前言
1.链表的分割
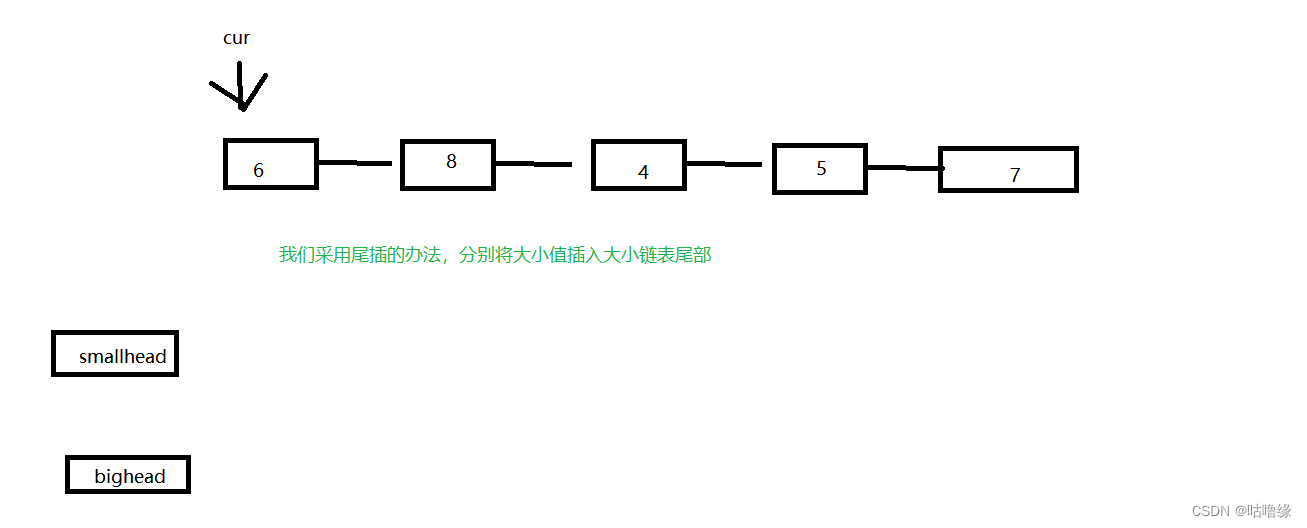
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
ListNode* smalltail, *smallhead;
ListNode* bigtail, *bighead;
smallhead = smalltail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
bighead = bigtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val < x)
{
smalltail->next = cur;
smalltail = smalltail->next;
}
else
{
bigtail->next = cur;
bigtail = bigtail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
smalltail->next=bighead->next;
bigtail->next=NULL;
pHead=smallhead->next;
free(smallhead);
free(bighead);
return pHead;
}
};
2.链表的回文结构
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
if(A==NULL)
return false;
else if(A->next==NULL)
return true;
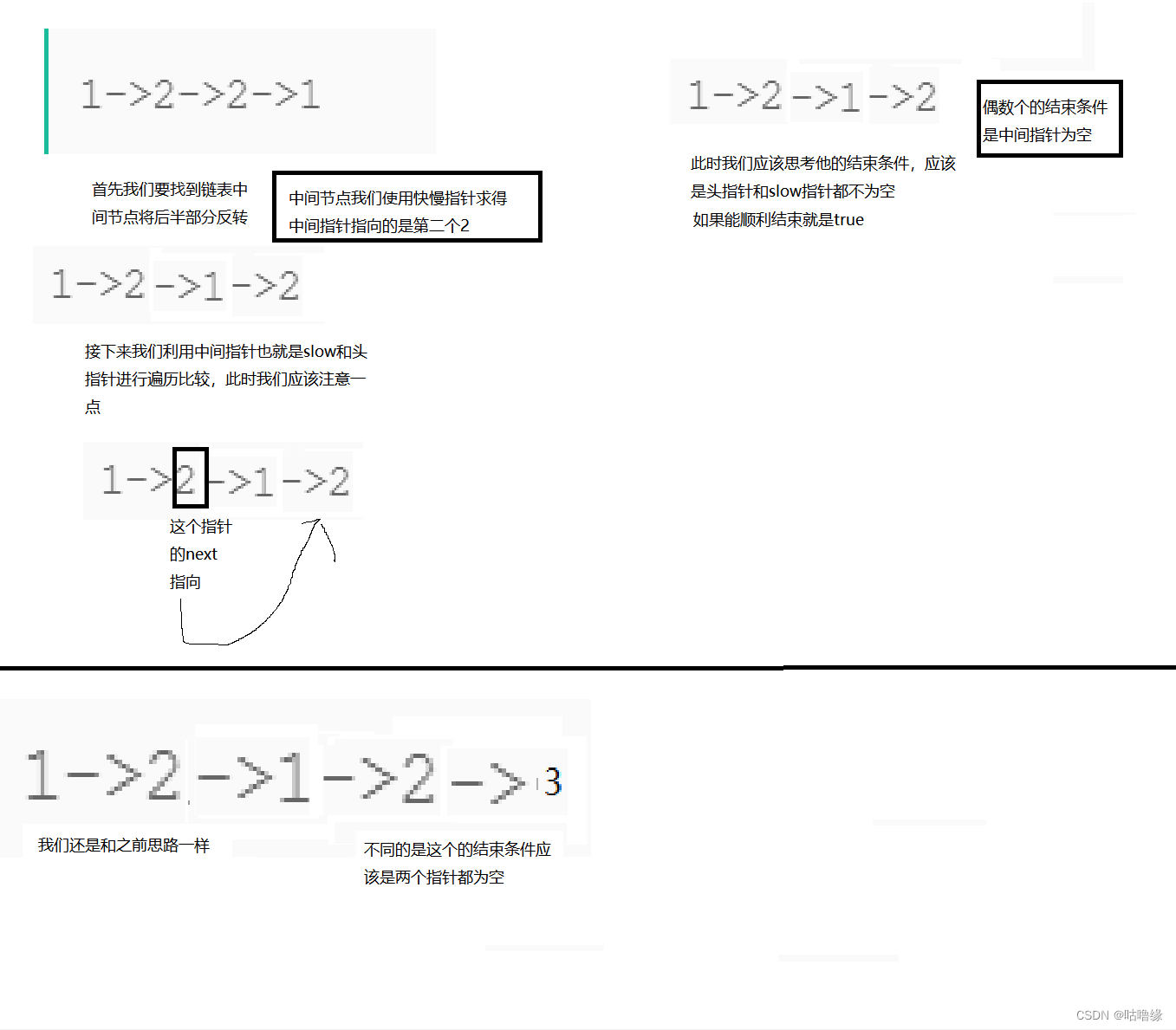
struct ListNode*fast=A;
struct ListNode*slow=A;
while (fast&&fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
struct ListNode*cur=slow;
struct ListNode*rhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode*next=cur->next;
cur->next=rhead;
rhead=cur;
cur=next;
}
while(A&&slow)
{
if((A->val)!=(rhead->val))
{
return false;
}
A=A->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return true;
}
};
3.相交链表

struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode *curA=headA,*curB=headB;
int lenA=0;
int lenB=0;
while(curA->next)
{
++lenA;
curA=curA->next;
}
while(curB->next)
{
++lenB;
curB=curB->next;
}
if(curA!=curB)
{
return NULL;
}
int pos=abs(lenA-lenB);
struct ListNode *longlist=headA,*shortlist=headB;
if(lenA<lenB)
{
longlist=headB;
shortlist=headA;
}
while(pos--)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
}
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
return shortlist;
}
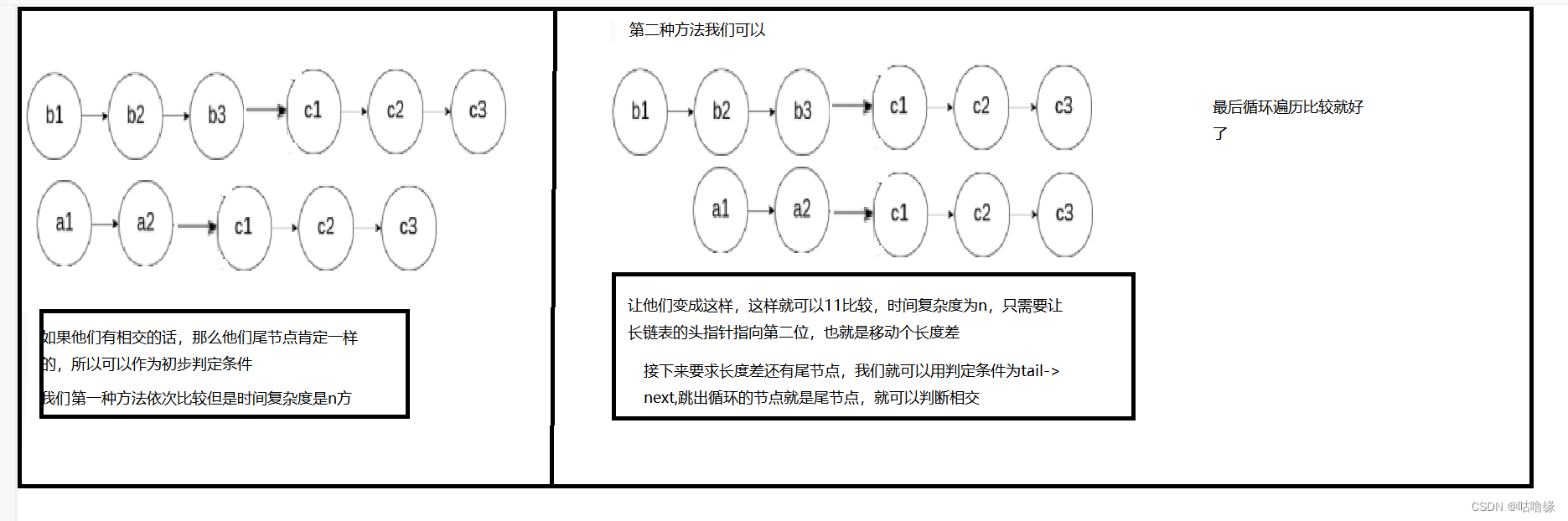
4.环形链表
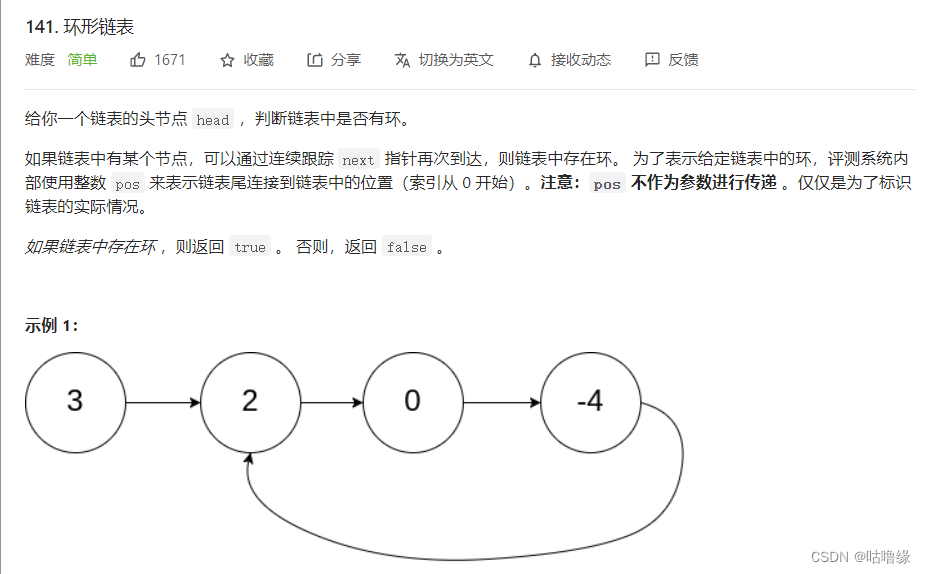
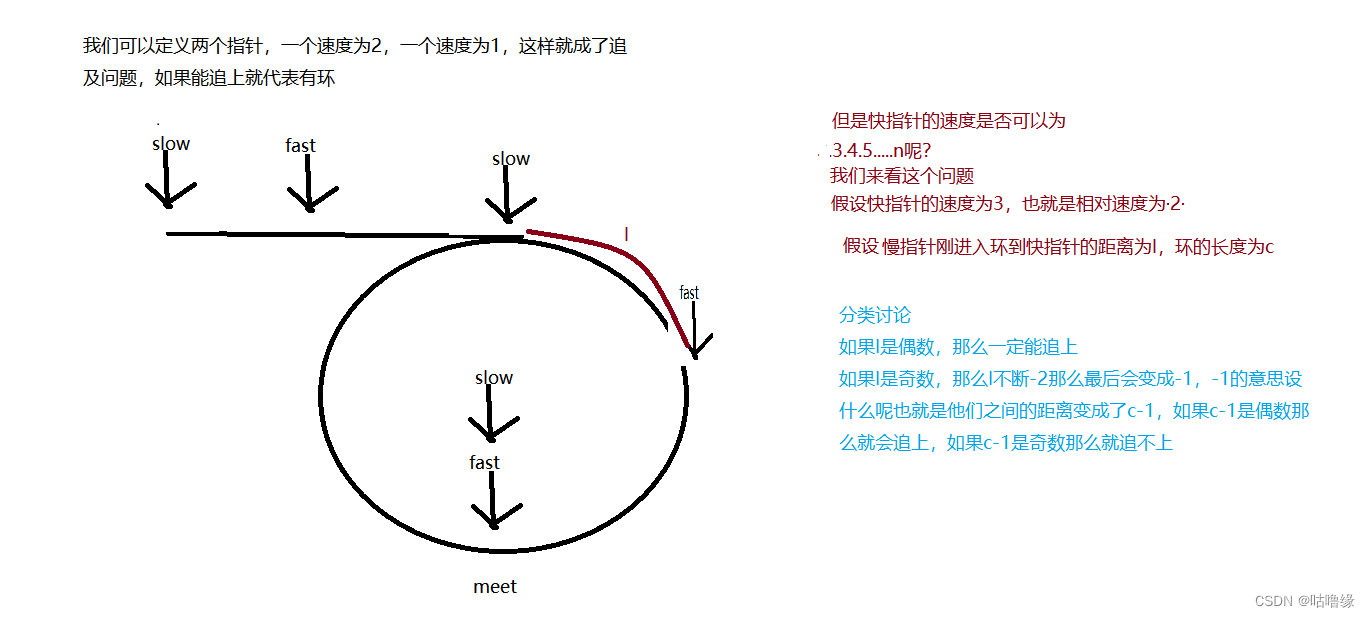
我们可以定义两个指针,一个速度为2,一个速度为1,这样就成了追及问题,如果能追上就代表有环
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *slow=head;
struct ListNode *fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
思路很简单轻松实现
5. 环形链表2
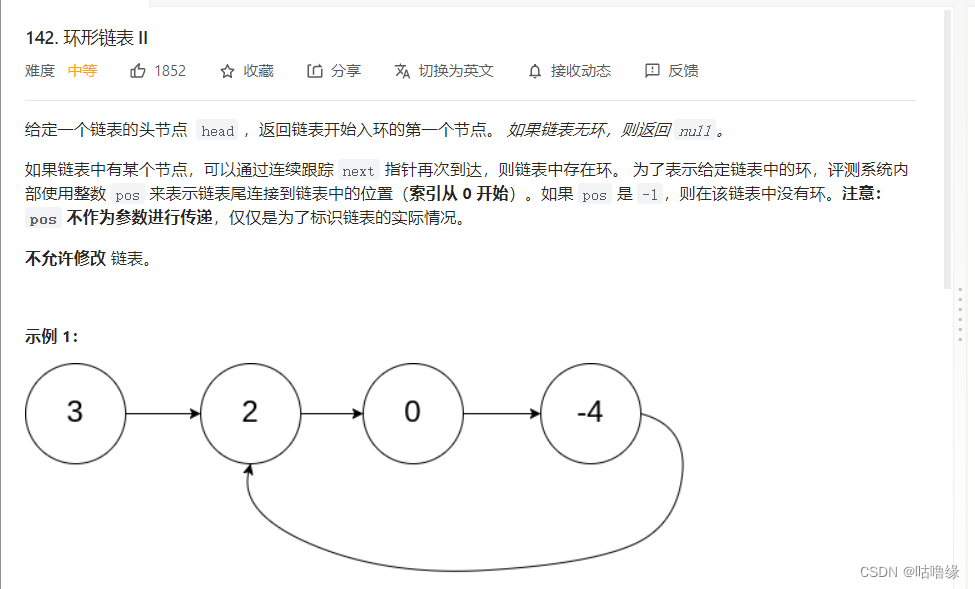
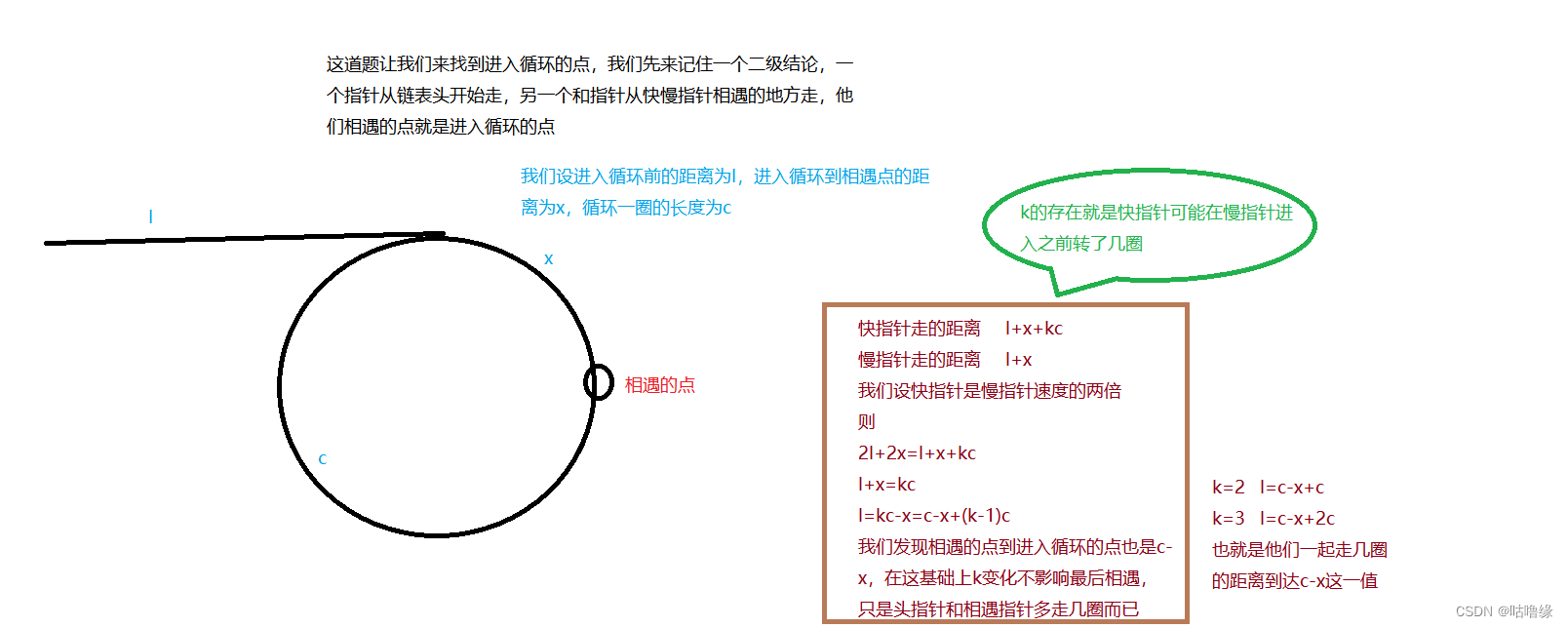
这道题让我们来找到进入循环的点,我们先来记住一个二级结论,一个指针从链表头开始走,另一个和指针从快慢指针相遇的地方走,他们相遇的点就是进入循环的点
我们先来代码实现一下
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *slow=head;
struct ListNode *fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
{
struct ListNode *meet=slow;
while(meet!=head)
{
head=head->next;
meet=meet->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
接下来我们来证明这个结论






















 648
648











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








