G - Mediator:
题目描述:

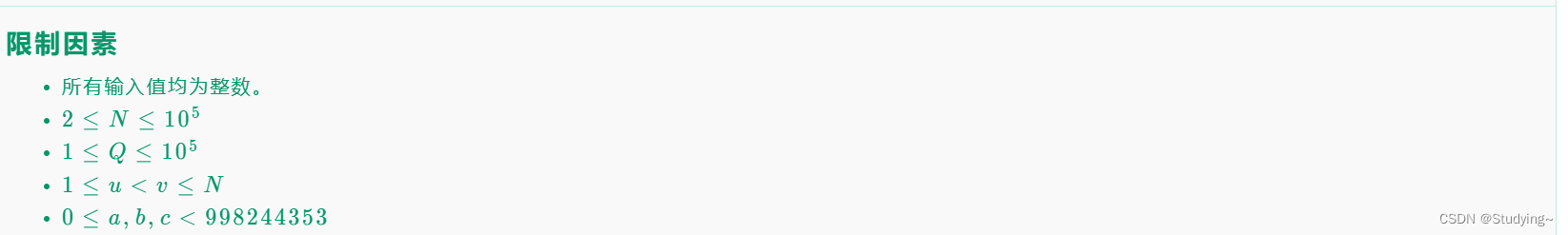
思路解析:
查询一是连接两个点,但是题目保证添加边时两个结点属于两个不同的联通块,那么可以直接相连即可。但是相连时,需要重新编写父子关系,那么就需要遍历某一个联通部分,所以在这里我们应该采用小联通块连接到大联通块的策略,那么这里需用并查集的思想。
查询二是两个点x和y,问连接x和y的点是谁,因为他是一个森林,所以这个点是唯一确定的,利用父子关系查即可,因为x和y只有两种情况,爷孙关系或者兄弟关系。
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = 1;
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt(); int q = f.nextInt();
Sz = new int[n+1]; a = new int[n+1]; fa = new int[n+1];
g = new Vector[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
g[i] = new Vector<>();
}
Arrays.fill(fa, -1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Sz[i] = 1; a[i] = i;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int t = 0; t < q; t++) {
long a = f.nextLong(); long b = f.nextLong(); long c = f.nextLong();
long type = 1 + (((a * (1 + ans)) % mod) % 2);
long X = 1 + (((b * (1 + ans)) % mod) % n);
long Y = 1 + (((c * (1 + ans)) % mod) % n);
int x = (int) X; int y = (int) Y;
if (type == 1){
join(x, y);
}else {
boolean st = false;
int Pa = fa[x]; int Pb = fa[y]; // 通过父子关系查询
if (Pa == Pb && Pa != -1){
ans = Pa;
st = true;
}
if (Pa != -1 && fa[Pa] == y){
ans = Pa;
st = true;
}
if (Pb != -1 && fa[Pb] == x){
ans = Pb;
st = true;
}
if (!st) ans = 0;
w.println(ans);
}
}
}
static Vector<Integer>[] g;
static int[] Sz;
static int[] fa;
static int[] a; // 树的根
public static int root(int x){
while (x != a[x]){
a[x] = a[a[x]];
x = a[x];
}
return x;
}
public static void join(int x, int y){
if (Sz[root(x)] > Sz[root(y)]){
int tmp = x; x = y; y = tmp;
}
dfs(x, y); // 重新编写父子关系,通过遍历较小的联通块。
merge(x, y);
g[x].add(y); // 连接
g[y].add(x);
}
public static void merge(int x, int y){ // 合并联通块
int Pa = root(x);
int Pb = root(y);
a[Pb] = Pa;
Sz[Pa] += Sz[Pb];
}
public static void dfs(int x, int f){
fa[x] = f;
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
int y = g[x].get(i);
if (y == f) continue;
dfs(y, x);
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}






 文章讲述了如何使用并查集数据结构解决图论问题,包括连接不同联通块的策略和查询两点间的连接点。代码展示了如何在Java中实现这些操作,涉及变量如n、q、Sz、fa、a等。
文章讲述了如何使用并查集数据结构解决图论问题,包括连接不同联通块的策略和查询两点间的连接点。代码展示了如何在Java中实现这些操作,涉及变量如n、q、Sz、fa、a等。
















 3984
3984











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










