1.线程创建
Thread类是JVM用来管理线程的一个类,换句话说,每个线程都有一个唯一的Thread对象与之关联(java代码中的Thread对象和操作系统中的线程是一一对应的)
1.1.继承Thread类,重写run方法
package asd;
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new MyThread();
t.start();
while(true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.2 继承Thread类,重写run方法,使用匿名内部类
package asd;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.3 实现Runnable类,重写run方法
package asd;
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread t = new Thread(runnable);
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.4 实现Runnable类,重写run方法,使用匿名内部类方法
package asd;
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}

2.线程中断
本质让来说,让一个线程终止,办法只有一种,让该线程的入口方法执行完毕.
2.1给线程中设定一个结束标志位:
死循环导致入口方法无法执行完毕,所以不能结束线程.
package asd;
public class Test7 {
public static boolean isQuit = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (!isQuit){
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("t 线程终止");
});
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
isQuit = true;
}
}

Thread类内置了一个标志位,让我们更方便的实现上述效果
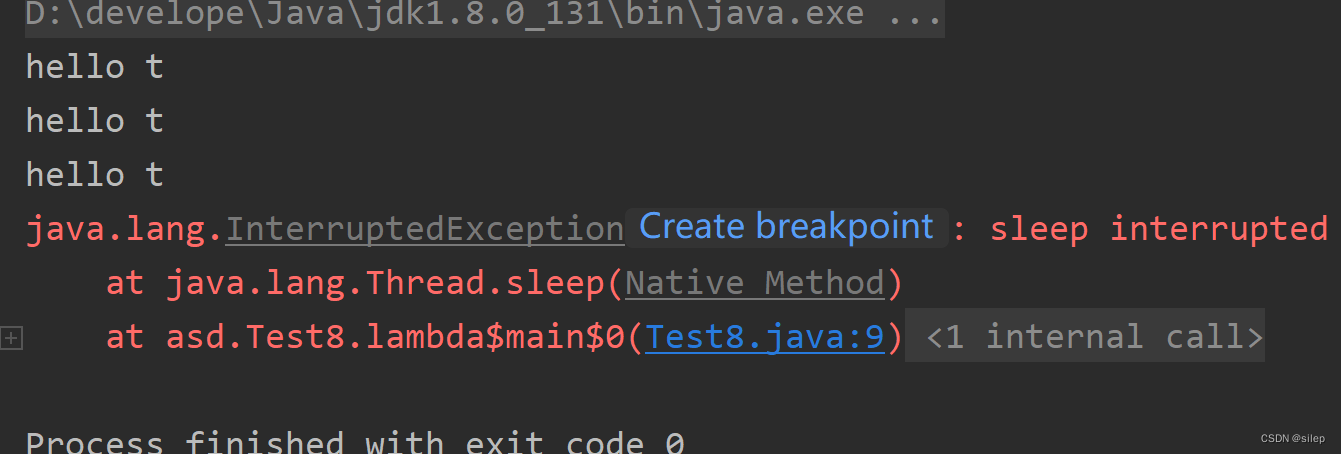
如果要结束循环,就得在catch中写一个break
package asd;
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {
interruptedException.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
}
});
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t.interrupt();
}
}
3.线程等待
join方法是在main线程中调用join方法,意思就是让main线程等待t线程先结束后,在执行.
package asd;
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() ->{
System.out.println("hello t");
});
t.start();
t.join();
System.out.println("hello main");
}
}

4.线程休眠
sleep方法使线程进入休眠状态,并设定休眠的时间
public static void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException 休眠当前线程 millis毫秒
public static void sleep(long millis,int nanos) throws InterruptedException
5.获取线程实例
Thread.currentThead()就能够获取到当前线程的引用(Thread实例的引用)
package asd;
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.getName());
}
};
t.start();
}
}
线程的名字只能通过Thread.getName().
package asd;
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
t.start();
}
}






















 1787
1787











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








