前言
大家好,我是练习编程时长两年半的昆工第一ikun,之前几天咋们分享了线性结构的内容,那么今天我们就来看看树形结构。
目录
4.层次遍历:按层来遍历(第一层->第二层->第三层......)
1.树的概念
树是由m(m>=0)个节点组成的有限集合
我们都知道数据结构中有线性结构、逻辑结构、树形结构、图形结构这四大结构,其中的树形结构的特点就是:第一个节点没有前驱,最后一个节点没有后继,中间节点有唯一前驱,可以有多个后继,也可以没有。下面我们就一起来看看今天要分享的内容——二叉树。
2.二叉树:
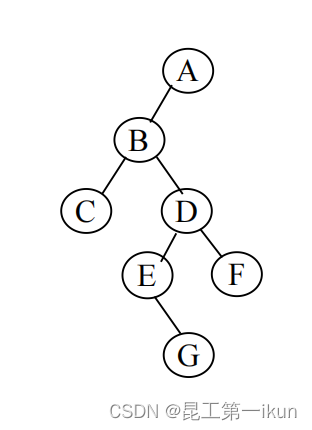
由m(m>=0)个节点组成的有限集合,二叉树一个节点的子节点一个为n(n<=2),并且二叉树严格区分左子树和右子树。说的通俗一点就是每一个节点最多只能有左右两个子节点,如下图
3.树的存储结构
(1)顺序存储
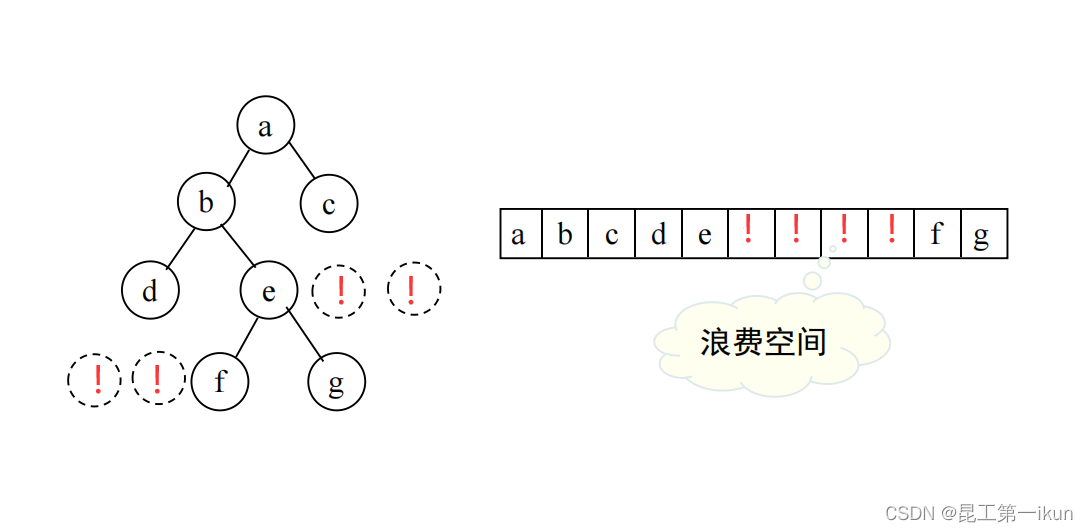
在进行二叉树的顺序存储之前,我们需要知道一个概念——完全二叉树,完全二叉树就是:只有最下面两层有度数小于2的节点,且最下面一层的叶节点集中在最左边的若干位置上。所以我们接下来要先将二叉树补成完全二叉树,再从上到下从左到右,将所有节点编号,依次存放在缓冲区中。这样就可以实现二叉树的顺序存储。
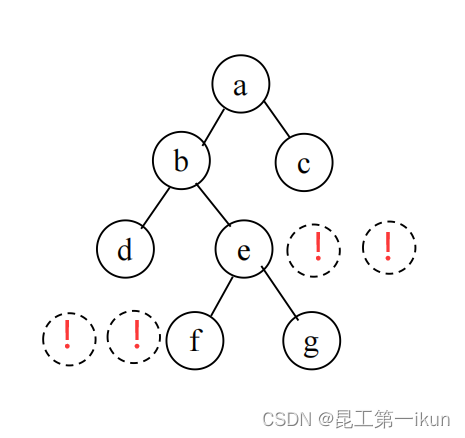
如上图所示,我们将二叉树空的左右子树用!代替补齐成一个完全二叉树。
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void tree_insert(char *tree)
{
char buf[64] = {0};
scanf("%s", buf);
strcpy(tree, buf);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char tree[50];
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
tree[i] = '!';
}
tree_insert(tree);
for(i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
if(tree[i] != '#') //规定一个特殊符号'#'来作为结束标志
{
if(tree[i] == '!') //规定一个特殊符号'!'来作为空的子树的标志
{
break;
}
printf("%c", tree[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
} 顺序存储简单易懂,并且代码也不复杂,但是它会导致空间的浪费,所以我们一般不使用顺序存储,而是使用下面将要介绍的链式存储。
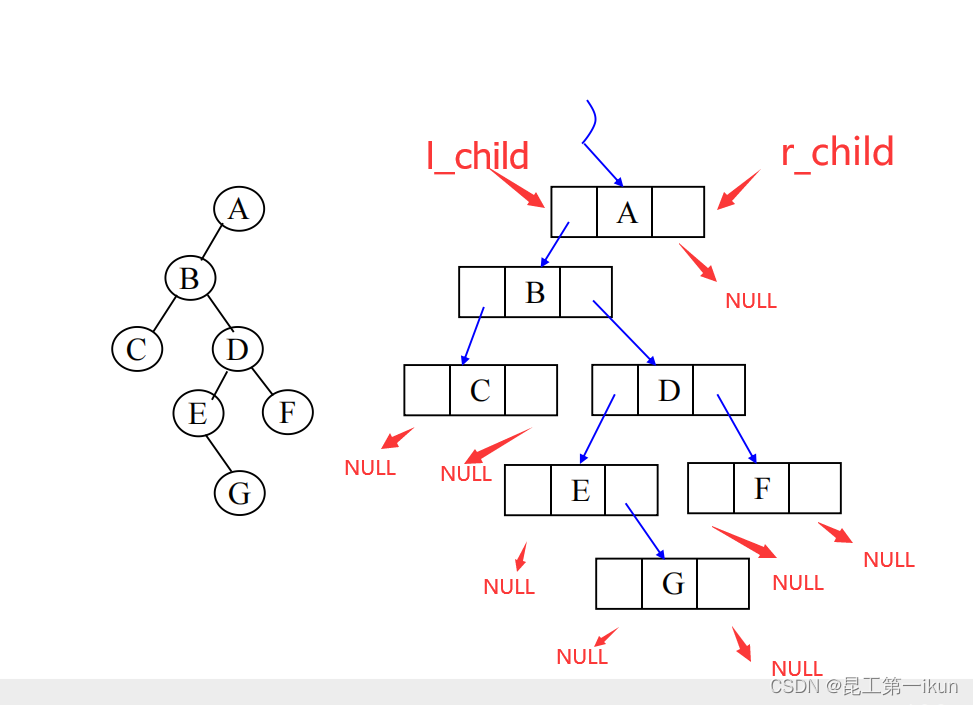
(2)链式存储
树中每个节点相关结构体:
typedef int data_t;
typedef struct tree_node
{
data_t data; //数据域
struct tree_node *l_child; //指向当前节点的左子树
struct tree_node *r_child; //指向当前节点的右子树
}T_node;使用链式存储我们首先要定义两个指针域分别来指向二叉树的左右子树,并且我们要使用递归函数来创建二叉树。
代码如下:
T_node *create_tree()
{
char ch;
scanf("%c", &ch);
T_node *root;
if(ch == '#'){
return NULL;
}
else{
root = (T_node *)malloc(sizeof(T_node));
if(NULL == root){
printf("malloc failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
root->data = ch;
root->l_child = create_tree();
root->r_child = create_tree();
return root;
}
}我们现在已经创建了一个链式存储的二叉树,下面我们将按照四钟方式遍历这个二叉树。
4.二叉树的遍历
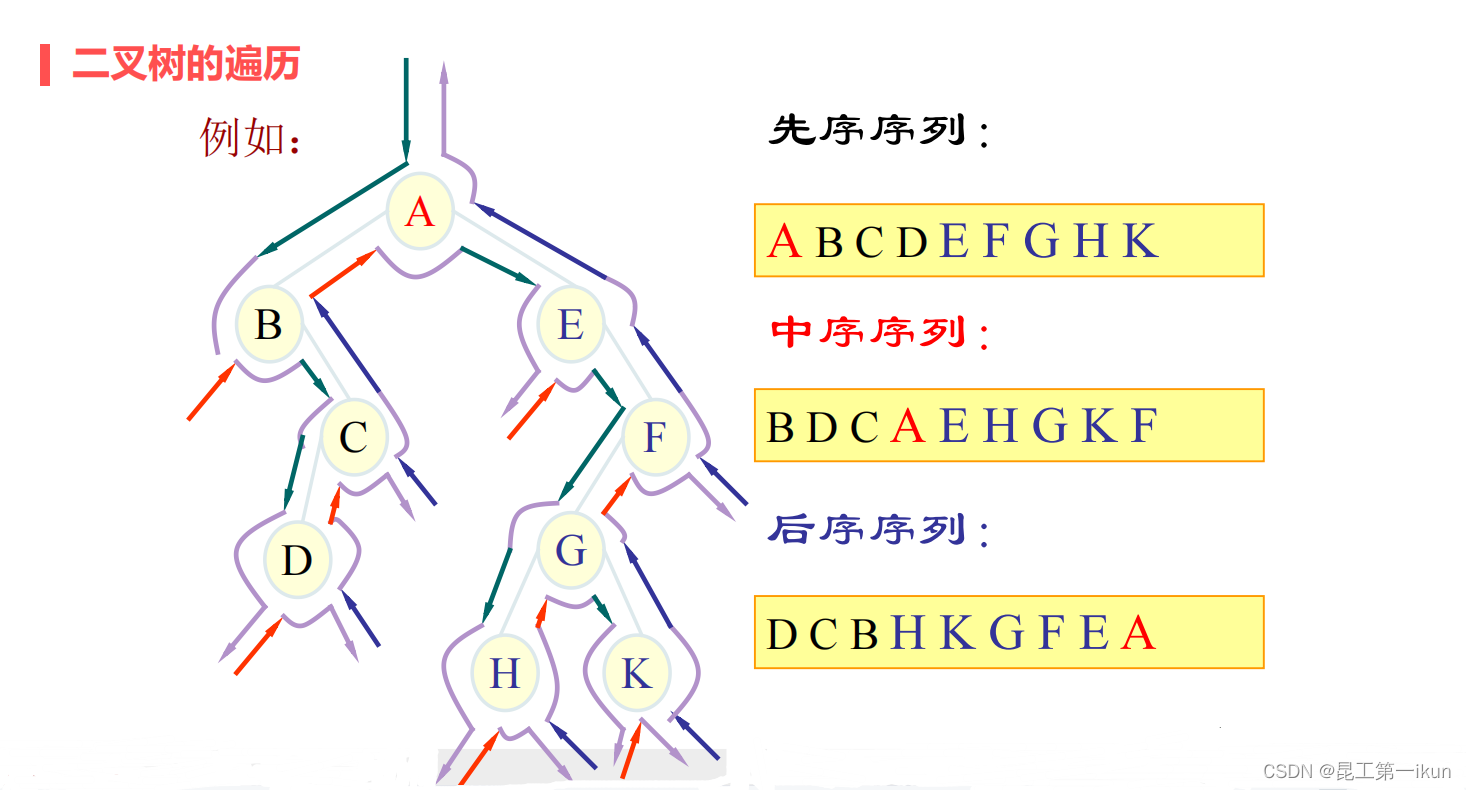
1.先序遍历:先访问树根,再访问左子树,最后访问右子树
2.中序遍历:先访问左子树,再访问树根,最后访问右子树
3.后序遍历:先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问树根
上面三种遍历方法如下图所示:
4.层次遍历:按层来遍历(第一层->第二层->第三层......)
层次遍历是按每一层来遍历,我们将用到队列的知识。
四钟遍历方法的代码如下:
①linktree.c函数功能代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "linktree.h"
T_node *create_tree()
{
char ch;
scanf("%c", &ch);
T_node *root;
if(ch == '#'){
return NULL;
}
else{
root = (T_node *)malloc(sizeof(T_node));
if(NULL == root){
printf("malloc failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
root->data = ch;
root->l_child = create_tree();
root->r_child = create_tree();
return root;
}
}
void f_print(T_node *root) //先序遍历
{
if(root != NULL){
printf("%c ", root->data);
f_print(root->l_child);
f_print(root->r_child);
}
return;
}
void m_print(T_node *root) //中序遍历
{
if(root != NULL){
printf("%c ", root->data);
m_print(root->l_child);
m_print(root->r_child);
}
return;
}
void l_print(T_node *root) //后序遍历
{
if(root != NULL){
printf("%c ", root->data);
l_print(root->l_child);
l_print(root->r_child);
}
return;
}
void c_print(T_node *root) //层次遍历
{
T_node *p[64];
int front, rear;
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
for(rear = 0; rear < 64; rear++){
p[rear] = NULL;
}
front = rear = 0;
p[front] = root;
rear++;
while(p[front] != NULL){
printf("%c ", p[front]->data); //访问当前出队节点
if(p[front]->l_child != NULL){ //若左孩子存在则左孩子入队
p[rear] = p[front]->l_child;
rear++;
}
if(p[front]->r_child != NULL){ //若有孩子存在则右孩子入队
p[rear] = p[front]->r_child;
rear++;
}
front++; //front向后移动
}
}②linktree.h头文件代码
#ifndef _LINKTREE_
#define _LINKTREE_
typedef char data_t;
typedef struct tree_node
{
data_t data; //数据域
struct tree_node *l_child; //指向当前节点的左孩子
struct tree_node *r_child; //指向当前节点的右孩子
}T_node;
T_node *create_tree();
void f_print(T_node *root); //先序遍历
void m_print(T_node *root); //中序遍历
void l_print(T_node *root); //后序遍历
void c_print(T_node *root); //层次遍历
#endif③main.c主函数代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include "linktree.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
T_node *root = create_tree(); //创建二叉树
f_print(root); //先序遍历
printf("\n************************\n");
m_print(root); //中序遍历
printf("\n************************\n");
l_print(root); //后序遍历
printf("\n************************\n");
c_print(root); //层次遍历
printf("\n************************\n");
return 0;
} ④运行结果
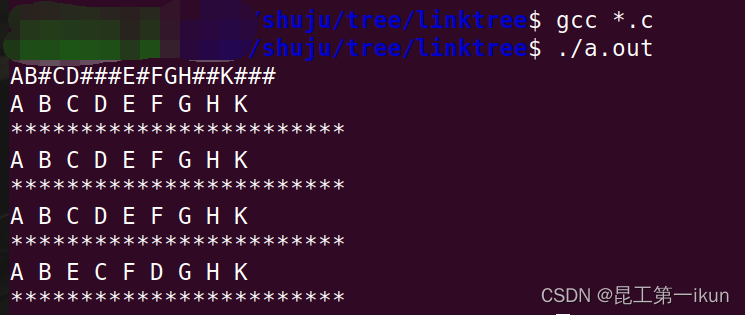
总结
好了,以上就是今天要分享的全部内容,我是练习编程时长两年半的昆工第一ikun,我们明天见。





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








