入 | alolobo |
|---|---|
| 输出 | 6 |
| 描述 | 最长子字符串之一是 "alolob",它包含2个'o' |
//如果偶数个o返回数组长度len,否则奇数个o返回len-1
2、最大时间
题目描述
给定一个数组,里面有 6 个整数,求这个数组能够表示的最大 24 进制的时间是多少,输出这个时间,无法表示输出 invalid。
| 输入 | [0,2,3,0,5,6] |
|---|---|
| 输出 | 23:56:00 |
| 描述 | 无 |
3、智能驾驶
有一辆汽车需要从 m * n 的地图左上角(起点)开往地图的右下角(终点),去往每一个地区都需要消耗一定的油量,加油站可进行加油。
请你计算汽车确保从从起点到达终点时所需的最少初始油量。
说明:
-
智能汽车可以上下左右四个方向移动
-
地图上的数字取值是 0 或 -1 或 正整数: -1 :表示加油站,可以加满油,汽车的油箱容量最大为100; 0 :表示这个地区是障碍物,汽车不能通过正整数:表示汽车走过这个地区的耗油量
-
如果汽车无论如何都无法到达终点,则返回 -1
import java.util.*;
public class MinimumInitialFuel {
int[][] minInitialFuel;
static class State implements Comparable<State> {
int x, y;
int fuel; //现在又fuel的油
int cost; //最少需要cost才能到这里
public State(int x, int y, int fuel, int cost) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.fuel = fuel;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(State other) {
return this.cost <= other.cost ? cost-other.cost : this.fuel-fuel; // 优先队列按照 cost 升序排列
}
}
public int minInitialFuel(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
// Directions for up, down, left, right
int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
// Priority Queue for BFS with minimum initial fuel
PriorityQueue<State> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new State(0, 0, 0, grid[0][0])); // Start from (0, 0) with 0 fuel and 0 cost
// Minimum initial fuel needed to reach each cell
minInitialFuel = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(minInitialFuel[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
minInitialFuel[0][0] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
State curr = pq.poll();
if (curr.x == m - 1 && curr.y == n - 1) {
return curr.cost; // Reach the destination
}
// Explore neighbors
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int nx = curr.x + dir[0];
int ny = curr.y + dir[1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
int newFuel = curr.fuel;
int cost = curr.cost;
if (grid[nx][ny] == -1) { // Refuel station
newFuel = 100; // Refuel to full tank
cost = curr.cost;
} else if (grid[nx][ny] == 0) { // Obstacle
continue;
} else { // Regular cell with positive fuel consumption
int neededFuel = grid[nx][ny];
newFuel -= neededFuel;
if(newFuel < 0){
cost = curr.cost - newFuel;
newFuel = 0;
}
}
if (cost <= 100 && cost < minInitialFuel[nx][ny]) {
minInitialFuel[nx][ny] = cost;
pq.offer(new State(nx, ny, newFuel, cost));
}
}
}
}
return -1; // Cannot reach destination
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MinimumInitialFuel solver = new MinimumInitialFuel();
// Example usage
int[][] grid1 = {
{10, 30, 30,20},
{30, 30, -1,10},
{0, 20, 20, 40},
{10, -1, 30, 40}
};
int[][] grid2 = {
{10, 0, 30, -1, 10},
{30, 0, 20, 0, 20},
{10, 0, 10, 0, 30},
{10, -1, 30, 0, 10}
};
int[][] grid3 = {
{10, 30, 30, 20},
{30, 30, 20, 10},
{10, 20, 10, 40},
{10, 20, 30, 40}
};
int minFuel = solver.minInitialFuel(grid1);
// System.out.println(solver.minInitialFuel);
for (int[] ints : solver.minInitialFuel) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("Minimum initial fuel needed: " + minFuel);
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








