目录
【解法一】:最后写出了一坨屎,虽然它是一坨屎,但是它能动,虽然它是一坨屎,但起码这是我自己拉的
【大佬解法】 stringstream的使用 以及 map的使用
884. 两句话中的不常见单词
句子 是一串由空格分隔的单词。每个 单词 仅由小写字母组成。
如果某个单词在其中一个句子中恰好出现一次,在另一个句子中却 没有出现 ,那么这个单词就是 不常见的 。
给你两个 句子 s1 和 s2 ,返回所有 不常用单词 的列表。返回列表中单词可以按 任意顺序 组织。
【解法一】:最后写出了一坨屎,虽然它是一坨屎,但是它能动,虽然它是一坨屎,但起码这是我自己拉的
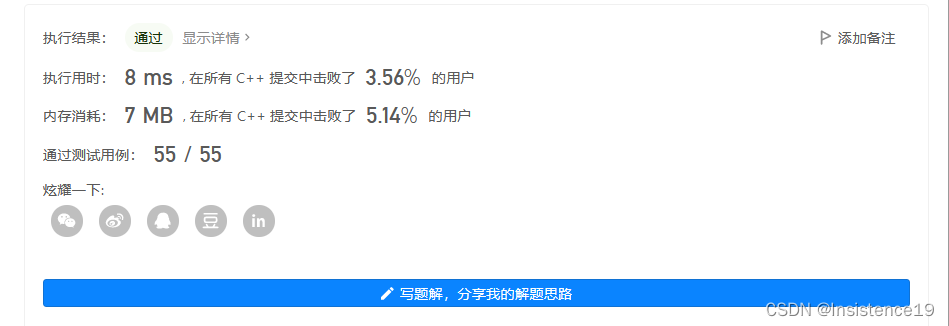
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> division(string s)
{
vector<string> res;
int pos = s.find(' ');
int begin = 0;
while(pos!=-1)
{
string temp(s.begin()+begin, s.begin()+pos);
res.push_back(temp);
begin = pos+1;
pos = s.find(' ', begin);
}
res.push_back(string(s.begin()+begin, s.end()));
return res;
}
vector<string> delete_repeat(vector<string> v)
{
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for(size_t i = 0; i < v.size();)
{
auto temp = v[i];
if(v[i+1] == temp)
{
while(i<v.size() && v[i]==temp)
{
auto it = v.begin()+i;
v.erase(it);
}
}
else
++i;
}
return v;
}
vector<string> uncommonFromSentences(string s1, string s2) {
vector<string> v1;
vector<string> v2;
v1 = division(s1);
v2 = division(s2);
for(size_t i = 0; i < v2.size(); ++i)
{
v1.push_back(v2[i]);
}
return delete_repeat(v1);
}
};【大佬解法】 stringstream的使用 以及 map的使用
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> uncommonFromSentences(string s1, string s2) {
map<string, int> mp;
vector<string> ans;
stringstream ss1, ss2;
string s;
ss1 << s1; ss2 << s2;
while(ss1 >> s) //抽出一个单词并停止
{
mp[s]++;//次数
}
while(ss2 >> s)
{
mp[s]++;
}
for(auto m : mp)
{
if(m.second == 1)ans.push_back(m.first); //统计次数为一的单词
}
return ans;
}
}; map可以定义俩个类型的容器,例如map<string, int> mp; 第一个为key值,一个容器内只能出现一次,而第二个为value值,是实现与之一对一映射的。
Map是STL 的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据处理能力
这里说下map内部数据的组织,map内部自建一颗红黑树(一种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的
stringstream
以空格分割获取单词块;
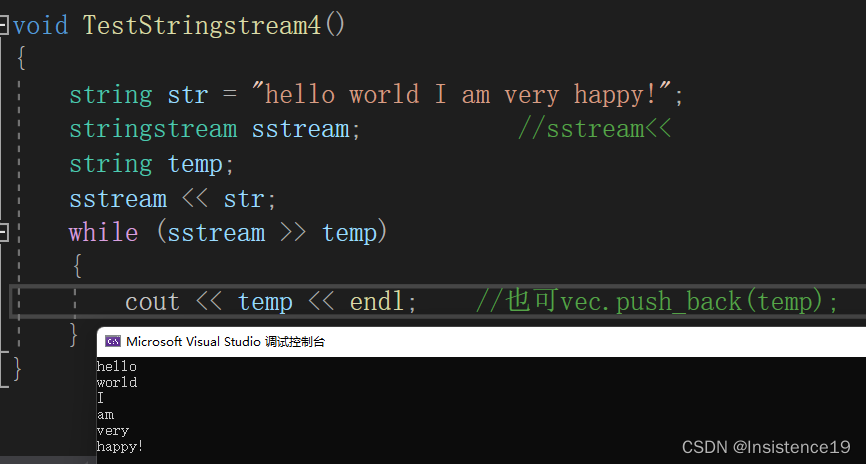
我写的单词分割函数:
vector<string> division(string s)
{
vector<string> res;
int pos = s.find(' ');
int begin = 0;
while(pos!=-1)
{
string temp(s.begin()+begin, s.begin()+pos);
res.push_back(temp);
begin = pos+1;
pos = s.find(' ', begin);
}
res.push_back(string(s.begin()+begin, s.end()));
return res;
}下面是对map的初步掌握已经对stringstream 的练习使用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<map>
#include<sstream>
void TestMap01()
{
// 插入元素
map<string, string> firend;
firend.insert (pair<string,string>("Bob", "12312121"));
firend.insert(pair<string, string>("yes", "12345"));
firend.insert(pair<string, string>("yes1", "12345"));
firend.insert(pair<string, string> ("yes2", "12345"));
firend.insert(pair<string, string>("yes3", "12345"));
firend.insert(pair<string, string>("yes4", "12345"));
auto it = firend.begin();
while (it != firend.end())
{
cout <<it->first<< " " << it->second << endl;
it++;
}
}
void TestMap02()
{
map<int, int> mp;
cout << mp[0] << endl;
mp[0]++;
cout << mp[0] << endl;
mp[3] = 100;
cout << mp[3] << endl;
cout << mp[3] + 2 << endl;
cout << mp[3] << endl;
}
void TestMap03()
{
stringstream ss;
string res;
int value = 1000;
ss << value;
ss >> res;
cout << res << endl;
}
void TestStringstream()
{
stringstream ss;
string res;
ss << "weixuanlv " << "1 2" << "shuaishuai";
ss >> res;
cout << res;
cout << ss.str() << endl;
}
void TestStringstream2()
{
stringstream ss;
string res;
ss << "weixuanlv is very handsome";
while (ss >> res)
{
cout << res << endl;
}
}
void TestStringstream3()
{
stringstream ss;
string res;
map<string, int> mp;
string s1 = "this apple is sweet";
ss << s1;
while (ss >> res)
{
mp[res]++;
}
auto it = mp.begin();
while (it != mp.end())
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
// TestMap01();
// TestMap02();
// TestMap03();
// TestStringstream();
// TestStringstream2();
TestStringstream2();
return 0;
}




















 103
103











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








