文章目录
前言
对于文章I/O(输入/输出流的概述),有了下文。这篇文章将具体详细展述如何向磁盘文件中输入数据,或者读取磁盘文件中的信息。这样就不会在java程序运行结束后,数据消失了。
一、文件输入\输入流是什么?
文件输入\输出流,是与指定的文件建立连接,将需要的数据永久保存到文件中,避免程序结束时的数据消失(当然也可以从文件中读取信息)。
二、使用方法
需要导入 java.io包
1.FileInputStream与FileOutputStream类
构造方法:
File file = new File("word.txt");
//先创建一个文件对象
//实例化字节输入输出流时,引入参数File对象,实现对该File对象进行操作
new FileOutputStream(file);
//第二布尔参数为true,该流输入文件信息时,文件之前的信息不会消失
new FileOutputStream(file,true);
new FileInputStream(file);使用时有三点需要注意:
(1)字节输入\输出流的使用过程中需要创建byte字节数组来读存数据的。
(2)需要使用try-catch-finally语句抛出异常
(3)需要使用close()方法关闭输入\输出流
实操展示:
项目:创建一个word.txt文件,使用FileOutputStream对象将文字输入进txt文件。同时使用FileInputStream对象将txt文件中存有的文字数据返回至终端。
import java.io.*;
public class PutStream{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("word.txt");
//输出数据到文件中
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try{
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
String string = "君不见高堂明镜悲白发,朝如青丝暮成雪";
byte b[] = string.getBytes();//字符串转换为字节数组
outputStream.write(b);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outputStream!=null){
try{
outputStream.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//读取数据
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte b2[] = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(b2);
//inputStream.read()返回int值文件中的字节数,len为文件字节流的字节数
System.out.println("文件中的数据是:"+new String(b2,0,len));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(inputStream!=null){
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
(1)若File对象创建时,没有对应的"word.txt",则会自动生成一个文件。
(2)实例化FileOutputStream和FileInputStream对象时需要抛出IOException。
(3)FileOutputStream对象write(byte[]),将byte数组内容写入到文件中。字符串对象通过getBytes()方法转化为字节数组储存。
(4)FileInputStream对象read(byte[]),将读取文件的字节流保存在byte数组对象中,返回int值为文件字节流的字节长度。实例化new String(byte[],int1,int2) 为byte[]数组实例化为字符串,实例化长度从int1到int2。
(5)在Finally代码块中的close()方法,使用过程中需要使用try-catch语句抛出IOException异常。
运行结果: 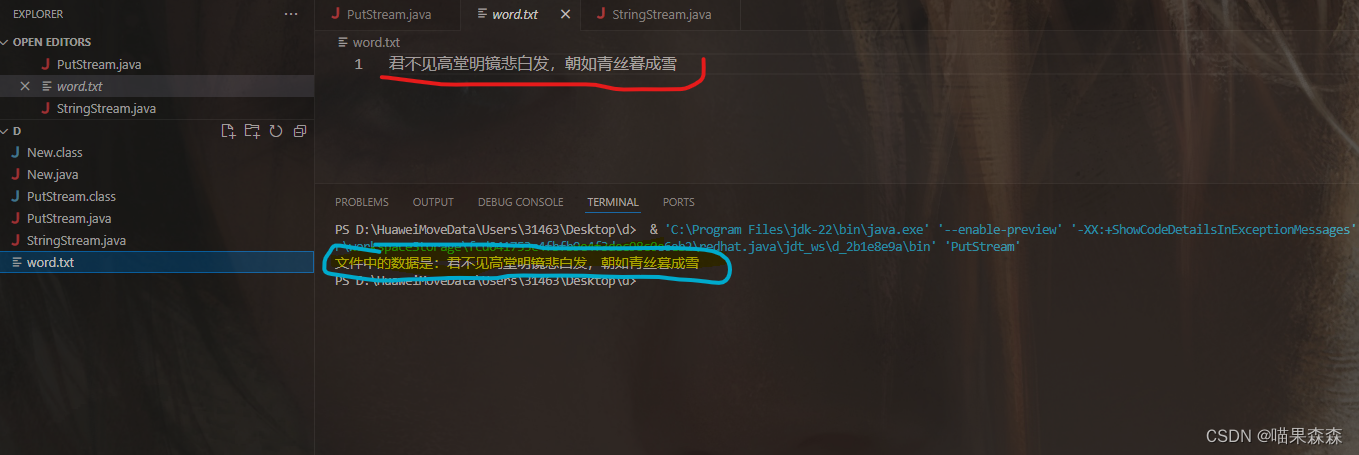
如图,创建了一个word.txt,永久保存了输入的信息,并且将里面的信息也反馈到控制台中。
2.FileReader与FileWriter类
构造方法:
File file = new File("word.txt");
//先创建一个文件对象
//实例化字符输入输出流时,引入参数File对象,实现对该File对象进行操作
new FileWriter(file);
//第二布尔参数为true,该流输入文件信息时,文件之前的信息不会消失
new FileWriter(file,ture);
new FileReader(file);使用时有三点需要注意:
(1)字符输出流的使用过程中需要创建char字节数组来读取数据的。
(2)需要使用try-catch语句抛出异常
(3)需要使用close()方法关闭输入\输出流(不需要抛出异常)
实操展示:
项目:创建一个word.txt文件,使用FileWriter对象将文字输入进txt文件。同时使用FileReader对象将txt文件中存有的文字数据返回至终端。
import java.io.*;
public class PutStream{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("word.txt");
//输出数据到文件中
FileWriter writer = null;
try{
writer= new FileWriter(file);
//字符串不用转换类型,直接写入即可
String string = "人生得意须尽欢,莫使金樽空对月";
writer.write(string);
writer.close(); //字符流直接关闭就行,不需要try-catch抛出异常
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//读取数据
FileReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(file);
//需要使用的是char字符数组来保存,读取的文件数据
char b2[] = new char[1024];
int len = reader.read(b2);
System.out.println("文件中的数据是:"+new String(b2,0,len));
reader.close(); //直接关闭读取流
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}(1)若File对象创建时,没有对应的"word.txt",则会自动生成一个文件。
(2)实例化FileWriter和FileReader对象时需要抛出IOException。
(3)FileWriter对象write(String),将字符串内容写入到文件中。
(4)FileInputStream对象read(char[]),将读取文件的字节流保存在char数组对象中,返回int值为文件字节流的字节长度。实例化new String(char[],int1,int2) 为char[]数组实例化为字符串,实例化长度从int1到int2。
(5)close()方法,在最后处关闭数据流即可。
总结
以上就是I\O中要讲的字节输入输出流,字符输入输出流的使用方法了,本文仅仅简单介绍了FileInputStream,FileOutputStream,FileReader,FileWriter的使用,而I\O提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理文件数据存读的函数和方法。























 3535
3535











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










