A
签到直接 / 1000 /1000 /1000输出即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define fep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); --i)
#define _for(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); ++i)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pdd pair<double,double>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define fs first
#define sc second
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<n/1000<<'\n';
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// freopen("C:\\Users\\24283\\CLionProjects\\untitled2\\1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}
B
B题主要是一个异或和的概念
异或和是一些数连续异或。
直接按题意模拟即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define fep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); --i)
#define _for(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); ++i)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pdd pair<double,double>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define fs first
#define sc second
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
using namespace std;
int a[110][110];
void solve() {
int n,m,x;
cin>>n>>m>>x;
int res=0;
rep(i,1,n){
rep(j,1,m){
cin>>a[i][j];
res+=a[i][j];
}
}
if(res!=x){
cout<<"wrong answer\n";
return;
}
//判断行得和
int hy=0,ly=0;
// rep(i,1,m) hy^=a[1][i];
// rep(i,1,n) ly^=a[i][1];
rep(i,1,n){
int ans=0;
rep(j,1,m){
ans^=a[i][j];
}
hy+=ans;
}
rep(i,1,m){
int ans=0;
rep(j,1,n){
ans^=a[j][i];
}
ly+=ans;
}
if(ly!=hy){
cout<<"wrong answer\n";
return;
}
cout<<"accepted\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// freopen("C:\\Users\\24283\\CLionProjects\\untitled2\\1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}
C
贪心、构造
考虑对答案的贡献。
如果一个数是小写字母对答案是没有贡献的后面只要出现一个大写字母就会对答案贡献1。
i
i
i是大写字母,如果
i
+
1
i+1
i+1是大写字母对答案会贡献1
如果
i
+
1
i+1
i+1是小写字母对答案
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define fep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); --i)
#define _for(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); ++i)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pdd pair<double,double>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define fs first
#define sc second
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
using namespace std;
int a[110][110];
void solve() {
string s;
cin>>s;
int ans=0;
rep(i,0,s.size()-2){
if(islower(s[i])&&isupper(s[i+1])){
ans++;
i++;
continue;
}
if(isupper(s[i])&& isupper(s[i+1])){
ans++;
i++;
continue;
}
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// freopen("C:\\Users\\24283\\CLionProjects\\untitled2\\1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}
D
昨天调了好久
之前一直没有注意入队出队的标记的问题
b
f
s
一定要在入队的时候标记
bfs一定要在入队的时候标记
bfs一定要在入队的时候标记,如果一个点在出队的时候标记可能会出现下面情况
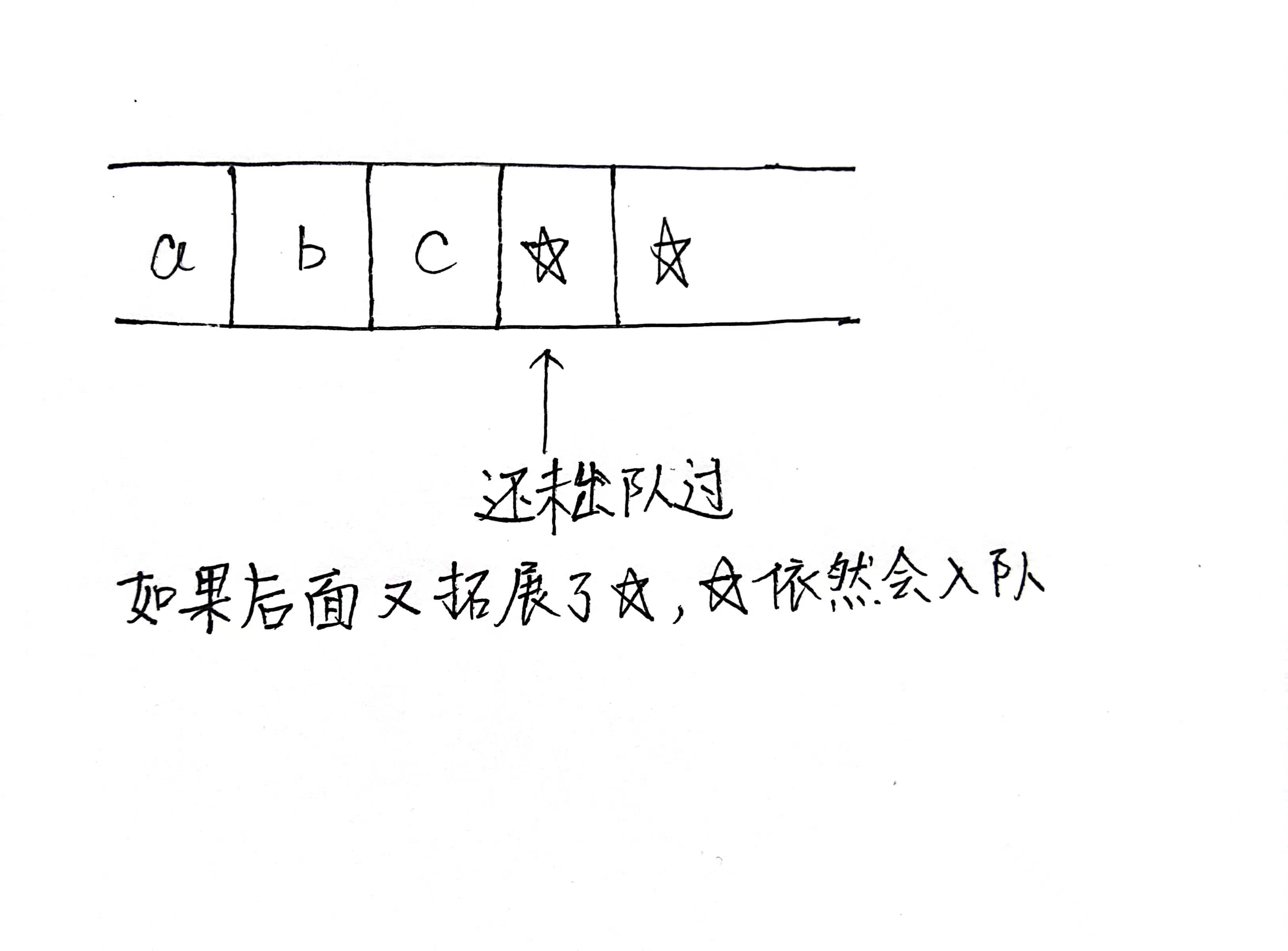
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define fep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); --i)
#define _for(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); ++i)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pdd pair<double,double>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define fs first
#define sc second
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
using namespace std;
int vis[1010][1010],d[1010][1010];
char mp[1010][1010];
int n,m;
int dx[]={0,0,0,1,-1};
int dy[]={0,1,-1,0,0};
void solve()
{
cin>>n>>m;
rep(i,1,n){
cin>>(mp[i]+1);
}
queue<pii>q;
q.push({1,1});
d[1][1]=0;
vis[1][1]=1;
while(q.size()){
auto u=q.front();
q.pop();
// vis[u.first][u.second]=1;
if(u.first==n&&u.second==m){
cout<<d[n][m]<<'\n';
return;
}
// vis[u.first][u.second]=1;
rep(i,1,4){
int xx=u.first+dx[i];
int yy=u.second+dy[i];
if(xx<1||xx>n||yy<1||yy>m||vis[xx][yy]) continue;
if(mp[xx][yy]==mp[u.first][u.second]) continue;
q.push({xx,yy});
vis[xx][yy]=1;
d[xx][yy]=d[u.first][u.second]+1;
}
}
cout<<-1<<'\n';
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// freopen("C:\\Users\\24283\\CLionProjects\\untitled2\\1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}
E
瞎搞的题目只需要构造3 * 3的矩阵其他随机就行
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define fep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); --i)
#define _for(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); ++i)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pdd pair<double,double>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define fs first
#define sc second
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
using namespace std;
int mp[1010][1010];
int n,m;
const unsigned zseed=time(0);
mt19937_64 zgen{zseed};
struct UI{
//随机数的分布器
//产生随机数的区间是[a,b]
uniform_int_distribution<int>u;
//随机数的生发器
mt19937_64& gen{zgen};
int get()
{
return u(gen);
}
UI(int a=0,int b=1):u(a,b){};
};
void solve() {
UI u{0,26};
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
mp[1][1]=mp[1][2]=3;
mp[2][1]=mp[3][1]=2;
mp[2][2]=mp[2][3]=mp[3][2]=1;
rep(i,1,n){
rep(j,1,m){
if(!mp[i][j]){
mp[i][j]=u.get();
}
}
}
rep(i,1,n){
rep(j,1,m){
cout<<(char)(mp[i][j]+'a');
}
cout<<'\n';
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// freopen("C:\\Users\\24283\\CLionProjects\\untitled2\\1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}
F
不包含长度不小于 2 的回文子串这个性质比较重要
先来看一下长度为2的回文串有哪些
aa
aba
abba
abcba
可以观察到一些性质
就是长度大于3的回文串会包含长度为2或3的回文串
所以好串的含义就是不包含长度为3的回文串
接着考虑假设第一个是r
那个第二个只能是e/d第三个就只能是d/e
这就启发我们修改成好串的情况只有3 * 2种
然后我们只需要在查询的时候比较一下6种那种是最小的
如何快速查询的这个可以用前缀和处理
但是设计到修改操作,所以这一需要一点点数据结构去维护
可以用树状数组去维护,线段树也是可以的.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i)
#define fep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); --i)
#define _for(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); ++i)
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pdd pair<double,double>
#define ll long long
#define db double
#define endl '\n'
#define fs first
#define sc second
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int tr[6][maxn];
int n,q;
string s;
string c[6]={"red","erd","dre","rde","edr","der"};
void add(int op,int x, int d){
for(;x<=2e5;x+=x&-x) tr[op][x]+=d;
}
int query(int op,int x){
int res=0;
for(;x;x-=x&-x) res+=tr[op][x];
return res;
}
int ask(int op,int l,int r){
return query(op,r)- query(op,l-1);
}
void solve() {
cin>>n>>q;
cin>>s;
s=" "+s;
// rep(i,1,n){
// cout<<s[i];
// }
// cout<<'\n';
// rep(i,1,n){
// cout<<c[0][(i-1)%3];
// }
// cout<<'\n';
//初始化树状数组
rep(j,0,5){
rep(i,1,n){
int wei=i%3;
int x=(s[i]!=c[j][wei]);
// cout<<i<<' '<<x<<'\n';
add(j,i,x);
}
}
//q次操作
while(q--){
int op;
cin>>op;
if(op==1){//修改
int x;
char chr,lst;
cin>>x>>chr;
lst=s[x];
//维护树状数组
rep(i,0,5){
int wei=x%3;
if(s[x]!=c[i][wei]){
add(i,x,-1);
}
//修改
s[x]=chr;
if(s[x]!=c[i][wei]){
add(i,x,1);
}
s[x]=lst;
}
s[x]=chr;
}else{//查询
int res=1e9;
int l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
rep(i,0,5){
res=min(res,ask(i,l,r));
}
cout<<res<<'\n';
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
// freopen("C:\\Users\\24283\\CLionProjects\\untitled2\\1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}








 文章涉及C++编程中的几个竞赛题目,包括异或和计算、字符串中大写字母对答案的贡献、回文子串检测、队列使用中的注意事项以及树状数组在解决查询问题的应用。
文章涉及C++编程中的几个竞赛题目,包括异或和计算、字符串中大写字母对答案的贡献、回文子串检测、队列使用中的注意事项以及树状数组在解决查询问题的应用。














 414
414











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








