一.两层结构时虚基类表内容分析
a.虚基类表是什么?
当有虚继承的时候就会产生虚基类表。
class Grand
{
public:
int m_grand;
};
class A1 : virtual public Grand
{
public:
int a1;
};A1虚继承了Grand,类A1就会产生一个虚基类表,虚基类表一般是8个字节,4个字节为一个单位,每多一个虚基类,虚基类表就会多四个字节。另外:虚基类表是在编译的时候就生成的 ,地址就确定好了。接下来我们来探究虚基类表里面到底存储了什么?
b.虚基类表5-8字节内容分析
class Grand
{
public:
int m_grand;
};
class A1 : virtual public Grand
{
public:
int a1;
};
int main()
{
cout<< sizeof(Grand) << endl; // 4
cout << sizeof(A1) << endl; // 12
A1 a;
a.m_grand=0;
return 0;
}类A1的内存布局是这样的:

在上一篇博客里我们说过,虚基类的成员总是在最下面的。
那么上述代码的第17行是怎样实现的呢?编译器是怎么找到m_grand在a对象里面的位置的呢?
编译器首先需要找到a对象的虚基类表指针,虚基类表指针里面5-8字节里面存储的是虚基类的成员首地址相对于虚基类表的偏移位置,在上述图解中可以看出vbptr与m_grand的偏移量是8,所以虚基类表里面的5-8字节里存储的是8;
c.继续观察各种形色的继承
虚继承Grand,实继承Grand2
class Grand
{
public:
int m_grand;
};
class Grand2
{
public:
int m_grand2;
};
class A1 : virtual public Grand1,public Grand2
{
public:
int a1;
};
int main()
{
cout<< sizeof(Grand) << endl;// 4
cout<< sizeof(Grand2) << endl;// 4
cout << sizeof(A1) << endl;// 16
return 0;
}图解分析:
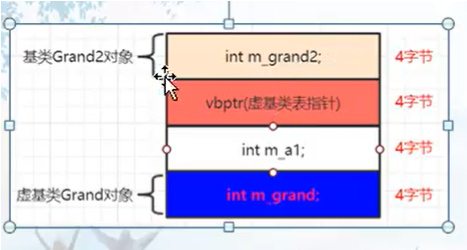
实继承基类的成员在上面
实继承Grand,虚继承Grand2
class Grand
{
public:
int m_grand;
};
class Grand2
{
public:
int m_grand2;
};
class A1 : public Grand, virtual public Grand2
{
public:
int a1;
};

两个都是虚继承的时候
class Grand
{
public:
int m_grand;
};
class Grand2
{
public:
int m_grand2;
};
class A1 :virtual public Grand, virtual public Grand2
{
public:
int a1;
};
当有两个虚基类的时候,虚基类表里面有12个字节,5-8字节是m_grand相对于虚基类表指针的偏移量,9-12字节是m_grand2相对于虚基类表指针的偏移量
总结:
a.虚基类表中的偏移量是按照继承顺序来存放的;
b.虚基类的成员一直存放在最下面;
d.虚基类表1-4字节内容分析
当既有虚继承又有实继承的时候,vbptr并不是在对象的最上面,例如:

虚基类表中1-4字节记录的就是 对象最开始的地址和虚基类表指针的偏移量。
只有访问虚基类里面的成员的时候才需要用虚基类表,其他成员不需要。
二.三层继承时虚基类表内容分析
class Grand
{
public:
int m_grand;
};
class A1 :virtual public Grand
{
public:
int a1;
};
class A2 :virtual public Grand
{
public:
int a2;
};
class C1 :public A1, public A2
{
public:
int c;
};
int main()
{
cout<< sizeof(Grand) << endl; //4
cout<< sizeof(A1) << endl;// 12
cout << sizeof(A2) << endl;// 12
cout << sizeof(C1) << endl;// 24
C1 c;
c.m_grand = 9;
return 0;
}
只有m_grand是虚基类的成员需要通过虚基类表来找位置,其他都不需要;
这个例子里面并没有用到vbptr2,只用到了vbptr1;
int main()
{
A2* p = new C1;
p->a2 = 9;
p->m_grand = 0;
return 0;
}这个时候用到了vbptr2.
结论:
问:什么时候访问成员变量速度较慢;
答:当访问虚基类里面的成员的时候,访问速度较慢;
我的内容可能写的比较潦草,如果需要笔记内容相对应的课程,请关注并私信我。
























 2357
2357

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








