管道
管道可以用来在两个进程之间传递数据,如: ps -ef | grep “bash”, 其中‘|’就是管道,其作用就是将 ps 命令的结果写入管道文件,然后 grep 再从管道文件中读出该数据进行过滤。
有名管道
有名管道可以在任意两个进程之间通信
有名管道的创建:
- 命令创建: mkfifo FIFO
- 系统调用创建
1. #include <sys/types.h>
2. #include <sys/stat.h>
3.
4. //filename 是管道名 mode 是创建的文件访问权限
5. int mkfifo(const char *filename, mode_t mode);下面我们一起通过一个例子学习有名管道——进程 a 要将从键盘获取的数据循环传递给另一个进程 b
a.c 的代码如下:
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. #include <stdlib.h>
3. #include <unistd.h>
4. #include <assert.h>
5. #include <string.h>
6. #include <fcntl.h>
7.
8. int main()
9. {
10. int fd = open("FIFO", O_WRONLY);
11. assert(fd != -1);
12.
13. printf("open FIFO success\n");
14.
15. while(1)
16. {
17. printf("please input: ");
18. char buff[128] = {0};
19.
20. fgets(buff, 128, stdin);
21.
22. write(fd, buff, strlen(buff) - 1);
23.
24. if(strncmp(buff, "end", 3) == 0)
25. {
26. break;
27. }
28. }
29.
30. close(fd);
31. exit(0);
32. }b.c 的代码如下:
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. #include <stdlib.h>
3. #include <unistd.h>
4. #include <assert.h>
5. #include <string.h>
6. #include <fcntl.h>
7.
8. int main()
9. {
10. int fd = open("FIFO", O_RDONLY);
11. assert(fd != -1);
12.
13. printf("open FIFO success\n");
14.
15. while(1)
16. {
17. char buff[128] = {0};
18. int n = read(fd, buff, 127);
19.
20. if(n <= 0 || 0 == strncmp(buff, "end", 3))
21. {
22. break;
23. }
24.
25. printf("%s\n", buff);
26. }
27.
28. close(fd);
29. exit(0);
30. }
无名管道
无名管道主要应用于父子进程间的通信。
无名管道的创建:
1. #include <unistd.h>
2. /*
3. pipe()成功返回 0,失败返回-1
4. fds[0]是管道读端的描述符
5. fds[1]是管道写端的描述符
6. */
7. int pipe(int fds[2])无名管道代码演示:
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. #include <stdlib.h>
3. #include <unistd.h>
4. #include <assert.h>
5. #include <string.h>
6.
7. int main()
8. {
9. int fd[2];
10.
11. int res = pipe(fd);
12. assert( res != -1 );
13.
14. pid_t pid = fork();
15. assert( pid != -1 );
16.
17. if( pid == 0 )
18. {
19. char buff[128] = {0};
20. read(fd[0], buff, 127);
21. printf("child read: %s\n", buff);
22. }
23. else
24. {
25. write(fd[1], "hello", 5);
26. }
27.
28. close(fd[0]);
29. close(fd[1]);
30. exit(0);
31. }管道的特点
- 无论有名还是无名,写入管道的数据都在内存中
- 管道是一种半双工通信方式(通信方式有单工、半双工、全双工)
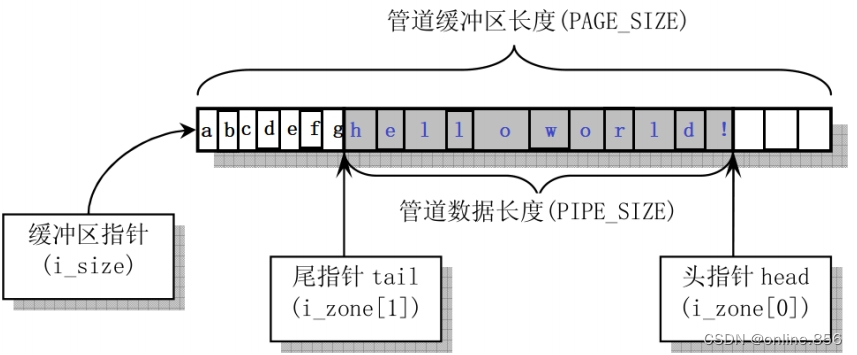
- 有名和无名管道的区别:有名可以在任意进程间使用,而无名主要在父子进程间管道的实现:





















 2071
2071











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








