对称矩阵及对称矩阵的压缩存储
设一个N*N的方阵A,A中任意元素Aij,当且仅当Aij == Aji(0 <= i <= N-1 && 0 <= j <= N-1),则矩阵A是对称矩阵。以矩阵的对角线为分隔,分为上三角和下三角。
压缩存储称矩阵存储时只需要存储上三角/下三角的数据,所以最多存储n(n+1)/2个数据。
对称矩阵和压缩存储的对应关系:下三角存储i>=j,SymmetricMatrix[i][j] == Array[i*(i+1)/2+j]。
 实现代码如下:
实现代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class SymmetricMatrix
{
public:
SymmetricMatrix(T * a, size_t size)
:_a(new T[size*(size+1)/2])
,_size(size*(size + 1) / 2)
,_n(size)
{
size_t index = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
if (i >= j)
{
_a[index++] = a[size*i + j];//按照一维数组的方式存入数据
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
}
~SymmetricMatrix()
{
if (_a)
{
delete[]_a;
_a = NULL;
_size = 0;
}
}
T& Access(size_t i, size_t j)
{
if (i < j)
{
swap(i, j);//当是上三角时,交换i和j
}
return _a[i*(i + 1) / 2 + j];
}
void display()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _n; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < _n; j++)
{
if (i >= j)
{
cout << _a[i*(i + 1) / 2 + j] << " ";
}
else
{
cout << _a[j*(j + 1) / 2 + i] << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
protected:
size_t _size;//存储数据的个数
T * _a;//存储之后的对称矩阵的指针
size_t _n;//对称矩阵的大小
};2.稀疏矩阵
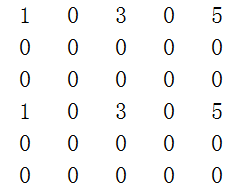
M*N的矩阵,矩阵中有效值的个数远小于无效值的个数,且这些数据的分布没有规律。
比如下面这个矩阵:
 (1)稀疏矩阵的压缩存储
(1)稀疏矩阵的压缩存储
压缩存储只存储极少数的有效数据。使用{row,col,value}三元组存储每一个有效数据,三元组按原矩阵中的位置,以行优先级先后顺序依次存放。
那么上面的矩阵压缩存储结果就是:
三元组的定义:
template<typename T>
struct Triple//三元组
{
Triple<T>::Triple()//无参的构造函数
{
}
Triple(size_t row, size_t col, T value)//构造函数
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
,_value(value)
{
}
size_t _row;//行
size_t _col;//列
T _value;//值
};压缩存储的实现代码:
template<typename T>
class SparseMatrix
{
public:
SparseMatrix()
{
}
//用vector顺序表来存储三元组的信息
SparseMatrix(T * a, size_t m, size_t n, const T & invalid)
:_rowsize(m)
,_colsize(n)
,_invalid(invalid)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)//按照二元数组的方式进行遍历
{
if (a[i*n + j] != invalid)//不是无效数据
{
Triple<T> cur(i, j, a[i*n + j]);
_a.push_back(cur);
}
}
}
}
protected:
vector <Triple<T>> _a;
size_t _rowsize;
size_t _colsize;
T _invalid;
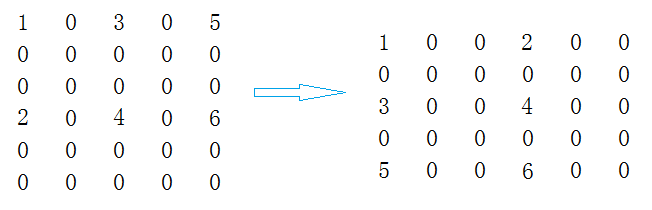
}; (2)稀疏矩阵的转置
将原矩阵的行、列对换,也就是将[i][j]和[j][i]位置上的数据对换。
普通转置(列转置)
按照原矩阵的列优先把vector中的三元组放入新的容器中,并且交换行和列的值
SparseMatrix<T> Transport()
{
assert(_a.size() < 0);
//创建新的矩阵,交换行列的值
SparseMatrix<T> ret;
ret._rowsize = _colsize;
ret._colsize = _rowsize;
ret._invalid = _invalid;
//两次循环
for (size_t i = 0; i < _colsize; i++)//按原矩阵的列扫描
{
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
if (_a[index]._col == i)
//如果三元组中的列值=i时
//交换行列的值,放入新的矩阵
{
Triple<T> tmp(_a[index]._col, _a[index]._row, _a[index]._value);
ret._a.push_back(tmp);
}
index++;
}
if (_a.size() == ret._a.size())
{
break;//两个容器的大小相同时,break
}
}
return ret;
}
用此方法可以有效的转置矩阵,我们来看一下此函数的时间复杂度:O(col * _a.size())——矩阵的列*矩阵的元素总和。
如果元素很多就会浪费很多的时间。有没有办法让两层循环变成一层循环呢?付出空间上的代价,换取时间效率。
快速转置
我们只用一层循环来遍历容器_a中所有元素,并把该元素放到指定的位置。这样我们就需要一个数组rowStar来存放第i个元素所在位置。在定义这个数组之前,我们还需要一个数组rowCount来实现统计矩阵第i行元素的数量。这样我们才能更方便的知道第i个元素应该存放的位置。
SparseMatrix<T> FastTransport()
{
assert(_a.size() > 0);
SparseMatrix<T> ret;
ret._rowsize = _colsize;//行列值互换
ret._colsize = _rowsize;
ret._invalid = _invalid;
int * rowCount = new int[_colsize];
int * rowStart = new int[_colsize];
//初始化rowCount和rowStart为0
memset(rowCount, 0, sizeof(int)* _colsize);
memset(rowStart, 0, sizeof(int) * _colsize);
//初始化
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
rowCount[_a[index]._col]++;
++index;
}
rowStart[0] = 0;
for (size_t i = 1; i < _colsize; i++)
{
rowStart[i] = rowStart[i - 1] + rowCount[i - 1];
}
ret._a.resize(_a.size());//复制顺序表_a,容量相同
index = 0;
Triple<T> tmp;
while (index < _a.size())
{
size_t rowIndex = _a[index]._col;//行数
size_t row = rowStart[rowIndex];//当前行的起始位置
//交换行和列
tmp._col = _a[index]._row;
tmp._row = _a[index]._col;
tmp._value = _a[index]._value;
ret._a[row] = tmp;//将tmp放入ret计算好的位置
rowStart[row]++;
index++;
}
delete[] rowCount;
delete[] rowStart;
return ret;
}此函数的时间复杂度为O(col + _a.size());和普通转置相比,效率提高了很多。
最后,附上完整代码(稀疏矩阵):
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
struct Triple//三元组
{
Triple<T>::Triple()//无参的构造函数
{
}
Triple(size_t row, size_t col, T value)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
,_value(value)
{
}
size_t _row;//行
size_t _col;//列
T _value;//值
};
template<typename T>
class SparseMatrix
{
public:
SparseMatrix()//无参的构造函数
{
}
//用vector顺序表来存储三元组的信息
SparseMatrix(T * a, size_t m, size_t n, const T & invalid)
:_rowsize(m)
,_colsize(n)
,_invalid(invalid)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (a[i*n + j] != invalid)
{
Triple<T> cur(i, j, a[i*n + j]);
_a.push_back(cur);
}
}
}
}
void Display()//打印矩阵
{
size_t index = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _rowsize; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < _colsize; j++)
{
if ((index < _a.size()) && _a[index]._row == i&&_a[index]._col == j)
{
cout << _a[index]._value << " ";
index++;
}
else
{
cout << _invalid << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
//普通转置
SparseMatrix<T> Transport()
{
assert(_a.size() 》 0);
//创建新的矩阵,交换行列的值
SparseMatrix<T> ret;
ret._rowsize = _colsize;
ret._colsize = _rowsize;
ret._invalid = _invalid;
//两次循环
for (size_t i = 0; i < _colsize; i++)//按原矩阵的列扫描
{
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
if (_a[index]._col == i)
//如果三元组中的列值=i时
//交换行列的值,放入新的矩阵
{
Triple<T> tmp(_a[index]._col, _a[index]._row, _a[index]._value);
ret._a.push_back(tmp);
}
index++;
}
if (_a.size() == ret._a.size())
{
break;//两个容器的大小相同时,break
}
}
return ret;
}
//快速转置
SparseMatrix<T> FastTransport()
{
assert(_a.size() > 0);
SparseMatrix<T> ret;
ret._rowsize = _colsize;//行列值互换
ret._colsize = _rowsize;
ret._invalid = _invalid;
int * rowCount = new int[_colsize];
int * rowStart = new int[_colsize];
//初始化rowCount和rowStart为0
memset(rowCount, 0, sizeof(int)* _colsize);
memset(rowStart, 0, sizeof(int) * _colsize);
//初始化
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
rowCount[_a[index]._col]++;
++index;
}
rowStart[0] = 0;
for (size_t i = 1; i < _colsize; i++)
{
rowStart[i] = rowStart[i - 1] + rowCount[i - 1];
}
ret._a.resize(_a.size());//复制顺序表_a,容量相同
index = 0;
Triple<T> tmp;
while (index < _a.size())
{
size_t rowIndex = _a[index]._col;//行数
size_t row = rowStart[rowIndex];//当前行的起始位置
//交换行和列
tmp._col = _a[index]._row;
tmp._row = _a[index]._col;
tmp._value = _a[index]._value;
ret._a[row] = tmp;//将tmp放入ret计算好的位置
rowStart[row]++;
index++;
}
delete[] rowCount;
delete[] rowStart;
return ret;
}
protected:
vector <Triple<T>> _a;//容器
size_t _rowsize;//行
size_t _colsize;//列
T _invalid;//非法值
};
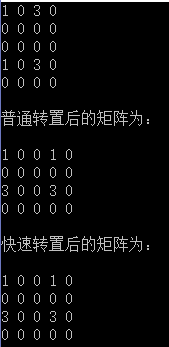
void Test()
{
int array[5][4] =
{
{ 1, 0, 3, 0, },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, },
{ 1, 0, 3, 0, },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, },
};
SparseMatrix<int> sm((int*)array, 5, 4, 0);
sm.Display();
SparseMatrix<int> sm1;
sm1 = sm.FastTransport();
cout << "转置后的矩阵为: " << endl << endl;
sm1.Display();
}本文出自 “不断进步的空间” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://10824050.blog.51cto.com/10814050/1765046







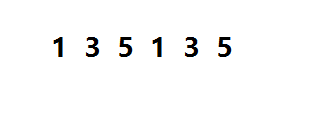















 307
307

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








