工作模式概述
简单模式

简单模式中只存在一个生产者,只存在一个消费者。生产者生产消息,消费者消费消息。消息只能被消费一次,也称为点对点模式。
简单模式适合在消息只能被单个消费者处理的场景下存在。
工作队列模式(Work Queue)
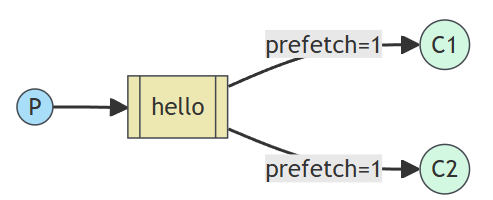
工作队列模式中存在一个消费者,多个生产者。生产者生产消息,消息队列将生产的消息分发给不同的消费者,每个消费者接收到不同的消息后开始进行消费。简单来说,工作模式下,消息不会被重复消费,不同的消费者消费的是不同的消息。
工作模式适合在集群环境中做异步处理。
发布订阅模式
交换机(Exchange)
作用:生产者将消息发送到Broker中,会先经过交换机,由交换机将消息按照一定规则路由到一个或者多个消息队列中(在简单模式和工作队列模式下,由生产者直接将消息投递到队列中,这种情况在RabbitMQ中根本不会出现)。
RabbitMQ交换机有四种类型:fanout、direct、topic、headers。不同类型有着不同的路由策略。AMQP协议其实是有六种交换机类型的(除了上述四种,还有system和自定义),只不过RabbitMQ只使用了其四种而已。
1. Fanout:广播,交换机将从生产者中获取的消息交给与之绑定的全部队列(对应工作模式中的发布订阅模式)。
2. Direct:定向,交换机将从生产者中获取的消息交给与之绑定的符合RoutingKey的队列(对应工作模式中的路由模式)。具体RoutingKey是啥,后面会讲到。
3. Topic:通配符,交换机将从生产者中获取的消息交给与之绑定的符合RoutingKey的队列(对应工作模式中的通配符模式)。定向和通配符中的RoutingKey是略有不同的,具体到工作模式的路由模式和通配符模式就会明白。
4. headers:此类交换器并不依赖于RoutingKey的匹配规则来路由消息,而是根据发送的消息内容中的headers属性进行匹配。headers类型的交换器性能会很差,而且也不实用,基本看不到它的存在,了解即可。
Exchange只负责转化消息,并不负责存储消息。因此如果没有任何交换机和队列绑定,或者发送的消息没有符合路由规则的队列,消息就会丢失。
RoutingKey,路由键。生产者发送消息给Broker时,指定的一个字符串,用来告诉交换机应该如何处理这个消息。
BindingKey,绑定键。在声明交换机和队列之后,使用一个BindingKey将交换机和队列绑定起来。这样,当生产者将消息发送给Broker之后,交换机接收到消息就能根据消息中的RoutingKey和BindingKey进行对比,从而知道将消息路由到某个或者某几个队列中了。
本质上,BindingKey属于RoutingKey的一种。换句话说,两者的作用并没有什么差别。不同的是,路由键是生产者向Broker发送消息时使用的,绑定键则是交换机和队列绑定时进行绑定,然后再交换机给队列发送消息时使用。当生产者将一个绑定了RoutingKey的消息发送给交换机之后,交换机根据存在的BindingKey来将消息路由给队列。
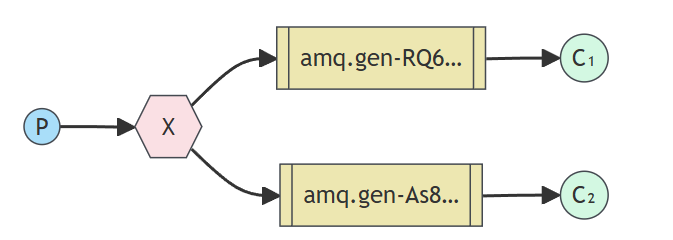
发布订阅模式存在一个生产者,多个消费者。生产者生产消息,交换机将消息复制多份,每个队列都会接收到相同的消息,每个消费者接收到消息之后开始进行消费。简单来说,消费者发送的消息,所有与之关联的队列都会收到相同的消息。
发布订阅模式适合消费需要被多个消费者同时接收的场景,例如实时播报或者广播消息。
路由模式
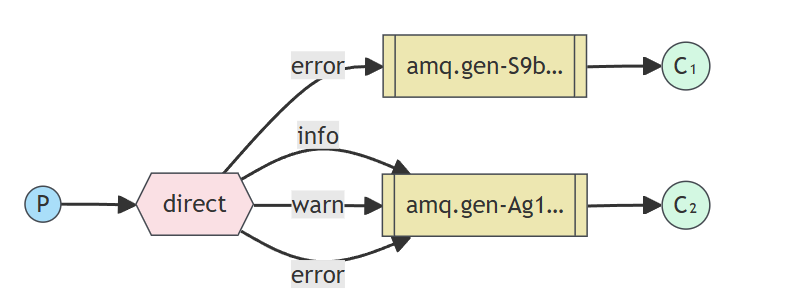
路由模式是发布订阅模式的变种,在发布订阅模式的基础上,增加了路由键。也就是说,消息到达交换机之后,不再是分发给所有关联的队列,而是根据绑定的路由规则来进行分发消息。
路由模式适合需要根据特定规则分发消息的场景。例如,系统日志打印,将不同级别的日志发送到不同的队列,最终输出到不同的文件。
通配符模式
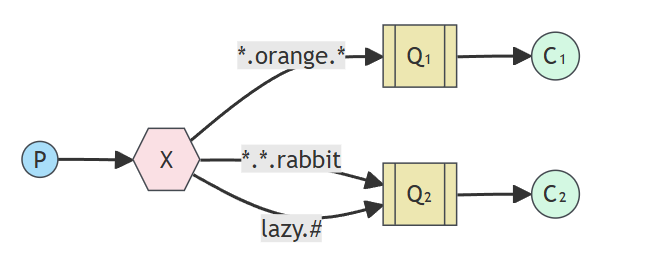
通配符模式又是路由模式的变种,在路由模式的基础上,增加了通配符的功能,使消息分发更加灵活。
总的来说,发布订阅模式是消息到达交换机之后,交换机无条件的将所有消息转发给队列。路由模式是消息到达交换机之后,交换机根据RoutingKey的规则,将数据筛选之后分发给不同的队列。通配符模式也是消息到达交换机之后,交换机根据RoutingKey的规则,将数据筛选之后分发给不同的队列,只不过该RoutingKey不再是一个确定的路由键,而是类似于正则表达式的方式来定义路由键。
通配符模式适合需要灵活匹配和过滤消息的场景。
RPC模式
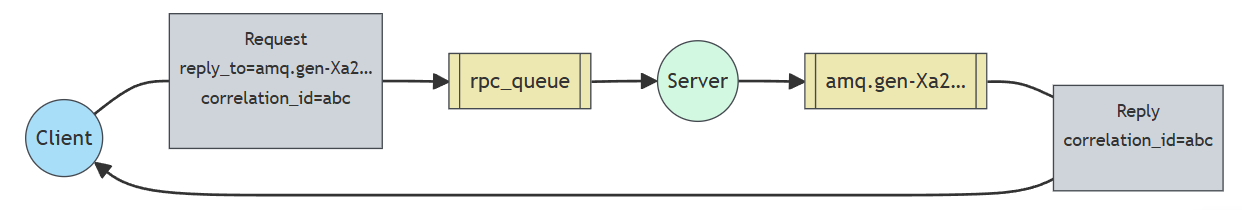
RPC模式没有生产者和消费者,比较类似于咋们的RPC远程调用,大概就是通过两个队列实现了一个可回调的过程。
1. 客户端发送消息到一个指定队列,并在消息属性中设置replyTo字段,这个字段指定了一个回调队列,用于接收服务器的响应,并且还设置了correctionId字段,用来确定响应是否为服务器所期望的。
2. 服务器接收到请求之后,处理请求并将响应消息发送到replyTo指定的回调队列中。
3. 客户端在回调队列上等待响应消息,一旦收到响应,客户端会检查消息的correctionId属性,以确定它是所期望的响应。
发布确认模式(Publisher Confirms)
发布确认模式是RabbitMQ提供的一种确保消息可靠发送到RabbitMQ服务器的机制。在这种模式下,生产者可以等待RabbitMQ服务器确认收到消息的通知,以确保消息已经被服务器所接收并进行了处理。
1. 生产者将channel设置为confirm模式(通过调用channel.confirmSelect(),发布的每一条消息都会获得一个唯一的ID,生产者可以将这些序列号与消息关联起来,以便跟踪消息的状态)。
2. 当消息被RabbitMQ接收并处理后,服务器会异步地向生产者发送一个确认(ACK)给生产者(内容包含了唯一ID),表示消息已经送达。
通过发布确认模式,生产者可以确保消息被RabbitMQ服务器接收并处理,从而避免了消息丢失的问题。
发布确认模式适合对数据安全性要求较高的场景,比如金融交易、订单处理。
SDK工作模式代码案例
简单模式
生产者代码
// 简单模式
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// TODO 创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("43.138.108.125"); // IP
connectionFactory.setPort(5672); // PORT
connectionFactory.setUsername("admin"); // 用户名
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin"); // 密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("mq-sdk-test"); // 虚拟主机
// TODO 创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
// TODO 获取信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.SIMPLE_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 声明交换机,使用内置交换机,无需声明
// TODO 发送消息
String msg = "hello simple";
channel.basicPublish("", Constants.SIMPLE_QUEUE, null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("简单模式生产者发送消息!");
// TODO 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}上述代码运行之后,在RabbitMQ的开源界面和IDEA终端上会有如下结果:


消费者代码
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// TODO 创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("43.138.108.125"); // IP
connectionFactory.setPort(5672); // PORT
connectionFactory.setUsername("admin"); // 用户名
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin"); // 密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("mq-sdk-test"); // 虚拟主机
// TODO 创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
// TODO 获取信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.SIMPLE_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 声明交换机,使用内置交换机,无需声明
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("成功接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.SIMPLE_QUEUE, true, consumer);
// TODO 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}上述代码运行之后,队列中的消息被该消费者接收,控制台输出下述内容:

工作队列模式
由于在接下来的代码中,创建连接工厂,创建连接,开启信道,释放资源都要存在。因此为了简化开发,将这些步骤封装成方法,方便后续调用。
public class Common { private static Connection connection; private static Channel channel; // 获取信道 public static Channel getChannel() throws IOException, TimeoutException { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); connectionFactory.setHost("43.138.108.125"); // IP connectionFactory.setPort(5672); // PORT connectionFactory.setUsername("admin"); // 用户名 connectionFactory.setPassword("admin"); // 密码 connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("mq-sdk-test"); // 虚拟主机 // TODO 创建连接 connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); // TODO 获取信道 channel = connection.createChannel(); return channel; } // 释放资源 public static void close() throws IOException, TimeoutException { channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
生产者代码
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// TODO 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机,使用内置交换机,因此无需声明
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 发送消息
/**
* 工作队列的模式是一个队列,多个消费者。
* 当存在多个消息时,不同的消费者会接收不同的消息,消息并不会重复消费
* 因此为了检验这个模式,发送多条消息
*/
String msg = "hello work queue";
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
channel.basicPublish("", Constants.WORK_QUEUE, null, (msg + ":" + i).getBytes());
}
System.out.println("工作队列模式消息发送成功!");
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}消费者代码
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
// TODO 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机,使用内置交换机,因此无需声明
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, consumer);
// TODO 释放资源
// Common.close();
}
}public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
// TODO 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机,使用内置交换机,因此无需声明
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, consumer);
// TODO 释放资源
// Common.close();
}
}在上述代码中,不要释放资源。将生产者的代码重新启动一次之后,就会发现如下内容。从消费者消费消息的输出情况来看,很容易得到工作模式最主要的内容:消费者消费的消息都是不同的消息,消息并不会被重复消费。


发布订阅模式
生产者代码
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT, true);
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1, Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "");
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2, Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "");
// TODO 发送消息
String msg = "hello 发布订阅模式";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("发布订阅模式发送消息成功!");
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}当上述代码启动之后,在开源界面中发生了如下变化。队列列表中新增了两个队列,交换机列表中新增了一条声明的交换机。


消费者代码
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT, true);
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1, Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "");
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1, true, consumer);
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT, true);
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2, Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "");
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2, true, consumer);
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}路由模式

路由模式实现的代码案例按照此图的需求来做。根据此图可以看出,当生产者发送消息时的路由键为error时,两个队列都能收到消息;但是当生产者发送消息时的路由键为info或者warn时,只有队列二可以收到消息。
生产者代码
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true);
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "error");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "info");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "warn");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "error");
// TODO 发送消息
// error的消息进入两个队列
// info和warn只会进入队列2
String[] msg = {"info", "error", "warn"};
for (String s : msg) {
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, s, null, s.getBytes());
}
System.out.println("路由模式发送消息成功!");
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}当运行上述代码之后,发现队列中的结果和预想结果一致。

消费者代码
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true);
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "error");
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, true, consumer);
Thread.sleep(20000); // 阻塞等待消息接收完成
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// TODO 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true);
// TODO 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
// TODO 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants. DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "error");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants. DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "info");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants. DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "warn");
// TODO 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, true, consumer);
Thread.sleep(20000); // 阻塞等待消息接收完成
// TODO 释放资源
Common.close();
}
}上述代码启动之后,在控制台输出消息如下:


通配符模式

根据上述图片为需求来写代码。#表示可以一次匹配多个单词,*则表示一次只能匹配一个单词。
生产者代码
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC, true);
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
// 绑定交换机和队列
/**
* #表示匹配一个或者多个词
* *表示只能匹配一个词
*/
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1, Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "*.orange.*");
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "*.*.rabbit");
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "lazy.#");
// 发送消息
/**
* 根据匹配规则,第二个将不会匹配成功
*/
String[] msg = new String[]{"a.orange.a", "a.b.orange.b.c", "c.c.rabbit", "lazy.a.b.v.c"};
for (String s : msg) {
channel.basicPublish(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, s, null, s.getBytes());
}
System.out.println("通配符模式消息发送成功!");
// 释放资源
channel.close();
}
}
消费者代码
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC, true);
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1, Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "*.orange.*");
// 消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1, true, consumer);
// 释放资源
channel.close();
}
}public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
// 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC, true);
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
// 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "*.*.rabbit");
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "lazy.#");
// 消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2, true, consumer);
Thread.sleep(2000);
// 释放资源
channel.close();
}
}下面分别为消费者1消费的内容和消费者2消费的内容:


RPC模式

客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// 发送消息
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.replyTo(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE) // 响应队列
.correlationId(uuid) // 唯一id,用来确认接收的响应
.build();
String msg = "hello rpc";
channel.basicPublish("", Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, properties, msg.getBytes());
// 接收响应
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("获取到的信息是:" + new String(body));
System.out.println("发送的id和接收的id:" + uuid + '\t' + properties.getCorrelationId());
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE, true, consumer);
// 释放资源
}
}服务器代码
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 获取信道
Channel channel = Common.getChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
// 接收消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("从客户端接收的消息为:" + new String(body));
System.out.println("客户端要求响应的队列:" + properties.getReplyTo());
// 处理客户端发送过来的消息并返回给客户端消息
AMQP.BasicProperties basicProperties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(properties.getCorrelationId())
.build();
String msg = "服务端返回消息";
channel.basicPublish("", properties.getReplyTo(), basicProperties, msg.getBytes());
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, true, consumer);
}
}当两个程序都启动时,客户端和服务器输出的结果分别是:

SpringBoot工作模式代码案例
模板

<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 43.138.108.125
port: 5672
username: admin
password: admin
virtual-host: mq-springboot-test@Component
public class RabbitTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
}
}工作队列模式
声明队列
@Configuration
public class WorkConfig {
// 声明队列
@Bean("workQueue")
public Queue workQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.WORK_QUEUE).build();
}
}生产者代码
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/work")
public class WorkController {
@Resource
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping
public String workQueue() {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("", Constants.WORK_QUEUE, "hello work spring");
return "成功";
}
}消费者代码
@Configuration
public class WorkListener {
/**
* @RabbitListener 是 Spring 框架中用于监听 RabbitMQ 队列的注解。
* 通过这个注解,可以定义一个方法,以便从 RabbitMQ 队列中接收消息
* 该注解支持多种参数类型,这些参数类型代表了从 RabbitMQ 接收到的消息和相关信息
*
* 常用的参数类型:
* 1. String :返回消息的内容
* 2. Message:SpringAMQP 的 Message 类,返回原始的消息体以及消息的属性,如果消息ID、内容和队列信息等等
* 3. Channel:RabbitMQ 的通道对象,可以用于进行更高级的操作,如手动确认消息
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.WORK_QUEUE)
public void workListener1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1消费的代码:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.WORK_QUEUE)
public void workListener2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2消费的代码:" + msg);
}
}当生产者发送6条消息之后,消费者消费消息如下输出结果:

发布确认模式
声明队列、交换机、绑定关系
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
// 声明队列
@Bean("fanoutQueue1")
public Queue fanoutQueue1() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1).build();
}
@Bean("fanoutQueue2")
public Queue fanoutQueue2() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2).build();
}
// 声明交换机
@Bean("fanoutExchange")
public Exchange fanoutExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();
}
// 声明绑定关系
@Bean("fanoutQueueBind1")
public Binding fanoutQueueBind1(@Qualifier("fanoutQueue1") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("fanoutExchange") FanoutExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange);
}
@Bean("fanoutQueueBind2")
public Binding fanoutQueueBind2(@Qualifier("fanoutQueue2") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("fanoutExchange") FanoutExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange);
}
}生产者代码
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/fanout")
public class FanoutController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping
public String fanoutQueue() {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", "hello fanout");
return "成功";
}
}启动程序之后,使用127.0.0.1:8080/fanout发送一条消息,得到如下结果:

消费者代码
@Configuration
public class FanoutListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1)
public void fanoutListener1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1获取消息为:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2)
public void fanoutListener2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2获取消息为:" + msg);
}
}当生产者发送3条消息之后,消费者获取的消息内容如下:

路由模式

声明队列、交换机、绑定关系
@Configuration
public class DirectConfig {
@Bean("directQueue1")
public Queue directQueue1() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1).build();
}
@Bean("directQueue2")
public Queue directQueue2() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2).build();
}
@Bean("directExchange")
public Exchange directExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();
}
@Bean("directQueueBind1")
public Binding directQueueBind1(@Qualifier("directQueue1") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("directExchange") DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("error");
}
@Bean("directQueueBind2")
public Binding directQueueBind2(@Qualifier("directQueue2") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("directExchange") DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("error");
}
@Bean("directQueueBind3")
public Binding directQueueBind3(@Qualifier("directQueue2") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("directExchange") DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("info");
}
@Bean("directQueueBind4")
public Binding directQueueBind4(@Qualifier("directQueue2") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("directExchange") DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("warn");
}
}
生产者代码
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/direct")
public class DirectController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping
public String directQueue() {
String[] msg = new String[]{"error", "info", "warn"};
for (String s : msg) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, s, "hello direct " + s);
}
return "成功";
}
}消费者代码
@Configuration
public class DirectListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1)
public void directListener1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1获取到的消息:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2)
public void directListener2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2获取到的消息:" + msg);
}
}通配符模式

声明队列、交换机、绑定关系
@Configuration
public class TopicConfig {
@Bean("topicQueue1")
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1).build();
}
@Bean("topicQueue2")
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2).build();
}
@Bean("topicExchange")
public Exchange topicExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();
}
/**
* *表示一个词
* #表示多个词
*/
@Bean("topicQueueBind1")
public Binding topicQueueBind1(@Qualifier("topicQueue1") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("topicExchange") TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("*.orange.*");
}
@Bean("topicQueueBind2")
public Binding topicQueueBind2(@Qualifier("topicQueue2") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("topicExchange") TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("*.*.rabbit");
}
@Bean("topicQueueBind3")
public Binding topicQueueBind3(@Qualifier("topicQueue2") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("topicExchange") TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("lazy.#");
}
}生产者代码
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/topic")
public class TopicController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping
public String topicQueue() {
String[] msg = new String[]{"a.orange.a", "a.b.orange.b.c", "c.c.rabbit", "lazy.a.b.v.c"};
for (String s : msg) {
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, s, "hello topic" + s);
}
return "成功";
}
}消费者代码
@Configuration
public class TopicListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1)
public void topicListener1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1获取到的消息" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2)
public void topicListener2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2获取到的消息" + msg);
}
}该篇文章中,对MQ的常用工作模式以及对应RabbitMQ的SDK示例和SpringBoot示例进行了简单表示。接下来就进入对RabbitMQ一些特性的文章上。
























 1233
1233

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










