
1. Object类
1.1 toString方法

package com.itheima.object.tostring;
import com.itheima.object.Student;
public class ToStringDemo {
/*
public String toString() 返回该对象的字符串表示
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
getClass().getName() : 类名称, 全类名(包名 + 类名)
Integer.toHexString() : 转十六进制
hashCode() : 返回的是对象内存地址 + 哈希算法, 算出来的整数
----------------------------------------------
细节: 使用打印语句, 打印对象名的时候, println方法, 源码层面, 会自动调用该对象的toString方法.
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(a.toString());
Student stu = new Student("张三", 23);
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
class A {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "大哥重写方法了";
}
}

1.2 equals方法
package com.itheima.object;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// this : stu1
// obj : stu2
// 判断此时的obj是不是学生类型
if (obj instanceof Student) {
// 向下转型的目的, 是为了调用子类特有的成员
Student stu = (Student) obj;
return this.age == stu.age && this.name.equals(stu.name);
}else {
return false;
}
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
// this: stu1
// o: stu2
// 两个对象做地址值的比较, 如果地址相同, 里面的内容肯定相同, 直接返回true.
if (this == o) return true;
// 代码走到这里, 代表地址肯定不同, 且stu1肯定不是null
// stu1不是null, stu2是null, 就直接返回false
// this.getClass() != o.getClass() : 两个对象的字节码是否相同
// 如果字节码不相同, 就意味着类型不相同, 直接返回false.
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
// 代码要是走到这里, 代表字节码相同, 类型肯定相同
// 向下转型
Student student = (Student) o;
// 比较
return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
package com.itheima.object.equals;
import com.itheima.object.Student;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class EqualsDemo {
/*
Object类中的equals:
public boolean equals(Object obj) : 对象之间进行比较, 返回true, 或者false.
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// this : stu1
// obj
return (this == obj);
}
结论: Object类中的equals方法, 默认比较的是对象内存地址
- 通常会重写equals方法, 让对象之间, 比较内容
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu1 = new Student("张三", 23);
Student stu2 = new Student("张三", 24);
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(stu1.equals(stu2));
System.out.println(stu1.equals(list));
}
}


package com.itheima.object.equals;
import com.itheima.object.Student;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Objects;
public class EqualsDemo {
/*
Object类中的equals:
public boolean equals(Object obj) : 对象之间进行比较, 返回true, 或者false.
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// this : stu1
// obj
return (this == obj);
}
结论: Object类中的equals方法, 默认比较的是对象内存地址
- 通常会重写equals方法, 让对象之间, 比较内容
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu1 = null;
Student stu2 = new Student("张三", 24);
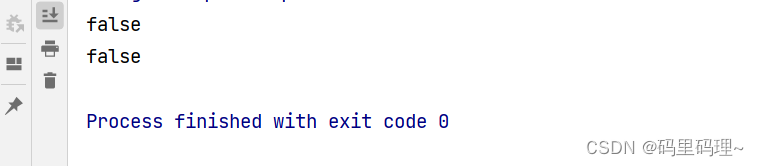
System.out.println(Objects.isNull(stu1));
System.out.println(Objects.isNull(stu2));
// 问题: Object.equals方法, 和 stu1.equals方法, 有什么区别?
// 细节: Object.equals方法, 内部依赖于我们自己编写的equals
// 好处: Object.equals方法, 内部带有非null判断
/*
// a : stu1
// b : stu2
public static boolean equals(Object a, Object b) {
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
a == b : 如果地址相同, 就会返回true, 这里使用的符号是短路 || , 左边为true, 右边就不再执行
- 结论: 如果地址相同, 方法直接返回为true
: 如果地址不相同, 就会返回false, 短路 || , 左边为false, 右边要继续执行.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
a != null : 假设 a 是 null 值
null != null : false
&& : 左边为false, 右边不执行, 记录着null值的a, 就不会调用equals方法
- 避免空指针异常 !
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
a != null : 假设 a 不是 null 值
stu1 != null : true
&& : 左边为true, 右边继续执行, a.equals(b), 这里就不会出现空指针异常
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
return (a == b) || (a != null && a.equals(b));
}
*/
System.out.println(Objects.equals(stu1, stu2));
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
}
}

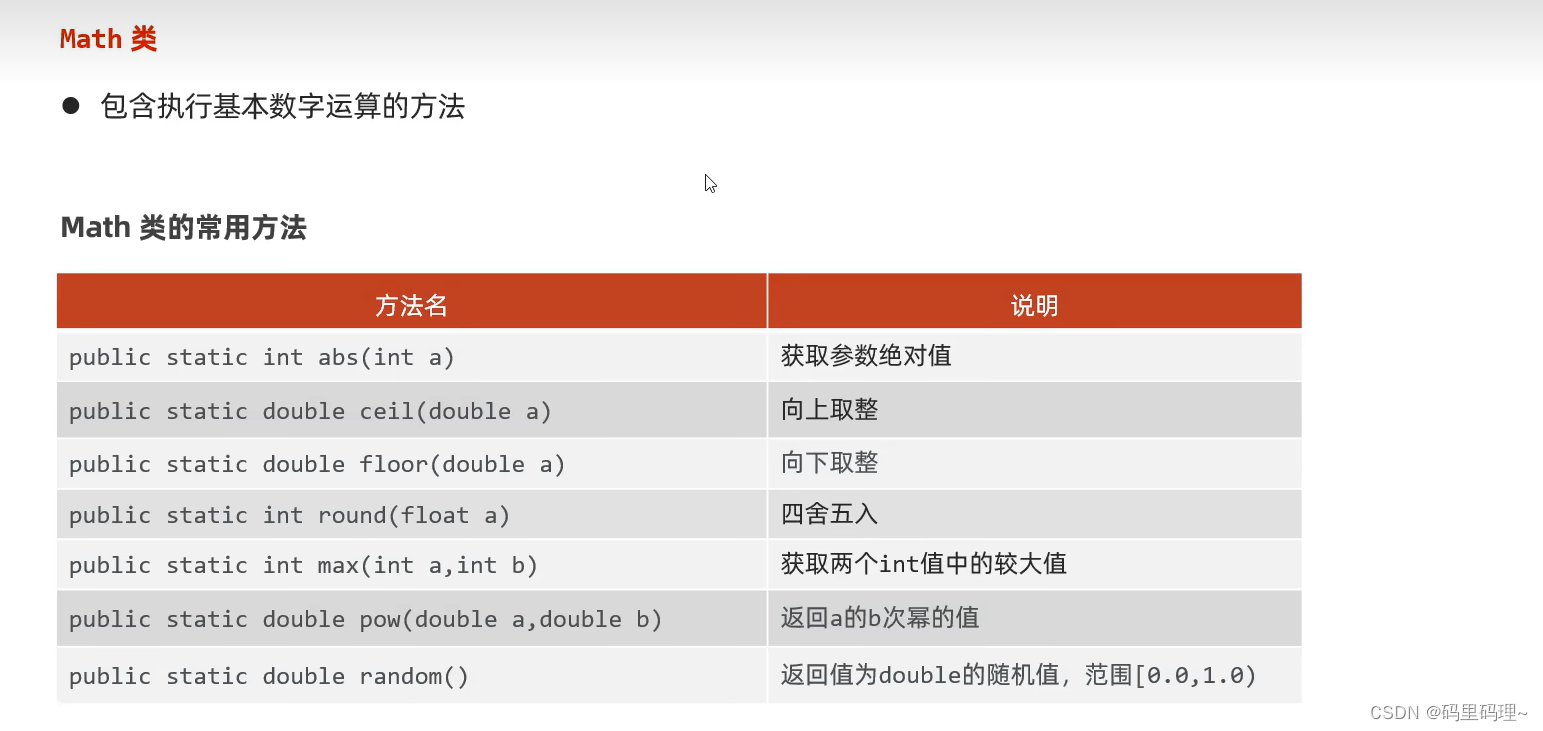
2. Math类
package com.itheima.math;
public class MathDemo {
/*
Math类 : 包含执行基本数字运算的方法
------------------------------------------------------
public static int abs (int a) : 获取参数绝对值
public static double ceil (double a) : 向上取整
public static double floor (double a) : 向下取整
public static int round (float a) : 四舍五入
public static int max (int a, int b) : 获取两个int值中的较大值
public static double pow (double a, double b) : 返回a的b次幂的值
public static double random () : 无参数, 返回值为double的随机值, 范围[0.0, 1.0)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.abs(-123)); // 123
System.out.println(Math.abs(-12.3)); // 12.3
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.0));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.2));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.5));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.9));
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println(Math.floor(3.4));
System.out.println(Math.floor(3.6));
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println(Math.max(10, 20));
System.out.println(Math.min(10, 20));
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3));
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println(Math.random());
}
}

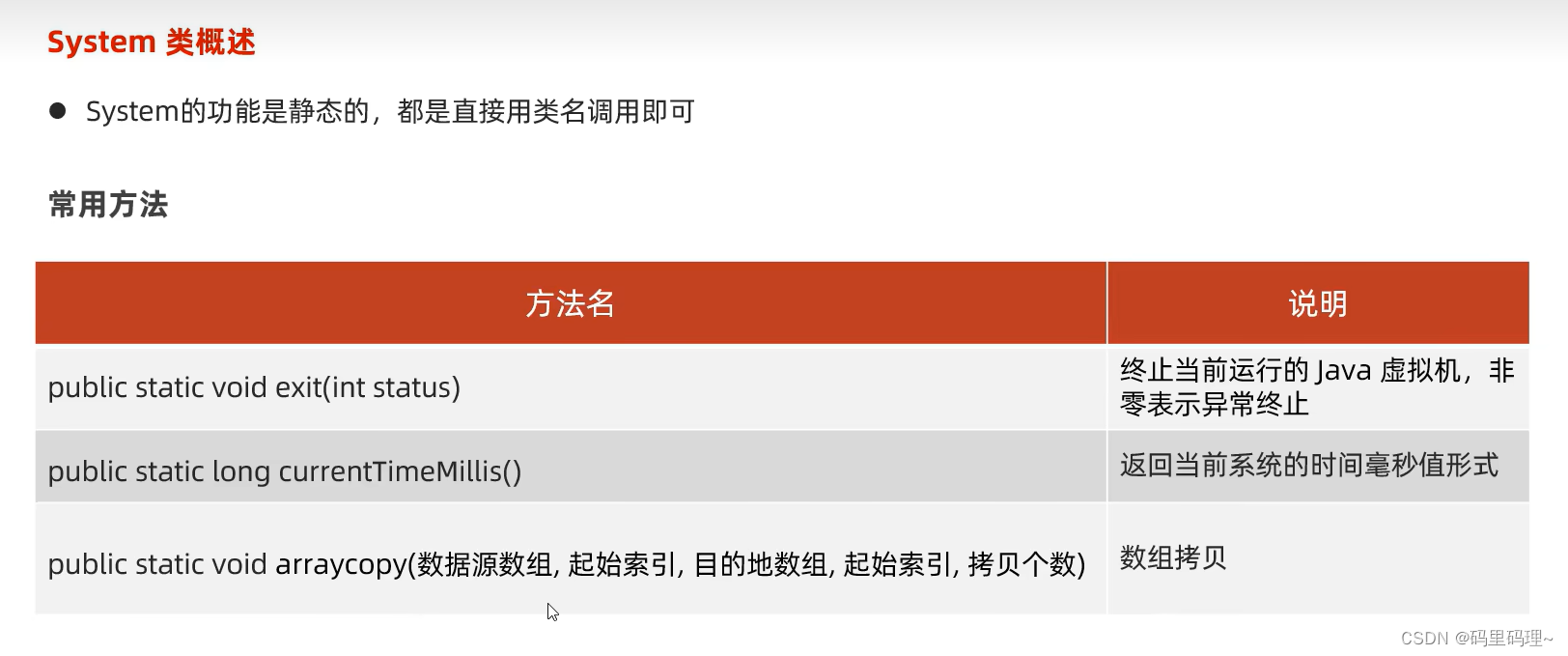
3. System类

4. BigDecimal类

package com.itheima.bigDecimal;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigDecimalDemo {
/*
BigDecimal类 : 解决小数运算中, 出现的不精确问题
BigDecimal创建对象 :
public BigDecimal(double val) : 不推荐, 无法保证小数运算的精确
---------------------------------------------------------------
public BigDecimal(String val)
public static BigDecimal valueof(double val)
*/
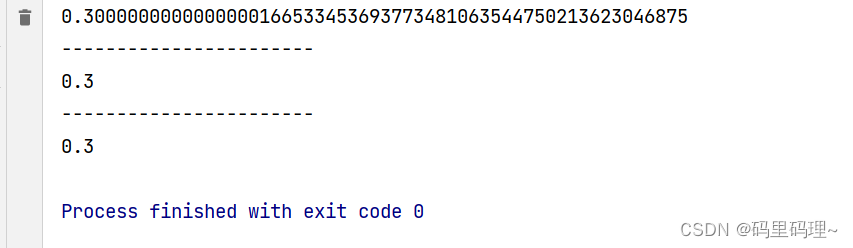
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(0.1);
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal(0.2);
System.out.println(bd1.add(bd2));
System.out.println("-----------------------");
BigDecimal bd3 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal bd4 = new BigDecimal("0.2");
System.out.println(bd3.add(bd4));
System.out.println("-----------------------");
BigDecimal bd5 = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1);
BigDecimal bd6 = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.2);
System.out.println(bd5.add(bd6));
}
}

5. 包装类
5.1 包装类介绍-Integer

package com.itheima.integer;
public class IntegerDemo {
/*
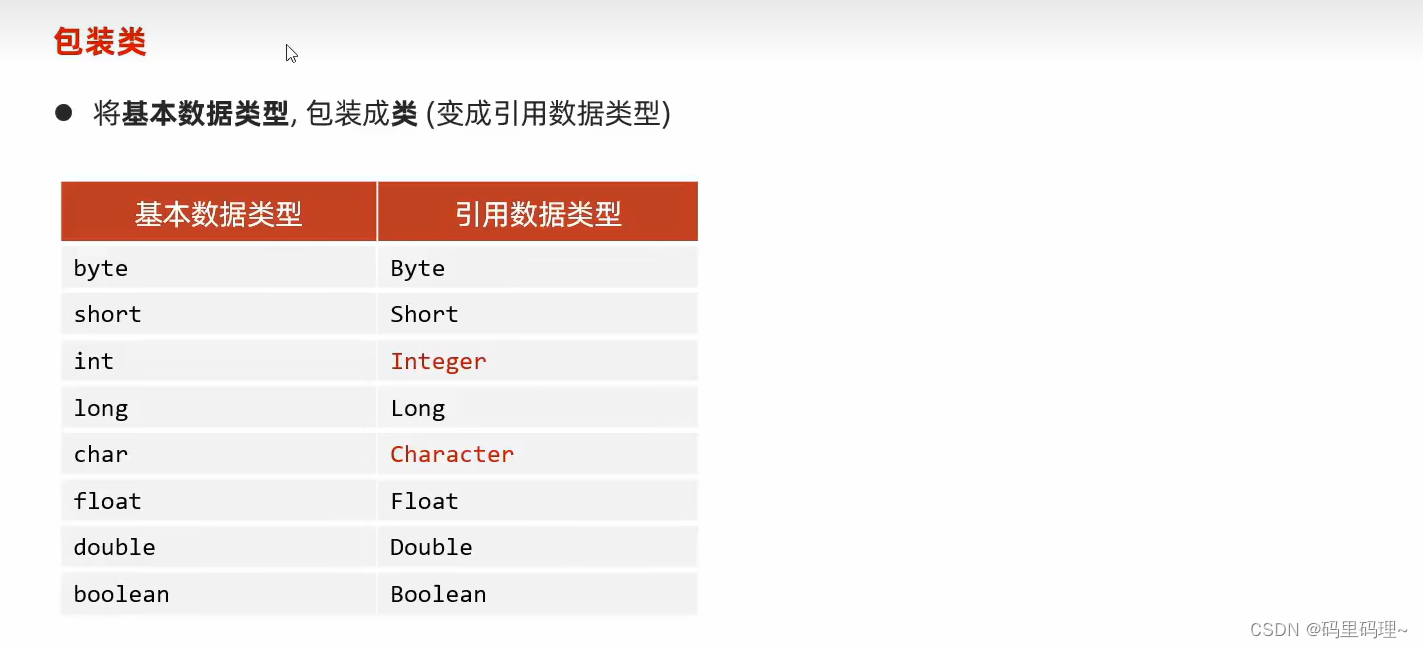
包装类 : 将基本数据类型, 包装成类, 变成引用数据类型
---------------------------------------------------------
手动装箱: 调用方法, 手动将基本数据类型, 包装成类
1. public Integer(int value) : 通过构造方法(已过时, 不推荐)
2. public static Integer valueOf(int i) : 通过静态方法
手动拆箱: 调用方法, 手动将包装类, 拆成(转换)基本数据类型
1. public int intValue() : 以 int 类型返回该 Integer 的值
--------------------------------------------------------------------
JDK5开始, 出现了自动拆装箱 :
1. 自动装箱 : 可以将基本数据类型, 直接赋值给包装类变量
2. 自动拆箱 : 可以将包装类的数据, 直接赋值给基本数据类型变量
结论: 基本数据类型, 和对应的包装类, 可以直接做运算了, 无需操心转换的问题了
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(num); // 转换为引用数据类型
int i = i1.intValue(); // 转换为基本数据类型
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
Integer i2 = num;
int ii = i2;
System.out.println(ii);
}
}
package com.itheima.integer;
public class IntegerMethodDemo {
/*
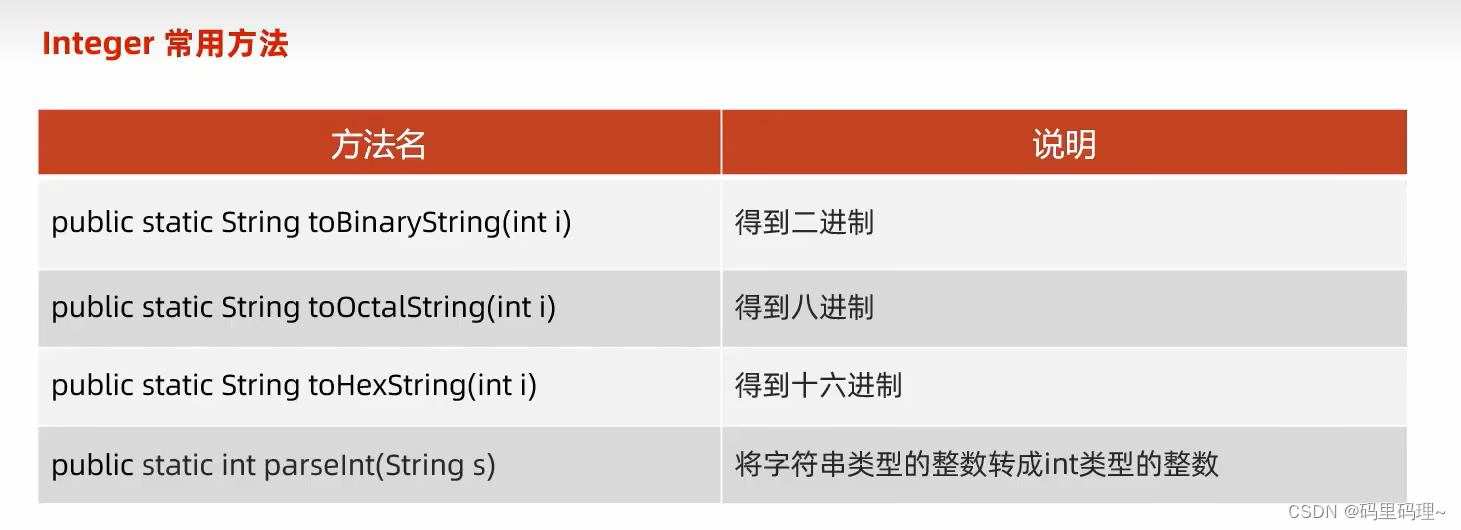
Integer 常用方法 :
public static String toBinaryString (int i) : 转二进制
public static String toOctalString (int i) : 转八进制
public static String toHexString (int i) : 转十六进制
public static int parseInt (String s) : 将数字字符串, 转换为数字
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 100;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(num));
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(num));
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(num));
String s = "123";
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(s) + 100);
}
}

package com.itheima.integer;
public class IntegerTest {
/*
已知字符串 String s = "10,50,30,20,40";
请将该字符串转换为整数并存入数组
随后求出最大值打印在控制台
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "10,50,30,20,40";
// 1. 根据逗号做切割
String[] sArr = s.split(",");
// 2. 准备一个整数数组, 准备存储转换后的数字
int[] nums = new int[sArr.length];
// 3. 遍历字符串数组
for (int i = 0; i < sArr.length; i++) {
// sArr[i] : 每一个数字字符串
// 4. 将数字字符串转换为整数, 并存入数组
nums[i] = Integer.parseInt(sArr[i]);
}
// 5. 求最大值
int max = nums[0];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
}
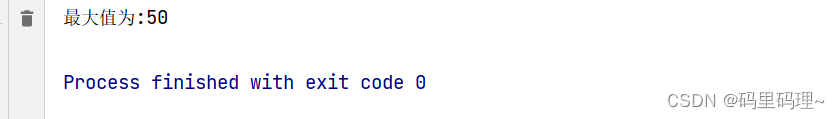
System.out.println("最大值为:" + max);
}
}
5.2 包装类面试题
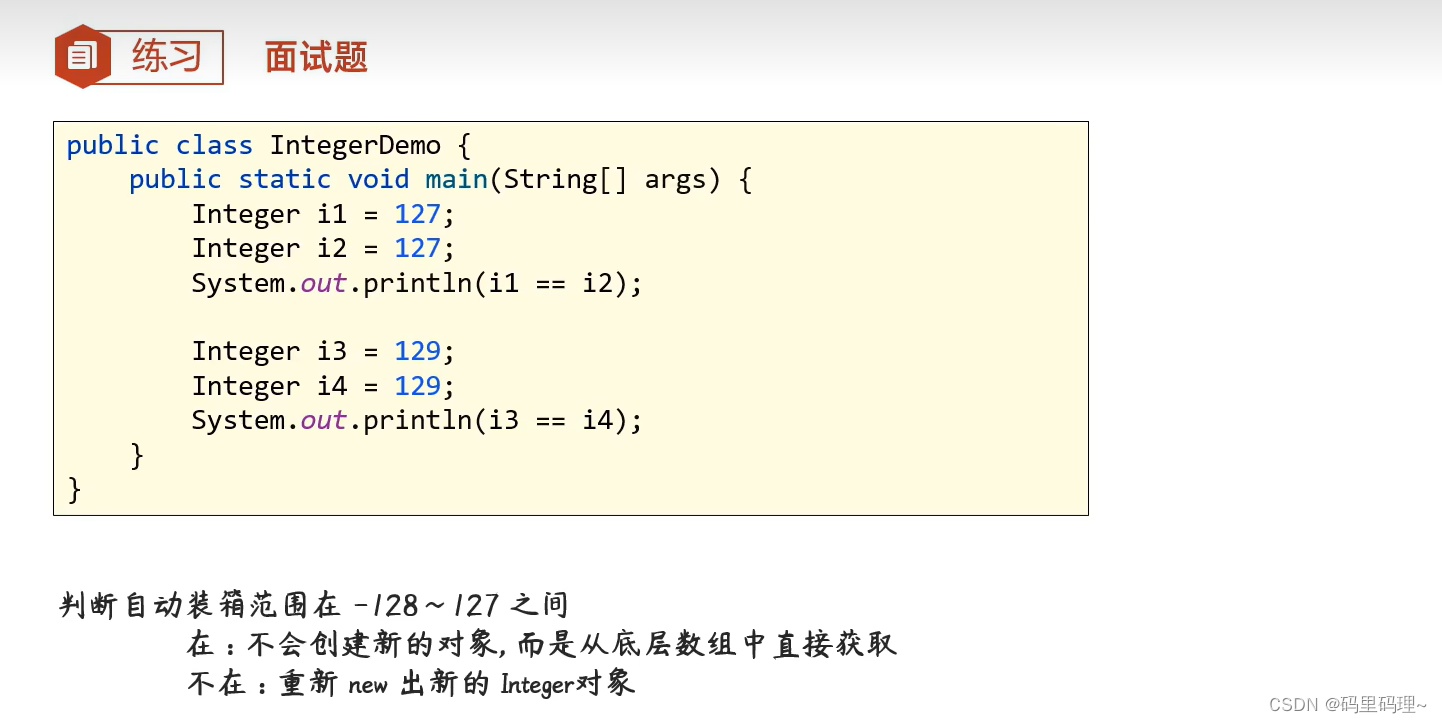
package com.itheima.integer;
public class InterView {
/*
看程序结果, 并说明原因
自动装箱的时候, 如果装箱的数据范围, 是 -128 ~ 127, ==号比较的结果就是true, 反之就是false
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
自动装箱的原理 : 自动带我们调用了 Integer.valueOf(127);
// i = 127
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
// -128 127
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
如果装箱的数据, 不在 -128 ~ 127 之间, 就会重新创建新的对象
如果装箱的数据, 在 -128 ~ 127 之间, 不会创建新的对象, 而是从底层的数组中, 取出一个提前创建好的Integer对象, 返回
- Integer类中, 底层存在一个长度为256个大小的数组, Integer[] cache
在数组中, 存储了256个Integer对象, 分别是 -128 ~ 127
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = 127;
Integer i2 = 127;
System.out.println(i1 == i2); // true (比较同一对象的地址-相同)
Integer i3 = 129;
Integer i4 = 129;
System.out.println(i3 == i4); // false
Long i11 = 129L;
Long i22 = 129L;
System.out.println(i11 == i22); // 比对象地址
System.out.println(i11.equals(i22)); // 比对象内容
}
}
















































 101
101

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










