目录
(一)NullPointerException(空指针异常)
(二)ArithmeticException(数学运算异常)
(三)ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(数组下标越界异常)
(五)NumberFormatException(数字格式不正确异常)
一、介绍
在Java中,将程序执行的不正常情况称为“异常”。
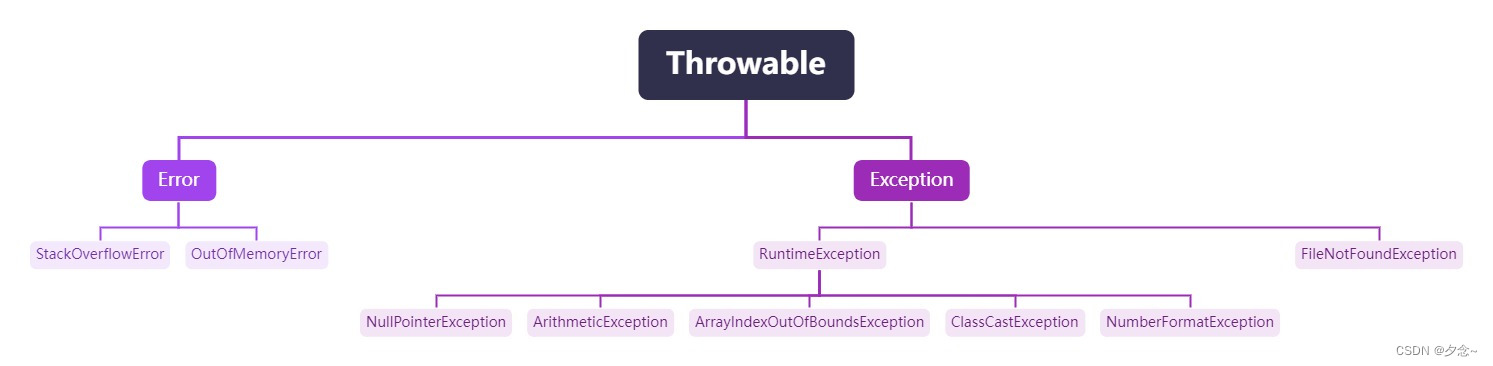
执行过程中的异常事件可分为两类:
(1)error(错误):Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等情况。
(2)Exception:因编程错误或外在因素产生的一般性问题,可使用针对性代码进行处理。如:空指针访问、试图读取不存在的文件等情况。异常又分为两大类:运行时异常和编译时异常。
注:运行时异常不要求强制处理,而编译时异常是必须处理的异常。
常用异常体系图
二、常见运行时异常
(一)NullPointerException(空指针异常)
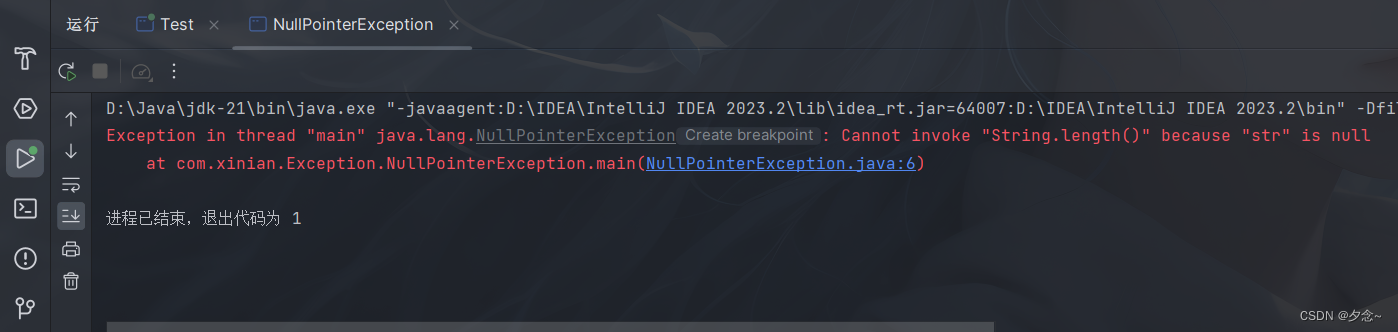
示例
public class NullPointerException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());//空指针异常
}
}运行结果
(二)ArithmeticException(数学运算异常)
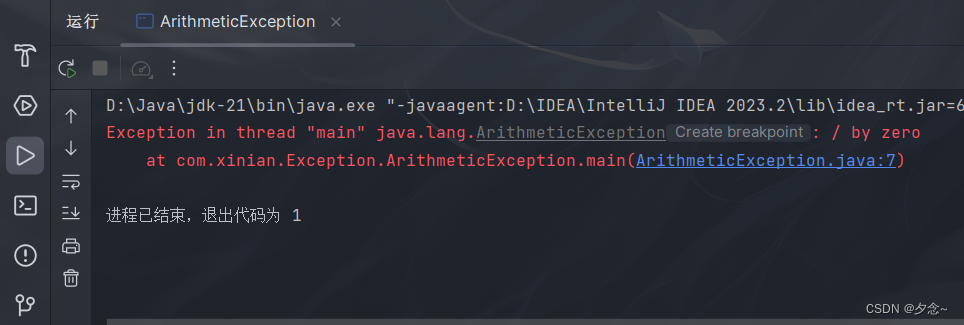
示例
public class ArithmeticException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 100;
int b = 0;
int c = a / b;//数学运算异常
System.out.println(c);
}
}运行结果
(三)ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(数组下标越界异常)
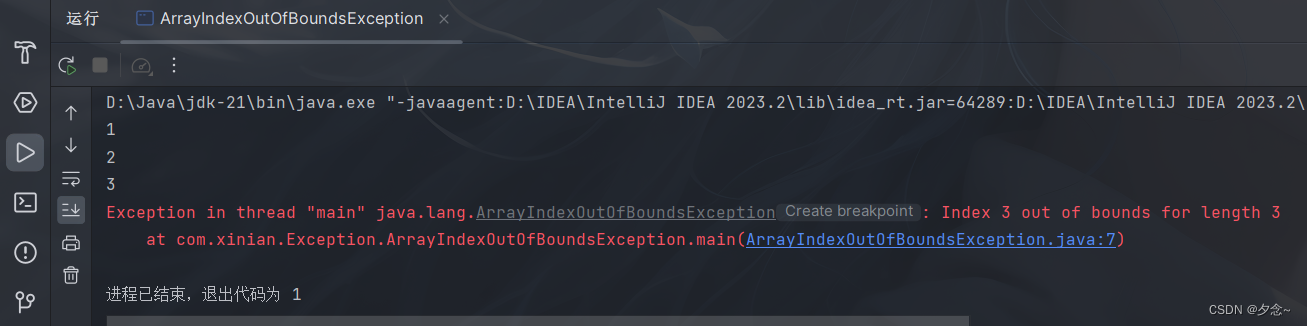
示例
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {//数组下标越界异常
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}运行结果
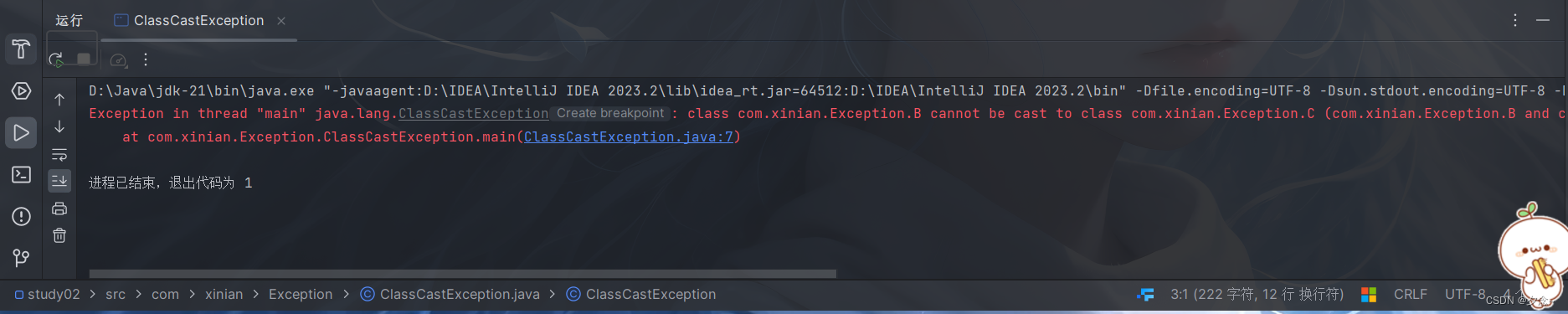
(四)ClassCastException(类型转换异常)
示例
public class ClassCastException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B();//向上转型
B b = (B)a;//向下转型
C c = (C)a;//类型转换异常
}
}
class A{
}
class B extends A{
}
class C extends A{
}运行结果
(五)NumberFormatException(数字格式不正确异常)
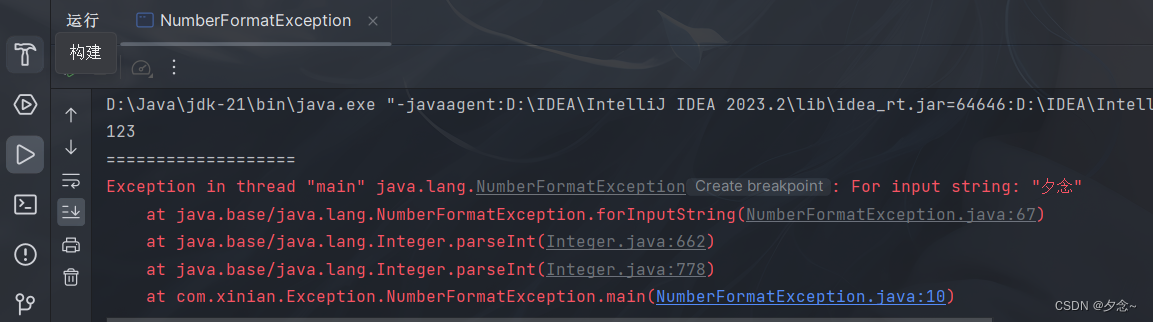
示例
public class NumberFormatException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);//将字符串转换为整数
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println("===================");
String str2 = "夕念";
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(str2);//数字格式不正确异常
System.out.println(num2);
}
}运行结果
三、异常处理
介绍
当异常发生时,对于异常的处理方式。
方式
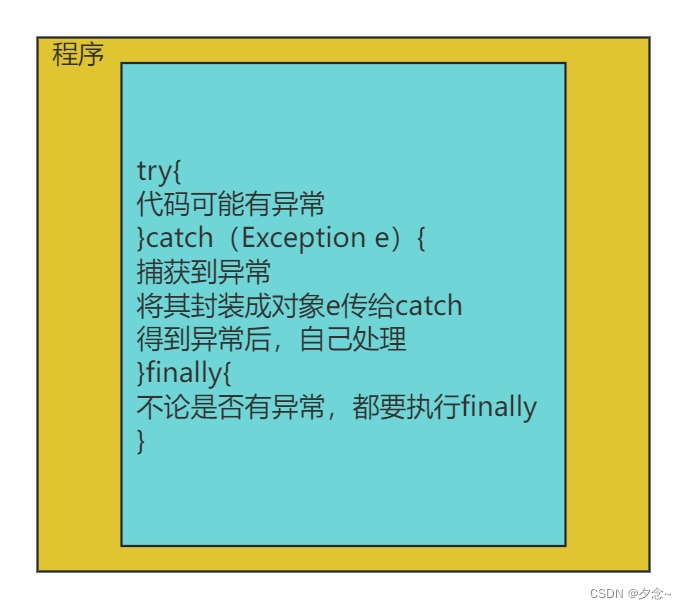
(一)try-catch-finally
在代码中捕获发生的异常自行处理。
注:可以有多个catch语句,捕获不同的异常。
示例
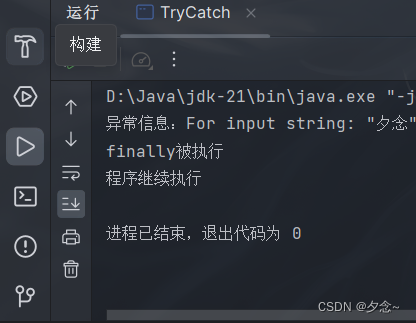
public class TryCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String str = "夕念";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);// 发生NumberFormatException异常
System.out.println("数字:"+ a);// 发生异常,不会执行
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("异常信息:" + e.getMessage());// 捕获异常,并打印异常信息
} finally {
System.out.println("finally被执行");// 无论是否发生异常,都会执行
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行");// 程序继续执行
}
}运行结果
(二)throws(抛出异常)
不知如何处理某种异常时,可以将该异常抛出,交由该方法的调用者处理。
注:throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类,也可以同时抛出多个异常。
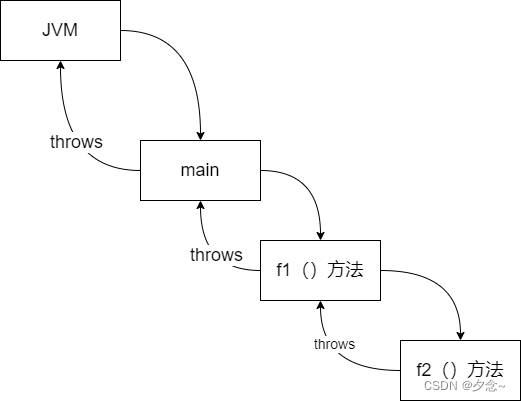
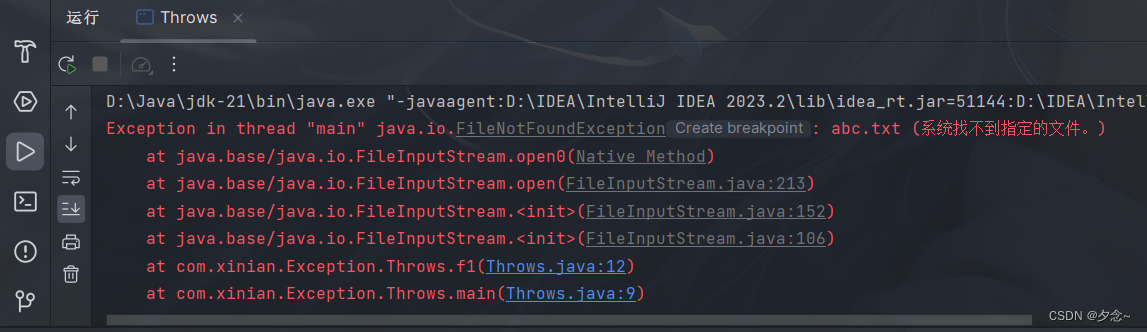
示例
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class Throws {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Throws t = new Throws();
t.f1();//调用f1()方法,抛出FileNotFoundException异常
}
public void f1() throws FileNotFoundException {//抛出FileNotFoundException异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("abc.txt");
}
}运行结果








 本文详细介绍了Java中的几种常见运行时异常,包括NullPointerException、ArithmeticException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException、ClassCastException和NumberFormatException,以及异常处理方法,如try-catch-finally和throws的使用。
本文详细介绍了Java中的几种常见运行时异常,包括NullPointerException、ArithmeticException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException、ClassCastException和NumberFormatException,以及异常处理方法,如try-catch-finally和throws的使用。














 149
149

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








