1数据结构
为了支持多种多处理器模型,linux提出了调用域及组的概念,一个调用域可以包含其它的调用域或者多个组,一个组通常包含一个或者多个cpu,组的数据结构是:
struct sched_group {
struct sched_group *next;//一个调用域可能会包含多个组,该next用于将 //sched_group串到调用域的链表上面
cpumask_t cpumask; //每个group中可能会包含一个或者多个cpu,这里的mask表 //示了该group所包含的cpu
unsigned long cpu_power;//通常是cpu的个数
};
下面是调用域的数据结构:
struct sched_domain {
struct sched_domain *parent; //调用域可以被别的调用域所包含,parent指向父调用域
struct sched_group *groups; //该调用域所包含的组
cpumask_t span;
unsigned long min_interval; //最小的时间间隔,用于检查进行负载均衡操作的时机是否到了
unsigned long max_interval; //同上
unsigned int busy_factor; //当处理器在不空闲的状态下时,进行负载均衡操作的时间间隔一般也长很多,该factor为其乘数银子
unsigned int imbalance_pct;
unsigned long long cache_hot_time;
unsigned int cache_nice_tries;
unsigned int per_cpu_gain;
int flags;
unsigned long last_balance;
unsigned int balance_interval; //负载均衡进行的时间间隔
unsigned int nr_balance_failed; //负载均衡迁移进程失败的次数
};
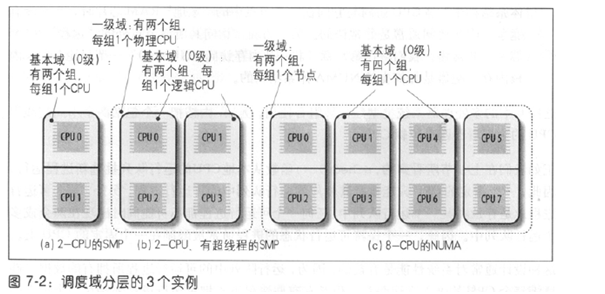
下图表现出了调用域和组之间的关系,这里我们关注2-cpu的smp和8-cpu的numa;2-cpu的SMP有一个调用域,调用域含两个组,每个组含有一个cpu;8-cpu的numa中包含两个调用域,最底层的调用域代表一个节点,每个最底层的调用域包含四个组,每个组有1个cpu,上层调用域包含两个基础的调用域。
2进行cpu负载均衡的时机
每经过一次时钟中断,scheduler_tick()就调用rebalance_tick()函数,rebalance_tick()函数会去触发cpu运行队列的负载均衡操作。该函数从最底层的调度域开始,一直到最上层的调度域进行检查,对于每个调度域都去查看是否到了调用load_balance()函数的时间,该函数会进行cpu的负载均衡操作。由当前cpu的idle状态和sched_domain的参数来确定调用load_balance()的时间间隔。
3 2-cpu smp和8-cpu numa cpu模型的调用域初始化
对调用域的初始化部分的代码在linux2.6.11版本里面是在arch_init_sched_domains()函数中,被sched_init_smp()函数所调用。
在sched.c中定义了一个数组static struct sched_group sched_group_phys[NR_CPUS];每个数组元素代表一个cpu组。另外定义了一个每cpu变量Sched.c (kernel):static DEFINE_PER_CPU(struct sched_domain, phys_domains);,系统为每个物理cpu都生成了一个调度域数据结构。
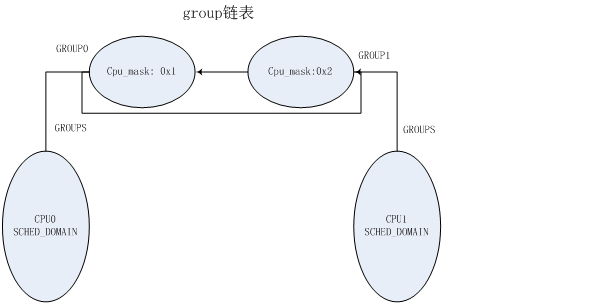
对于2-cpu smp的情形来说,其初始化后,调度域和各个组之间的关系是:
在这个里面虽然每个cpu都有个调度域的数据结构,但调度域的groups链表指向的都是同一个group链表
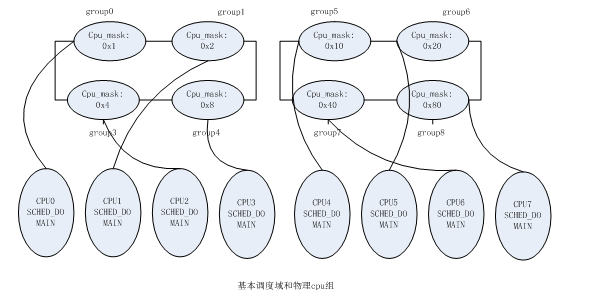
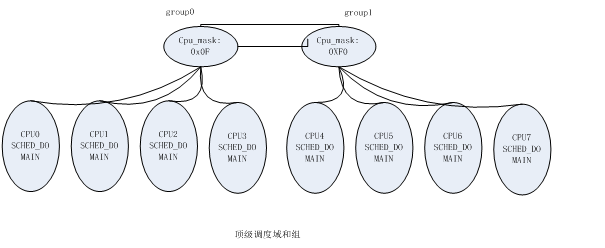
8-cpu numa的组和调度域关系:
4cpu负载均衡的源码解析
4.1rebalance_tick()
static void rebalance_tick(int this_cpu, runqueue_t *this_rq,
enum idle_type idle)
{
unsigned long old_load, this_load;
unsigned long j = jiffies + CPU_OFFSET(this_cpu);
struct sched_domain *sd;
//当前运行队列中可运行的进程数决定了当前运行队列的
//cpu_load参数
old_load = this_rq->cpu_load;
this_load = this_rq->nr_running * SCHED_LOAD_SCALE;
if (this_load > old_load)
old_load++;
//将运行队列的cpu load值设定为上一次的cpu_load和本次cpu_load的平均值
this_rq->cpu_load = (old_load + this_load) / 2;
//从该cpu所属的调度域开始,依次遍历各个更高级的调用域
for_each_domain(this_cpu, sd) {
unsigned long interval;
//在该调度域上不需要做负载均衡
if (!(sd->flags & SD_LOAD_BALANCE))
continue;
//若当前cpu不处于空闲状态的话,其调用load_balance的时间间隔会比较长
interval = sd->balance_interval;
if (idle != SCHED_IDLE)
interval *= sd->busy_factor;
//将时间间隔ms转换成jiffies
interval = msecs_to_jiffies(interval);
if (unlikely(!interval))
interval = 1;
//当前的时间戳和上次balance的时间大于其间隔的话,调用load_balance进行负载的均衡
if (j - sd->last_balance >= interval) {
//load_balance会去寻找最繁忙的cpu组中的最繁忙的cpu,将其进程迁移过来一部分
if (load_balance(this_cpu, this_rq, sd, idle)) {
/* We've pulled tasks over so no longer idle */
idle = NOT_IDLE;
}
sd->last_balance += interval;
}
}
}
4.2load_balance()
static int load_balance(int this_cpu, runqueue_t *this_rq,
struct sched_domain *sd, enum idle_type idle)
{
struct sched_group *group;
runqueue_t *busiest;
unsigned long imbalance;
int nr_moved;
spin_lock(&this_rq->lock);
schedstat_inc(sd, lb_cnt[idle]);
//查找最繁忙的cpu组
group = find_busiest_group(sd, this_cpu, &imbalance, idle);
//所有的组都是平衡的,不需要做均衡
if (!group) {
schedstat_inc(sd, lb_nobusyg[idle]);
goto out_balanced;
}
//找到最繁忙的组中最繁忙的运行队列
busiest = find_busiest_queue(group);
if (!busiest) {
schedstat_inc(sd, lb_nobusyq[idle]);
goto out_balanced;
}
//最繁忙的运行队列是当前cpu的运行队列,不需要做均衡
if (unlikely(busiest == this_rq)) {
WARN_ON(1);
goto out_balanced;
}
schedstat_add(sd, lb_imbalance[idle], imbalance);
nr_moved = 0;
if (busiest->nr_running > 1) {
double_lock_balance(this_rq, busiest);
//将imbalance个进程从最繁忙的运行队列上迁移到当前的cpu运行队列上面
nr_moved = move_tasks(this_rq, this_cpu, busiest,
imbalance, sd, idle);
spin_unlock(&busiest->lock);
}
spin_unlock(&this_rq->lock);
//nr_moved == 0,表示没有迁移成功
if (!nr_moved) {
schedstat_inc(sd, lb_failed[idle]);
sd->nr_balance_failed++;
if (unlikely(sd->nr_balance_failed > sd->cache_nice_tries+2)) {
int wake = 0;
spin_lock(&busiest->lock);
//active_balance表明该运行队列是否唤醒迁移线程来进行负载均衡,
//push_cpu记录了由哪个cpu来唤醒了其迁移线程
if (!busiest->active_balance) {
busiest->active_balance = 1;
busiest->push_cpu = this_cpu;
wake = 1;
}
spin_unlock(&busiest->lock);
//唤醒最繁忙运行队列上的迁移内核线程,对进程进行迁移
if (wake)
wake_up_process(busiest->migration_thread);
sd->nr_balance_failed = sd->cache_nice_tries;
}
if (sd->balance_interval < sd->max_interval)
sd->balance_interval++;
} else {
sd->nr_balance_failed = 0;
//进程迁移成功,重置调用域的balance_interval参数
sd->balance_interval = sd->min_interval;
}
return nr_moved;
out_balanced:
spin_unlock(&this_rq->lock);
/* tune up the balancing interval */
//不需要进行进程的迁移,适当的加大负载均衡的间隔时间,说明
//当前的负载均衡做的比较好
if (sd->balance_interval < sd->max_interval)
sd->balance_interval *= 2;
return 0;
}
4.3move_tasks()
static int move_tasks(runqueue_t *this_rq, int this_cpu, runqueue_t *busiest,
unsigned long max_nr_move, struct sched_domain *sd,
enum idle_type idle)
{
prio_array_t *array, *dst_array;
struct list_head *head, *curr;
int idx, pulled = 0;
task_t *tmp;
if (max_nr_move <= 0 || busiest->nr_running <= 1)
goto out;
//先从过期队列上进行进程的迁移,这样对硬件cache的
//影响比较小
if (busiest->expired->nr_active) {
array = busiest->expired;
dst_array = this_rq->expired;
} else {
array = busiest->active;
dst_array = this_rq->active;
}
new_array:
idx = 0;
skip_bitmap:
//从优先级最高的可运行进程开始进行迁移
if (!idx)
idx = sched_find_first_bit(array->bitmap);
else
idx = find_next_bit(array->bitmap, MAX_PRIO, idx);
if (idx >= MAX_PRIO) {
if (array == busiest->expired && busiest->active->nr_active) {
array = busiest->active;
dst_array = this_rq->active;
goto new_array;
}
goto out;
}
//找到对应优先级队列的队列末尾的进程,该进程应该是被
//放入的最早的一个进程了
head = array->queue + idx;
curr = head->prev;
skip_queue:
tmp = list_entry(curr, task_t, run_list);
curr = curr->prev;
//判断该进程能否进行迁移
if (!can_migrate_task(tmp, busiest, this_cpu, sd, idle)) {
//该优先级别的队列是否遍历完毕
if (curr != head)
goto skip_queue;
idx++;
//该优先级别的任务队列遍历完毕,去遍历下一个优先级的任务队列
goto skip_bitmap;
}
schedstat_inc(this_rq, pt_gained[idle]);
schedstat_inc(busiest, pt_lost[idle]);
//将队列迁移到本地的任务队列
pull_task(busiest, array, tmp, this_rq, dst_array, this_cpu);
pulled++;
if (pulled < max_nr_move) {
//该优先级别的队列是否遍历完毕
if (curr != head)
goto skip_queue;
idx++;
//该优先级别的任务队列遍历完毕,去遍历下一个优先级的任务队列
goto skip_bitmap;
}
out:
return pulled;
}






















 1127
1127

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








