目录
编译器无法对自定义类型进行 使用 == 运算符的操作,因为一个自定义类型中有多重内置类型变量,内置类型函数,编译器怎么知道是用一个对象中的那些属性来进行对比呢?
一、运算符重载的引入
①没有设计资源泄露的赋值
给大家先整个Date类:
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day) // 有参构造函数
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date(Date& d) // 拷贝构造函数
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
Date() // 自定义构造函数
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};看一下方法:

上面提到了反汇编,看一下d3 = d2 的汇编代码吧:
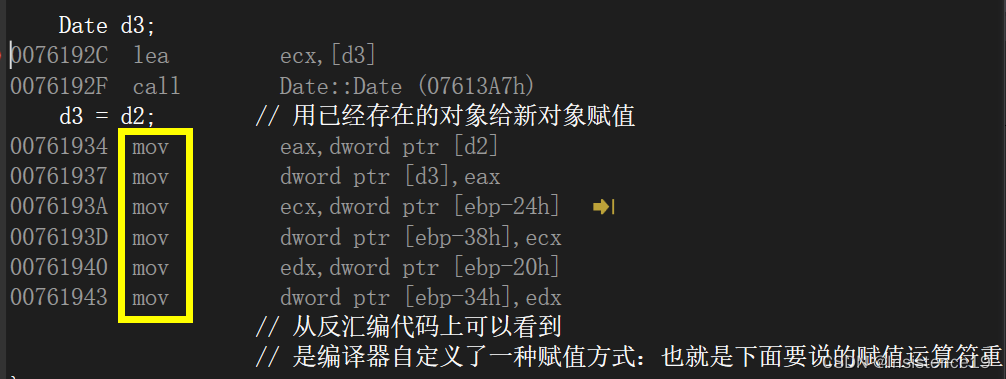
可以看到这里是一堆mov指令的使用,并没有调用我们所期望的赋值运算符的重载。
这也正是我上一节博客所写到的浅拷贝问题。编译器采用了自己的方式完成了对已经存在的对象的赋值。并不会发生什么错误。
可是如果我的代码里面涉及到了资源管理呢?会出现其他错误嘛?
②我们下来试一试栈Stack.(涉及资源泄露)
class Stack
{
public:
//void Init()
Stack() //默认的构造函数
{
_array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
if (NULL == _array)
{
assert(false);
printf("fail \n");
return;
}
_size = 0;
_capacity = 10;
}
void Push(int data)
{
_array[_size] = data;
_size++;
}
~Stack()
{
if (_array)
{
free(_array);
_array = NULL;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
}
private:
int* _array;
int _size;
int _capacity;
};
void Test1()
{
Stack s1;
s1.Push(1);
s1.Push(2);
s1.Push(3);
s1.Push(4);
Stack s2;
s2 = s1;
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}里面只有简单的Push函数、构造函数和析构函数,不过就可以说明问题了,先看对比:
我们都是用一个已经定义好的对象给另外一个对象赋值,
下一步:
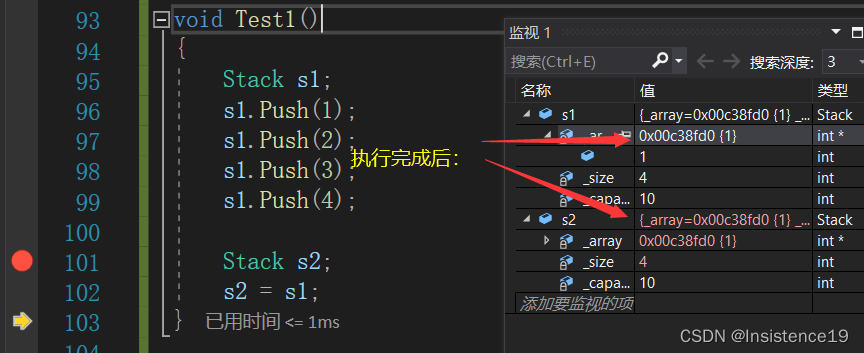
发生报错:
分析:
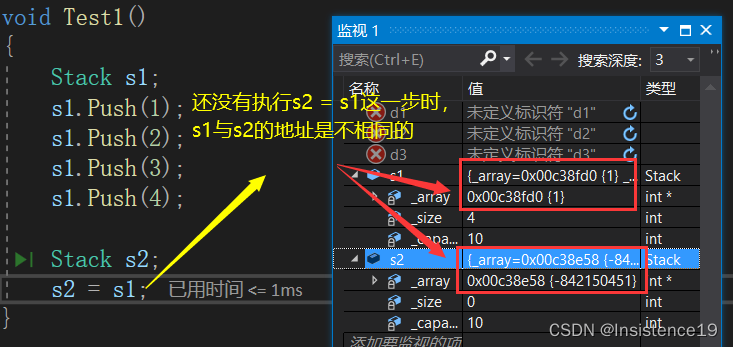
一:我们从析构函数那里学到的,后构造出来的函数先析构,所以这里后构造出来的s2先进行析构,然后到析构s1的时候编译器发生报错,报错的原因是什么呢?上一节博客我写到了一个问题,因为他们两个进行了浅拷贝(值拷贝),s1与s2按内容进行字节拷贝,s2变成了与s1完全一致的一个对象,如果这时候对俩个对象进行先后析构的话,能产生编译中断的原因也就显而易见了。
二:在这里,我把赋值前后的s1与s2的地址作出了比对,s2的地址被拷贝成为与s1一致的地址,说明他们俩个对象共用了同一个内存空间,那我之前构造出来的s2的内存空间也就无法访问了,这里也就产生了资源泄露这个问题。
引入:
那么如何解决这个问题呢?我们c++有这样一个默认函数:
当涉及到资源管理时,赋值运算符重载是必须要实现的。
二、如何实现运算符重载
①实现俩个对象的相等判断
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day) // 构造函数
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date()
{}
Date(const Date& d) //拷贝构造函数
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
bool IsEqual(Date& d) // 用于检测内置类型是否相等的IsEqual函数
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 11, 18);
Date d2(d1);
if (d1.IsEqual(d2))
{
cout << "d1 == d2" << endl;
}
return 0;
}上面的函数调用,是通过函数的介入来判断俩个对象是否相等,有没有让用户觉得更简单直观的方法呢?
我们知道 == 运算符可以直接进行判断俩个变量是否相等,比如:
int a = 3;
int b;
if (a == b)
cout << "a == b" << endl;那么可以将这俩个变量替换为俩个对象嘛?
比如这样:可是得到了编译器的否认。
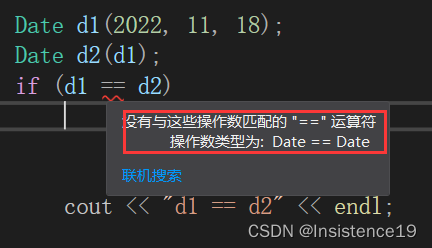
结论:
编译器无法对自定义类型进行 使用 == 运算符的操作,因为一个自定义类型中有多重内置类型变量,内置类型函数,编译器怎么知道是用一个对象中的那些属性来进行对比呢?
②让编译器知道我们比较的规则——运算符重载
格式:
返回值类型 operator 操作符(参数列表)
使用:
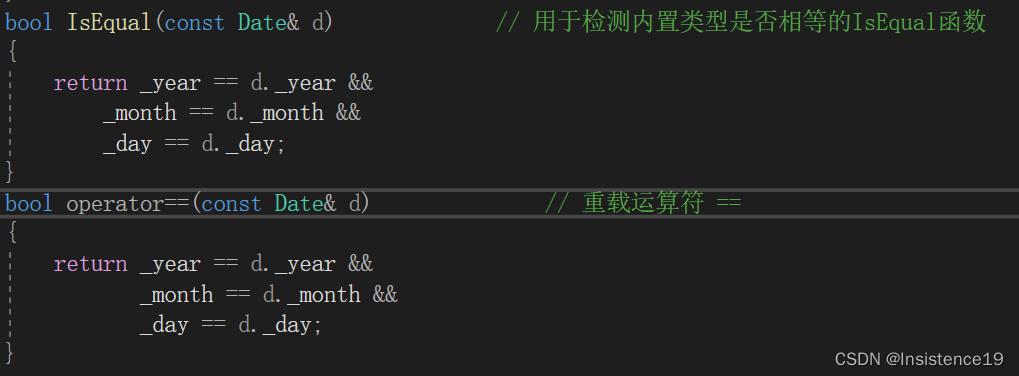
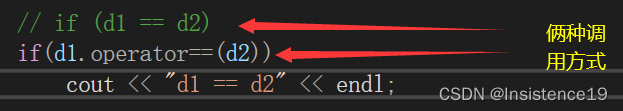

可以正常使用了!!!
③注意事项
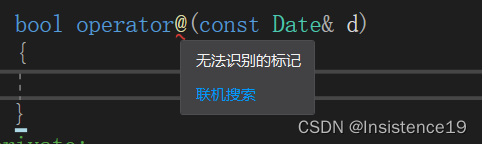
1、不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
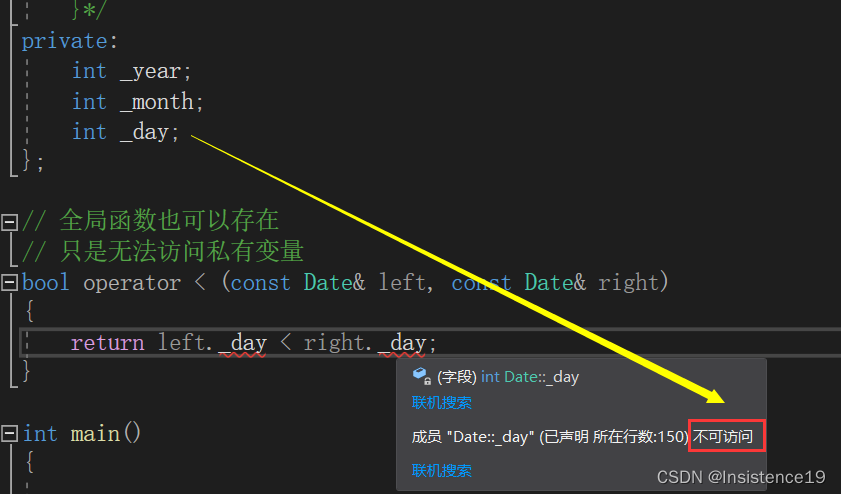
2、可以定义全局重载函数,但是无法访问私有变量。
4、重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数5、用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不能改变其含义
6、作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为 隐藏的this
7、 .* :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。这个经常在笔试选择题中出现。8、用户没有显式实现时,编译器会生成一个默认赋值运算符重载,以值的方式逐字节拷贝。
三、重载运算符的代码详解
① 相等运算符(==)
bool operator==(Date& d1)
{
if (d1._day == _day && d1._month == _month && d1._year == _year)
return true;
}② 赋值运算符( = )
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}1,、为什么参数是const Date& d?
使用引用作为函数参数,在传参的过程中可以减少一次拷贝构造,提升了效率,因为如果参数是(Date d)我的Date d就要进行拷贝构造出一块空间,来存储d,使用const可以防止在传参过程中对参数对象的改变。
2、为什么有返回值?
我们所知道的a = b = c(汇编代码如下:);依次执行的过程为用c给b赋值,再用b给a赋值。
 为了保证我们传值的连续性,所以给函数带上了返回值,以达到d1 = d2 = d3;的连续赋值的目的。
为了保证我们传值的连续性,所以给函数带上了返回值,以达到d1 = d2 = d3;的连续赋值的目的。
3、为什么返回值是Date&?
首先我们需要达到返回值是一个对象这个目的,所以使用了Date
进一步为了进行代码优化使用了以引用作为函数返回值。少了一次对返回结果的拷贝构造。
4、为什么返回一个*this?
我们实现的类内的运算符重载函数,它具有类的一个this指针外,还有一个参数对象,返回的也就是一个对象的内容。
因为要实现a = b = c这样的顺序赋值,假如执行b = c这一步时,this指向的就是左值b,d所代表的就是右值c。
5、if判断防止自己给自己赋值
6、赋值运算符必须定义为成员函数。
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 赋值运算符重载成全局函数,注意重载成全局函数时没有this指针了,需要给两个参数
Date& operator=(Date& left, const Date& right)
{
if (&left != &right)
{
left._year = right._year;
left._month = right._month;
left._day = right._day;
}
return left;
}编译报错:必须是非静态成员。
分析:
赋值运算符必须设置为类内成员函数,因为如果设置成为全局函数,当进行d1 = d2操作时,编译器会在类中重载出来一个默认的赋值运算符函数,这时俩个赋值运算符重载函数发生了冲突,也就无法实现编译了。
③前置++与后置++
前置++(先自加一,再赋值)
// 前置++
// 注意:this指向的对象函数结束后不会销毁,故以引用方式返回提高效率
Date& operator++()
{
_day += 1;
return *this;
}后置++: 先赋值,在自加一
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date temp(*this);
_day += 1;
return temp;
}1、temp作用
将加一之前的部分保存,以用来后面的返回。
2、返回值类型为Date
我们知道返回值类型可以使用引用就使用引用,可是因为这里是以值的方式进行返回,所以使用Date。
3、参数类型为int
后置++重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递,编译器自动传递
如果与前置++仅有返回值类型不同那么是不能构成重载的,所以这时候我们给后置++补上一个int.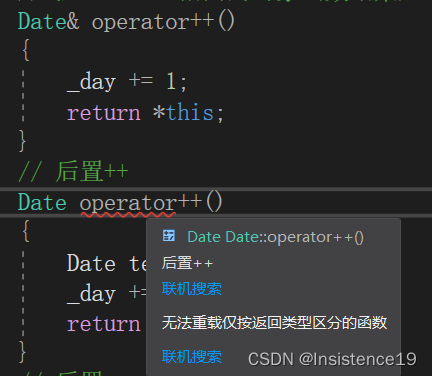
④ 其他运算符代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
#if 0
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day) // 有参构造函数
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date(Date& d) // 拷贝构造函数
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
Date() // 自定义构造函数
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
void Test1()
{
Date d1(2022, 11, 18);
Date d2(d1);
Date d3;
d3 = d2; // 用已经存在的对象给新对象赋值
// 从反汇编代码上可以看到
// 是编译器自定义了一种赋值方式:也就是下面要说的赋值运算符重载
}
void Test2()
{
Date d1(2022, 11, 18);
Date d2 = d1; // 调用拷贝构造定义一个新的对象
// 调用的默认的拷贝构造函数
}
int main()
{
Test1();
Test2();
return 0;
}
#endif
#if 0
class Stack
{
public:
//void Init()
Stack() //默认的构造函数
{
_array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
if (NULL == _array)
{
assert(false);
printf("fail \n");
return;
}
_size = 0;
_capacity = 10;
}
void Push(int data)
{
_array[_size] = data;
_size++;
}
~Stack()
{
if (_array)
{
free(_array);
_array = NULL;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
}
private:
int* _array;
int _size;
int _capacity;
};
void Test1()
{
Stack s1;
s1.Push(1);
s1.Push(2);
s1.Push(3);
s1.Push(4);
Stack s2;
s2 = s1;
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}
#endif
#if 0
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day) // 构造函数
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date()
{}
Date(const Date& d) //拷贝构造函数
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
bool IsEqual(const Date& d) // 用于检测内置类型是否相等的IsEqual函数
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
bool operator==(const Date& d) // 重载运算符 ==
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
// 1、必须为编译器所支持的运算符
/*bool operator@(const Date& d)
{
}*/
// 3、重载运算符必须有一个类类型的参数
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
return *this;
}
int operator+(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
Date& operator+=(Date& d, int day)
{
d._day += day;
return d;
}
2、全局重载函数
全局函数也可以存在
只是无法访问私有变量
//bool operator < (const Date& left, const Date& right)
//{
// return left._day < right._day;
//}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 11, 18);
Date d2(d1);
if (d1.IsEqual(d2))
{
cout << "d1 == d2" << endl;
}
/
int a = 3;
int b = 3;
if (a == b)
cout << "a == b" << endl;
if (d1 == d2)
// if(d1.operator==(d2))
cout << "d1 == d2" << endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
#if 0
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day) // 构造函数
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date()
{}
Date(const Date& d) //拷贝构造函数
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
bool operator==(Date& d1)
{
if (d1._day == _day && d1._month == _month && d1._year == _year)
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 11, 18);
Date d2(d1);
if (d1 == d2)
cout << "d1 == d2" << endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
#if 1
class Date
{
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int days[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int day = days[month];
if (month == 2
&& ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
day += 1;
}
return day;
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
cout << " " << this << " " << endl;
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~Date()
{
cout << "随便打印点啥……" << endl;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day)
{
_day += day;
return *this;
}
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day)
{
_day -= day;
return *this;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
}
// 前置++
// 注意:this指向的对象函数结束后不会销毁,故以引用方式返回提高效率
Date& operator++()
{
_day += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date temp(*this);
_day += 1;
return temp;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date temp(*this);
_day -= 1;
return temp;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
_day -= 1;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
return _year > d._year &&
_month > d._month &&
_day > d._day;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return _year >= d._year &&
_month >= d._month &&
_day >= d._day;
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
return _year < d._year &&
_month < d._month &&
_day < d._day;
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return _year <= d._year&&
_month <= d._month&&
_day <= d._day;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return _year != d._year&&
_month != d._month&&
_day != d._day;
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
return _day - d._day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
#endif
//void operator=(const Date& left, const Date& right)
//{
// left._year = right._year;
// left._month = right._month;
//
//}
//int a = 10, b = 20, c = 30;
#if 0
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 赋值运算符重载成全局函数,注意重载成全局函数时没有this指针了,需要给两个参数
Date& operator=(Date& left, const Date& right)
{
if (&left != &right)
{
left._year = right._year;
left._month = right._month;
left._day = right._day;
}
return left;
}
#endif
//int main()
//{
// /*Date(2022, 11, 19);
// a = b = c;*/
// return 0;
//}
#if 0
class A
{
void func1()
{
A aa;
}
int a;
};
class B
{
public:
friend class A;
void func2()
{
B bb;
}
private:
int b;
};
class C
{
friend class B;
void func3()
{
C cc;
B bb;
cc.
}
int c;
};
#endif





















 3517
3517











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








