8. 共享模型之工具
8.1 自定义线程池
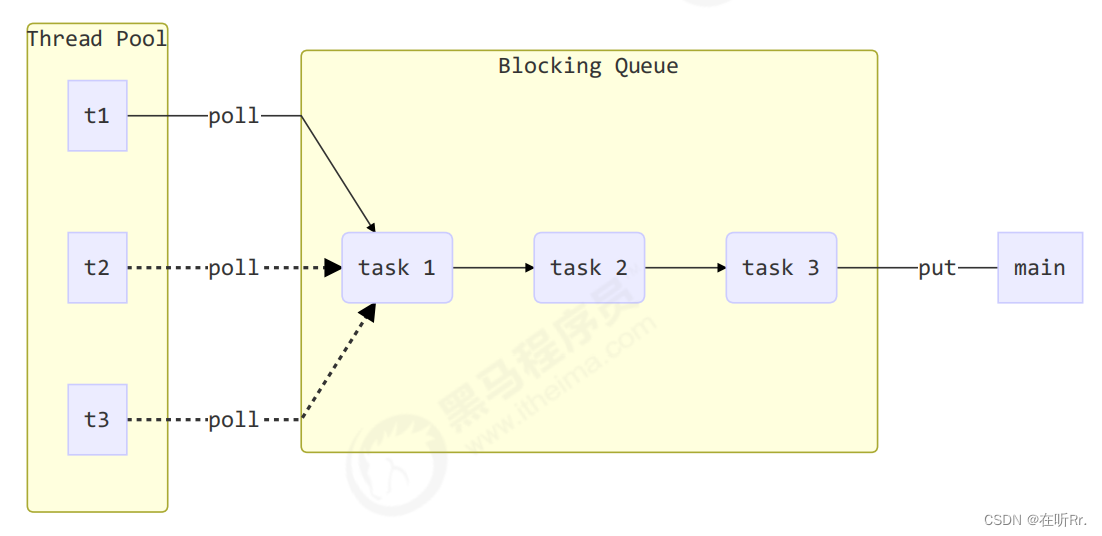
8.1.1 第一版
1. 自定义任务队列
/**
* 任务队列
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列 Deque-双端队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3. 消费者(thread)条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4. 消费者获取任务
public T take() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 5. 生产者添加任务
public void put(T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("{}加入等待队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}2. 自定义线程池
/**
* 线程池
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1. 任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2. 线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3. 核心线程数
private int coreNumber;
// 4. 构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreNumber) {
this.coreNumber = coreNumber;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>();
}
// 5. 执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// a. coreNumber 数量的 task 直接被 worker 执行
// b. 超出 coreNumber 数量的 task 进入 taskQueue
synchronized (workers) {
// 最大运行效率 - 线程数同 CPU core 数相等
if (workers.size() < coreNumber) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增{}并执行{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1)当 task 不为空时,执行任务
// 2)当 task 执行完毕后,再从任务队列中获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {
task.run();
task = null;
}
}
}
}3. 测试
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MyThreadPool")
public class MyThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2); // 2 个 CPU core
// 4 个 task
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("执行 task:打印 {}", j);
});
}
}
}4. 某次运行结果
09:23:37 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-0,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@649d209a
09:23:37 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-1,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@3c5a99da
09:23:37 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@5a01ccaa加入等待队列
09:23:37 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@71c7db30加入等待队列
09:23:37 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 0
09:23:37 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 1
09:23:37 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 2
09:23:37 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 3问题一:未设置任务队列容量,生产者可向任务队列中无限制的添加任务,可能出现内存溢出异常
8.1.2 第二版
1. 自定义任务队列
/**
* 任务队列
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列 Deque-双端队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3. 生产者(main)条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4. 消费者(thread)条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5. 容量(任务列表所能容纳的最大任务数)
private int capacity;
// 6. 构造方法
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 7. 消费者获取任务
public T take() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 8. 生产者添加任务
public void put(T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity){
try {
log.debug("{}等待加入等待队列",task);
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("{}加入等待队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}2. 自定义线程池
/**
* 线程池
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1. 任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2. 线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3. 核心线程数
private int coreNumber;
// 4. 构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreNumber) {
this.coreNumber = coreNumber;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(2);
}
// 5. 执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// a. coreNumber 数量的 task 直接被 worker 执行
// b. 超出 coreNumber 数量的 task 进入 taskQueue
synchronized (workers) {
// 最大运行效率 - 线程数同 CPU core 数相等
if (workers.size() < coreNumber) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增{}并执行{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1)当 task 不为空时,执行任务
// 2)当 task 执行完毕后,再从任务队列中获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {
task.run();
task = null;
}
}
}
}3. 测试
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MyThreadPool")
public class MyThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2); // 2 个 CPU core
// 4 个 task
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("执行 task:打印 {}", j);
});
}
}
}4. 某次运行结果
09:34:42 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-0,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@649d209a
09:34:42 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-1,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@3c5a99da
09:34:42 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@5a01ccaa加入等待队列
09:34:42 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 0
09:34:42 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 1
09:34:42 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@71c7db30加入等待队列
09:34:42 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@19bb089b等待加入等待队列
09:34:42 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 3
09:34:42 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 2
09:34:42 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@19bb089b加入等待队列
09:34:42 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 4问题二:若生产者不再向任务列表中添加任务,但线程仍旧会无限制地等待获取任务
8.1.3 第三版
1. 自定义任务队列
/**
* 任务队列
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列 Deque-双端队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3. 生产者(main)条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4. 消费者(thread)条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5. 容量(任务列表所能容纳的最大任务数)
private int capacity;
// 6. 构造方法
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 7. 消费者获取任务(超时等待)
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 8. 生产者添加任务
public void put(T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity) {
try {
log.debug("{}等待加入等待队列", task);
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("{}加入等待队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}2. 自定义线程池
/**
* 线程池
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1. 任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2. 线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3. 核心线程数
private int coreNumber;
// 4. 超时等待时间及单位
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit unit;
// 5. 构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreNumber, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
this.coreNumber = coreNumber;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(2);
this.timeout = timeout;
this.unit = unit;
}
// 6. 执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// a. coreNumber 数量的 task 直接被 worker 执行
// b. 超出 coreNumber 数量的 task 进入 taskQueue
synchronized (workers) {
// 最大运行效率 - 线程数同 CPU core 数相等
if (workers.size() < coreNumber) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增{}并执行{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1)当 task 不为空时,执行任务
// 2)当 task 执行完毕后,再从任务队列中获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, unit)) != null) {
task.run();
task = null;
}
}
}
}3. 测试
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MyThreadPool")
public class MyThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2,2000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 2 个 CPU core
// 4 个 task
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("执行 task:打印 {}", j);
});
}
}
}4. 某次运行结果
10:19:49 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-0,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@649d209a
10:19:49 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-1,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@3c5a99da
10:19:49 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@5a01ccaa加入等待队列
10:19:49 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@71c7db30加入等待队列
10:19:49 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@19bb089b等待加入等待队列
10:19:49 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 0
10:19:49 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 1
10:19:49 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 3
10:19:49 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 2
10:19:49 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@19bb089b加入等待队列
10:19:49 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@11531931加入等待队列
10:19:49 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 4
10:19:49 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 执行 task:打印 5
进程已结束,退出代码 0问题三:核心线程数是一个固定值,当生产者源源不断地向任务队列中添加任务时,若我是消费者,我觉得我要炸了
8.1.4 第四版
1. 自定义任务队列
/**
* 任务队列
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列 Deque-双端队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3. 生产者(main)条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4. 消费者(thread)条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5. 容量(任务列表所能容纳的最大任务数)
private int capacity;
// 6. 构造方法
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 7. 消费者获取任务(超时等待)
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 8. 生产者添加任务(超时等待)
public boolean offer(T task, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.size() == capacity) {
try {
if (nanos <= 0) {
log.debug("{}未加入等待队列", task);
return false;
}
log.debug("{}等待加入等待队列", task);
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("{}加入等待队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}2. 自定义线程池
/**
* 线程池
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1. 任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2. 线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3. 核心线程数
private int coreNumber;
// 4. 超时等待时间及单位
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit unit;
// 5. 构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreNumber, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
this.coreNumber = coreNumber;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(2);
this.timeout = timeout;
this.unit = unit;
}
// 6. 执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// a. coreNumber 数量的 task 直接被 worker 执行
// b. 超出 coreNumber 数量的 task 进入 taskQueue
synchronized (workers) {
// 最大运行效率 - 线程数同 CPU core 数相等
if (workers.size() < coreNumber) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增{}并执行{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
taskQueue.offer(task, timeout, unit);
}
}
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1)当 task 不为空时,执行任务
// 2)当 task 执行完毕后,再从任务队列中获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, unit)) != null) {
log.debug("执行{}", task);
task.run();
task = null;
}
}
}
}3. 测试
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MyThreadPool")
public class MyThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 2 个 CPU core
// 4 个 task
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.debug("打印 {}", j);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
}4. 某次运行结果
10:49:33 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-0,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@649d209a
10:49:33 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增Thread[Thread-1,5,main]并执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@3c5a99da
10:49:33 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@5a01ccaa加入等待队列
10:49:33 [Thread-0] c.ThreadPool - 执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@649d209a
10:49:33 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@71c7db30加入等待队列
10:49:33 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@19bb089b等待加入等待队列
10:49:33 [Thread-1] c.ThreadPool - 执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@3c5a99da
10:49:34 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@19bb089b未加入等待队列
10:49:34 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@11531931等待加入等待队列
10:49:35 [main] c.BlockingQueue - com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@11531931未加入等待队列
10:49:38 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 打印 0
10:49:38 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 打印 1
10:49:38 [Thread-0] c.ThreadPool - 执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@5a01ccaa
10:49:38 [Thread-1] c.ThreadPool - 执行com.rui.seven.MyThreadPool$$Lambda$1/2030562336@71c7db30
10:49:43 [Thread-0] c.MyThreadPool - 打印 2
10:49:43 [Thread-1] c.MyThreadPool - 打印 3
进程已结束,退出代码 0若无 task 需被线程执行,释放线程
修改 run 方法
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1)当 task 不为空时,执行任务
// 2)当 task 执行完毕后,再从任务队列中获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, unit)) != null) {
log.debug("执行{}", task);
task.run();
task = null;
}
synchronized (workers){
log.debug("{}被释放",this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}同一件事,不同人可能会作出不同选择。
拒绝策略 - 选择
以生产者为例
生产者有五种选择:
1. 无限制地等待,直到任务队列不为 full,将 task 添加到任务队列
queue.put(task);
2. 超时等待
queue.offer(task, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
3. 放弃添加
[空]
4. 抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException(task + "抛出异常");
5. 由生产者执行任务
task.run();
8.1.5 第五版
1. 自定义拒绝策略接口
/**
* 拒绝策略
*/
@FunctionalInterface
interface RejectPolicy<T> {
void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task);
}2. 自定义任务队列
/**
* 任务队列
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列 Deque-双端队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3. 生产者(main)条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4. 消费者(thread)条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5. 容量(任务列表所能容纳的最大任务数)
private int capacity;
// 6. 构造方法
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 7. 消费者获取任务(超时等待)
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
try {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 8. 生产者添加任务
public void put(T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity) {
try {
log.debug("{}等待加入任务队列", task);
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("{}加入任务队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 9. 生产者添加任务(超时等待)
public boolean offer(T task, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.size() == capacity) {
try {
if (nanos <= 0) {
log.debug("{}未加入任务队列", task);
return false;
}
log.debug("{}等待加入任务队列", task);
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("{}加入任务队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 10. 生产者添加任务(拒绝策略)
public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (queue.size() == capacity) {
rejectPolicy.reject(this, task);
} else {
log.debug("{}加入任务队列", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}3. 自定义线程池
/**
* 线程池
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1. 任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2. 线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3. 核心线程数
private int coreNumber;
// 4. 超时等待时间及单位
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit unit;
// 5. 拒绝策略
private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;
// 6. 构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreNumber, int capacity, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {
this.coreNumber = coreNumber;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(capacity);
this.timeout = timeout;
this.unit = unit;
this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;
}
// 6. 执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// a. coreNumber 数量的 task 直接被 worker 执行
// b. 超出 coreNumber 数量的 task 进入 taskQueue
synchronized (workers) {
// 最大运行效率 - 线程数同 CPU core 数相等
if (workers.size() < coreNumber) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增{}并执行{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task);
}
}
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1)当 task 不为空时,执行任务
// 2)当 task 执行完毕后,再从任务队列中获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, unit)) != null) {
log.debug("执行{}", task);
task.run();
task = null;
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("{}被释放", this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
}4. 测试
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MyThreadPool")
public class MyThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, (queue, task) -> {
// 1. 无限制地等待,直到任务队列不为 full,将 task 添加到任务队列
// queue.put(task);
// 2. 超时等待
// queue.offer(task, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 3. 放弃添加
// log.debug("放弃添加{}",task);
// 4. 抛出异常
// throw new RuntimeException(task + "抛出异常");
// 5. 由生产者执行任务
// task.run();
});
// 4 个 task
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.debug("打印 {}", j);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
}5. 运行结果
[略]
吃饭时间到啦.jpg
说些废话
本篇文章为博主日常学习记录,故而会概率性地存在各种错误,若您在浏览过程中发现一些,请在评论区指正,望我们共同进步,谢谢!























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








