进程与线程
进程
- 程序是指令和数据的有序集合,是一个静态概念。进程是程序在处理机上的一次执行过程,是一个动态概念
- 进程是一个具有一定独立功能的程序,一个实体,每一个进程都有它自己的地址空间
- 进程的状态
- 就绪状态(Ready)
- 运行状态(Running)
- 阻塞状态(Blocked)
线程
- 是进程中的一个执行路径,共享一个内存空间,线程之间可以自由切换,并发执行
- 一个进程中最少有一个线程
- 并行: 两个任务同时执行(多个CPU)
- 并发:两个任务同时请求运行,而处理器只能接受一个任务,就会把两个任务安排轮流执行,由于CPU时间片运行时间较短,就会感觉两个任务在同时执行
线程的基本使用
- 继承Thread类
- 实现Runnable接口
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.start(); //启动线程(准备就绪)
MyRunnale mr = new MyRunnale();
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr);
t2.start();
}
}
/**
* 继承Thread类
*/
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-"+i);
}
}
}
/**
* 实现Runnable接口
*/
class MyRunnale implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-"+i);
}
}
}
线程休眠
public static void sleep(long millis)
//使当前正在执行的线程以指定的毫秒数暂停(暂时停止执行)【以毫秒为单位的睡眠时间长度】,释放CPU的时间片,具体取决于系统定时器和调度线程的精度和准确性。线程不会丢失任何显示器的所有权
//IllegalArgumentException如果millis值为负数抛出异常
//InterruptedException 如果任何线程中断当前线程,抛出异常,当前线程的中断状态将被清除
public static void sleep(long millis,int nanos)
//throws InterruptedException
static Thread currentThread() //返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用
Thread,sleep(500);
join与中断线程
- public final void join()
- 与**join(0)**相同
- InterruptedException 中断异常
public class ThreadDemo2 {
/**
* join方法:
* 加入线程,让调用的线程先执行指定时间或执行完毕
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable2 mr2 = new MyRunnable2();
Thread t = new Thread(mr2);
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(i == 20){
// try {
// t.join(); //让线程t先执行完毕
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// }
t.interrupt(); //中断线程,只是作了中断标记
}
}
}
}
class MyRunnable2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
if(Thread.interrupted()){ //测试中断状态,此方法会把中断状态清除
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
//自定义标记中断
public class ThreadDemo2 {
/**
* join方法:
* 加入线程,让调用的线程先执行指定时间或执行完毕
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable3 mr3 = new MyRunnable3();
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr3);
t2.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(i == 20){
mr3.flag = false;
}
}
}
}
class MyRunnable3 implements Runnable{
public boolean flag = true;
public MyRunnable3(){
flag = true;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(flag){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==="+(i++));
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
守护线程与yield
public final void setDaemon(boolean on) //将此线程标记为daemon线程或用户线程。当运行的唯一线程都是守护进程线程时,java 虚拟机将退出
public final boolean isDaemon() //测试这个线程是否为守护线程
public static void yield() //暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程
long getId() //返回该线程的标识符
String getName() //返回该线程的名称
void setName(String name) //改变线程名称,使之与参数name相同
boolean isAlive() //测试线程是否厨余活动状态
void setPriority(int newPriority) //更改线程的优先级
static int MAX_PRIORITY //线程可以具有的最高优先级
static int MIN_PRIORITY //线程可以具有的最低优先级
static int NORM_PRIORITY //分配给线程的默认优先级
public class ThreadDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable4 mr4 = new MyRunnable4();
Thread t = new Thread(mr4);
//优先级高可以提高该线程抢CPU的时间片的概率
t.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
//线程分为守护线程和用户线程 当进程中没有用户线程时,JVM会退出
t.setDaemon(true); //把线程设置为守护线程
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println("main--"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
class MyRunnable4 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println("--"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(i==5){
Thread.yield(); //让出本次时间片
}
}
}
}
线程同步
-
在多线程操作中,多个线程有可能同时处理同一个资源,这就是多线程中的共享数据
-
解决数据共享问题,必须使用同步,所谓同步就是指多个线程在同一个时间段内只能有一个线程执行指定代码,其他线程要等待此线程完成之后才可以继续执行
-
线程同步
- 同步代码块 synchronized(要同步的对象){要同步的操作};
- 同步方法 public synchronized void method(){要同步的操作};
- Lock(ReentrantLock);
-
同步准则
- 使代码块保持简短,把不随线程变化的预处理和后处理移出synchronized块
- 不要阻塞,如InputStream.read()
- 在持有锁的时候,不要对其他对象调用其同步方法
public class ThreadDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable5 mr5 = new MyRunnable5();
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr5);
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr5);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class MyRunnable5 implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 10; //售票
private Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) {
// method();
synchronized (obj){
if(ticket>0){
ticket--;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("您购买的票剩余"+ticket+"张");
}
}
}
}
//同步方法:同步的对象时当前对象(this)
private synchronized void method(){
if(ticket >0){
ticket--;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("您购买的票剩余"+ticket+"张");
}
}
//互斥锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//Lock实现同步
private synchronized void method2(){
lock.lock(); //锁
try{
if(ticket >0){
ticket--;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("您购买的票剩余"+ticket+"张");
}
}finally {
lock.unlock(); //释放锁 try finally 避免死锁
}
}
}
生产者消费者案例
public class ProducterCustomerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Food food = new Food();
Producter p = new Producter(food);
Customers c = new Customers(food);
Thread t1 = new Thread(p);
Thread t2 = new Thread(c);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
/**
* 消费者
*/
class Customers implements Runnable{
private Food food;
public Customers(Food food) {
this.food = food;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
food.get();
}
}
}
/**
* 生产者
*/
class Producter implements Runnable{
private Food food;
public Producter(Food food){
this.food = food;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if(i%2==0){
food.set("锅包肉","酸甜口味,爽");
}else {
food.set("佛跳墙","大补,滋阴补阳");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 食物
*/
class Food {
private String name;
private String desc;
private boolean flag = true; //true不是可以生产,false表示可以消费
/**
* 生产产品
*/
public synchronized void set(String name,String desc){
if(!flag){
//不能生产
try {
this.wait(); //线程进入等待状态,释放监视器的所有权(对象锁)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
this.setName(name);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
this.setDesc(desc);
flag = false;
this.notify(); //唤醒等待的线程(其中一个)
}
/**
* 消费
*/
public synchronized void get(){
if(flag){
//不能消费
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(this.getName()+"->"+this.getDesc());
flag = true;
this.notify();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Food{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc='" + desc + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Food(String name, String desc) {
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
public Food() {
}
}
线程生命周期
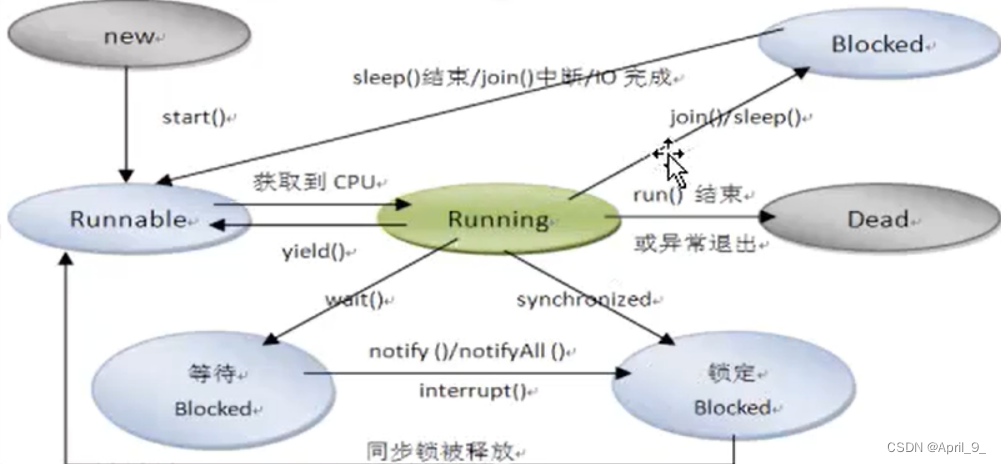
线程池
-
预先创建线程。在还没有任务到来之前,创建一定数量的线程,放入空闲队列中,然后对这些资源进行复用,减少频繁的创建和销毁对象
-
线程池的顶级接口Executor【执行已提交的Runnable任务的对象】
-
线程池接口ExecutorService
-
具体类 java.util.concurrent包
- Executors类
生成常用的线程池
newSingleThreadExecutor
//创建一个单线程的线程池。这个线程池只有一个线程在工作,相当于单线程串行执行所有任务。如果这个唯一的线程因为异常结束,那么会有一个新的线程来替代它。此线程池保证所有任务的执行顺序按照任务的提交顺序执行
newFixedThreadPool
//创建固定大小的线程池。每次提交一个任务就创建一个线程,直到线程达到线程池的最大大小。线程池的大小一旦达到最大值就会保持不变,如果某个线程因为执行异常而结束,那么线程池会补充一个新线程
newCachedThreadPool
//创建一个可缓存的线程池。如果线程池的大小超过了处理任务所需要的线程,那么就会回收部分空闲(60秒不执行任务)的线程,当任务数增加时,此线程池又可以智能的添加新线程来处理任务。此线程池不会对线程池大小做限制,线程池大小完全依赖于操作系统(JVM)能够创建的最大线程大小 ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
newScheduledThreadPool
//创建一个大小无限的线程池,此线程池支持定时以及周期性执行任务的需求
public class ThreadDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService es = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
es.execute(new MyRunnable6());
es.shutdown(); //结束
}
}
class MyRunnable6 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("run ..."+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
es.execute(new MyRunnable6());
es.execute(new MyRunnable6());
es.shutdown(); //结束
}
}
class MyRunnable6 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程池
ScheduledExecutorService es = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
//延迟三秒
es.schedule(new MyRunnable6(),3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
es.shutdown(); //结束
}
}
class MyRunnable6 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}






















 5366
5366











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








