这场套路题比较多,思维量少,主要都是离散化处理 + 二分。
1888A - Chemistry
题意:给定一个只含有字母的字符串,要求删掉k个字符后,对其各字符重排能形成回文。
思路:若最后剩余奇数个字符,则必然有一个字母的个数为奇数,其余都为偶数,若剩余偶数个字符,必须保证剩余的所有字母个数都为偶数。
// Problem: A. Chemistry
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 905 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1888/problem/A
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
void solve()
{
int n , k;
cin >> n >> k;
int cnt[26];
memset(cnt , 0 , sizeof cnt);
int odd = 0;
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){
cnt[s[i] - 'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i ++){
if(cnt[i] & 1){
odd ++;
}
}
if((n - k) & 1){
k -= (odd - 1);
if(k < 0){
cout<<"NO\n";
}
else{
cout<<"YES\n";
}
}
else{
k -= odd;
if(k < 0 || k % 2 == 1){
cout<<"NO\n";
}
else{
cout<<"YES\n";
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1888B - Raspberries
题意:给定一个数组,每次操作能够将数组其中一个数加一,要求能够使数组逐个相乘后能被k整除的最小操作数。
思路:观察到k = 2、3、4、5,当k为素数时,只需要考虑将数组中其中一位加到k的倍数即可。当k = 4 即非素数时,有两种操作方法:1、将其中一个数变为4的倍数。2、将两个数变为2的倍数。分别求最小操作数即可。
// Problem: B. Raspberries
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 905 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1888/problem/B
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
void solve()
{
int n , k;
cin >> n >> k;
if(k != 4){
int out = 100;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){
int x;
cin>>x;
out = min(out , x % k ? k - x % k : 0);
}
cout<<out<<endl;
}
else{
int out1 = 100, out2 = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){
int x;
cin >> x;
out1 = min(out1 , x % k ? k - x % k : 0);
if(out2 < 2 && !(x & 1)){
out2 ++;
}
}
cout << min(out1 , 2 - out2)<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1888D2 - Dances (Hard Version) 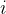
题意:给定长度为 n - 1 的数组 a 和长度为 n 的数组 b 。 定义 为数字 i 与 数组a合并之后构成的长度为n的数组。接下来能够进行若干次操作:将c 、 b数组同时删去一个数。定义
为将b、c数组重新排序后能够使得
的最小操作数。求解
。
思路:显然需要对b、c数组进行从小到大排序,要使得操作数尽可能的少,需要删掉b数组的前k个数跟c数组的后k个数。于是我们需要记录一个辅助数组, 令
。换句话说也就是要让
至少需要删掉
个数,需要的最少操作数为
。在
i 逐渐变大的过程之中,起先 i 这个数是在数组的第一位的。之后慢慢会与后面相邻数互换位置。例如:当
在数组第
位时,当
时,实现互换,其中
,
需要重新找,而找这个
的过程也是逐步递增的,因此只需要双指针
来表示数字
在当前数组第
位,以及
。每次交换由于只有
会改变,因此只需要比较这两个和当前最小操作数即可。由于
的取值可能很大,而数组的大小不多,因此需要离散化处理,i 在递增的过程中并不总是会改变操作数,能改变操作数的条件为
或者
,如此便能实现离散化。
// Problem: D1. Dances (Easy version)
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 905 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1888/problem/D1
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 3000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
void solve()
{
LL n , m;
cin >> n >> m;
LL c[n + 5];
LL b[n + 5];
LL a[n + 5];
LL out = 0;
a[0] = 1;
b[n] = 1e18;
a[n] = m;
for(int i = 1 ; i < n; i ++)
cin>>a[i];
sort(a , a + n);
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
cin>>b[i];
sort(b , b + n);
LL ans = 0;
LL l = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){
while(a[i] >= b[l]) l ++;
c[i] = l;
}
l = 1;
LL id = 0 ,r = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ;i ++){
ans = max(c[i] - i , ans);
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ;){
while(l < n && i > a[l]){
c[l - 1] = c[l];
ans = max(c[l - 1] - (l - 1) , ans);
l ++;
}
a[l - 1] = i;
while(r < n && i >= b[r]) r ++;
c[l - 1] = r;
ans = max(c[l - 1] - (l - 1) , ans);
LL next = min(m + 1 , min(a[l] + 1 , b[r]));
out += (next - i) * ans;
i = next;
}
cout<<out<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1888E - Time Travel
题意:一个无向图,共有n个点和m条边,且共有 t 个时间段限制,每条边只会在相应的时间段有效。下面共有按顺序的 k 个时间段。对于每个时间段你可以选择不走或者走一条边。试问能否从第一个时间段开始从1号节点走到n号节点。
思路:本题同今年CSP-J 2023 旅游巴士差不多,在堆优化的dijkstra算法上将距离改为时间段即可。对于每个点而言,到达的时间越早越好(因为后继就有更多的时间段可供选择)。因此用set存储每个时间段的次序大小。假设当前时间为 , 从
走到
为
到
这条边所处时间段的大于
的次序。用最短路求出到达各点的最短时间即可。
// Problem: E. Time Travel
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 905 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1888/problem/E
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=2e05+10;
const LL INF=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
struct node{
int num;
int dis;
bool operator > (const node &t) const
{
return dis > t.dis;
}
}tmp;
int dis[N];
int isv[N];
int n , k , s;
vector<node>tr[N];
set<int>st[N];
void dij(int s)
{
for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++){
dis[i] = INF;
}
priority_queue<node,vector<node> , greater<node> > q;
q.push({s,0});
dis[s] = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
tmp = q.top();
int x = tmp.num;
int t = tmp.dis;//时间
q.pop();
if(isv[x] == 1)
continue;
isv[x] = 1;
int len = tr[x].size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++ )
{
node now = tr[x][i];
int tt = now.dis;//目标时间
auto it = st[tt].upper_bound(t);
int len = *it;
int e = tr[x][i].num;
if(dis[e] > len)
{
dis[e] = len;
q.push({e,dis[e]});
}
}
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n >>k;
s = 1;
int x;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= k ; i++){
cin>>x;
while(x --){
int a , b;
cin >> a >> b;
tr[a].pb({b , i});
tr[b].pb({a , i});
}
}
cin>>x;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= x; i ++){
int time;
cin>>time;
st[time].insert(i);
}
for(int i = 0 ; i <= k ; i ++){
st[i].insert(INF);
}
dij(1);
if(dis[n] != INF){
cout<<dis[n];
}
else{
cout<<-1;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
// cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}1888F - Minimum Array
题意:给定一个数组a,下面给了q行,每行包含了,代表了 a 中
上所有元素加上
。
求整个过程中出现的按照次序最小的数组。
思路:区间加自然想到了用差分数组来表示,构造辅助数组b, ,对于每一轮操作,只需要令
。而对于最小的数组而言,只需要让b中第一个非零元素小于0即可。而想要动态的维护最小的非0元素下标,只需要用set即可。若碰到了更小的数组,更新一下此时的询问组数索引,然后将b数组清空,在清空的过程只需要将set中有的值清空即可,然后再清空set。最终通过最小数组的询问组数索引来求出最小数组即可。
// Problem: C. Minimum Array
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 905 (Div. 1)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1887/problem/C
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 3000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N=1e05+10;
const LL mod=1e09+7;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >t;
priority_queue<LL> q;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
struct Node{
LL l , r , num;
};
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
LL a[n + 5] = {0};
int min_idx = -1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
cin>>a[i];
LL dif[n + 5];
memset(dif , 0 , sizeof dif);
set<int>st;
int op;
cin>>op;
Node o[op];
for(int i = 0 ; i < op ; i ++){
cin>>o[i].l>>o[i].r>>o[i].num;
dif[o[i].l] += o[i].num;
dif[o[i].r + 1] -= o[i].num;
if(dif[o[i].l] != 0)
st.insert(o[i].l);
else
st.erase(o[i].l);
if(dif[o[i].r + 1] != 0)
st.insert(o[i].r + 1);
else
st.erase(o[i].r + 1);
auto it = st.begin();
int ans = *it;
if(ans != 0){
if(dif[ans] < 0){
min_idx = i;
for(auto it : st){
dif[it] = 0;
}
st.clear();
}
}
}
memset(dif , 0 , sizeof dif);
for(int i = 0 ; i <= min_idx ; i ++){
dif[o[i].l] += o[i].num;
dif[o[i].r + 1] -= o[i].num;
}
LL chan = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
chan += dif[i];
a[i] += chan;
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}






















 2756
2756

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








