参考链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/9361915
https://www.zhihu.com/question/26408259/answer/123230350
https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/2-2-A-q-learning/
ε-greedy是选择行为的策略,如ε=0.9,则按照90%的概率利用最优Q值选择行为,10%的概率随机选择行为,这样做的好处是可能找到一种新途径的最优解。
γ即衰减系数discount factor,这个参数决定了未来奖励在学习中的重要性,如果γ=0,模型将学习不到任何未来的奖励信息,变得短视,只关注当前的利益;如果γ>=1,期望价值被不断累加并没有衰减,这样期望价值可能会发散。γ一般设为一个比1稍微小的数。
α是学习率,决定了新货取得样本信息覆盖之前掌握到的信息比率,通常设为比较小的值,保证学习过程的稳定,同时确保收敛性,α越大,原来训练结果的保留就越少。
实例1:
在-----T中寻找T的位置,随机产生在-的位置,到达T即为成功。
运行结果:产生Q表
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import time
n_status = 6 # -----T,共6个位置
actions = ['left', 'right'] # 动作
epsilon = 0.9 # ε
alpha = 0.1 # 学习率α
gamma = 0.9 # 衰减系数γ
max_episodes = 13 # 13次寻找的经历
# 初始化Q表
Q_table = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((n_status, len(actions))), columns=actions)
def choose_action_by_epsilon_greedy(status):
# 采用ε-greedy算法,当前可供选择的行动期望价值都为0时,随机选择,
# 这样可以避免初始阶段都使用一个动作造成无法收敛
if random.random() < epsilon:
status_action = Q_table.iloc[status, :]
status_action = status_action.reindex(np.random.permutation(status_action.index))
action_name = status_action.idxmax()
else:
action_name = np.random.choice(actions)
return action_name
def get_environment_feedback(s, action_name):
if action_name == 'right':
# 只有到终点才会得到奖励
r = 1 if s == n_status-2 else 0
s_ = s + 1
else:
r = 0
s_ = s if s == 0 else s-1
return s_, r
def display_status(s, episode, steps):
if s == n_status-1:
print('\r{}'.format('Episode: %d, total_steps: %d' % (episode, steps)))
time.sleep(1)
else:
status_list = ['-'] * (n_status-1) + ['T']
status_list[s] = 'o'
print('\r{}'.format(''.join(status_list)), end='')
time.sleep(0.3)
# Q-learning过程
def Q_learning():
for episode in range(max_episodes):
s = np.random.choice(range(n_status-1))
step = 0
display_status(s, episode, step)
while s != n_status-1:
a = choose_action_by_epsilon_greedy(s)
s_, r = get_environment_feedback(s, a)
Q_old = Q_table.loc[s, a]
Q_new = r + gamma * Q_table.iloc[s_, :].max()
Q_table.loc[s, a] = (1-alpha)*Q_old + alpha*Q_new
s = s_
step = step + 1
display_status(s, episode, step)
return Q_table
print(Q_learning())实例二:在迷宫中寻找宝藏,规避陷阱
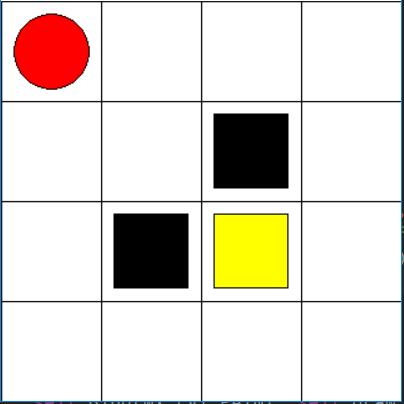
红色圆圈为智能体,黑色方格为陷阱,黄色为宝藏。(0,0)为起点,走到黑色方格,得到奖励-1,并重新开始;走到黄色方格,得到奖励+1,并重新开始。
程序使用wxPython库实现强化学习过程的同步可视化过程,此机制主要参考wxPython的Timer类和python的yield结合使用。
参考链接:http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390349402 Timer类和yield结合使用
yield参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/coder2012/p/4990834.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/BigFishFly/p/6337081.html
程序中Maze类为迷宫可视化实现,QLearning为强化学习流程,具体说明参见程序:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import wx
unit = 80 # 一个方格所占像素
maze_height = 4 # 迷宫高度
maze_width = 4 # 迷宫宽度
class Maze(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, parent):
# +16和+39为了适配客户端大小
super(Maze, self).__init__(parent, title='maze', size=(maze_width*unit+16, maze_height*unit+39))
self.actions = ['up', 'down', 'left', 'right']
self.n_actions = len(self.actions)
# 按照此元组绘制坐标
self.coordinate = (0, 0)
self.rl = QLearning(self.actions)
self.generator = self.rl.RL_Q_learning()
# 使用EVT_TIMER事件和timer类可以实现间隔多长时间触发事件
self.timer = wx.Timer(self) # 创建定时器
self.timer.Start(200) # 设定时间间隔
self.Bind(wx.EVT_TIMER, self.build_maze, self.timer) # 绑定一个定时器事件
self.Show(True)
def build_maze(self, event):
# yield在生成器运行结束后再次调用会产生StopIteration异常,
# 使用try_except语句避免出现异常并在异常出现(程序运行结束)时关闭timer
try:
self.generator.send(None) # 调用生成器更新位置
except Exception:
self.timer.Stop()
self.coordinate = self.rl.status
dc = wx.ClientDC(self)
self.draw_maze(dc)
def draw_maze(self, dc):
dc.SetBackground(wx.Brush('white'))
dc.Clear()
for row in range(0, maze_height*unit+1, unit):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = 0, row, maze_height*unit, row
dc.DrawLine(x0, y0, x1, y1)
for col in range(0, maze_width*unit+1, unit):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = col, 0, col, maze_width*unit
dc.DrawLine(x0, y0, x1, y1)
dc.SetBrush(wx.Brush('black'))
dc.DrawRectangle(unit+10, 2*unit+10, 60, 60)
dc.DrawRectangle(2*unit+10, unit+10, 60, 60)
dc.SetBrush(wx.Brush('yellow'))
dc.DrawRectangle(2*unit+10, 2*unit+10, 60, 60)
dc.SetBrush(wx.Brush('red'))
dc.DrawCircle((self.coordinate[0]+0.5)*unit, (self.coordinate[1]+0.5)*unit, 30)
class QLearning(object):
def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, epsilon_greedy=0.9):
self.actions = actions
self.alpha = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon = epsilon_greedy
self.max_episode = 10
self.id_status = {} # id和位置元组的字典,因为DataFrame中直接以元组为下标无法索引行
self.status = (0, 0) # 用于记录在运行过程中的当前位置,然后提供给Maze对象
# 本次设定未知Q表中的状态,所以使用check_status_exist函数将状态添加到Q表
self.Q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float32)
def choose_action_by_epsilon_greedy(self, status):
self.check_status_exist(status)
if random.random() < self.epsilon:
status_action = self.Q_table.loc[self.id_status[status], :]
status_action = status_action.reindex(np.random.permutation(status_action.index))
action_name = status_action.idxmax()
else:
action_name = np.random.choice(self.actions)
return action_name
def get_environment_feedback(self, s, action_name):
is_terminal = False
if action_name == 'up':
if s == (2, 3):
r = 1
is_terminal = True
elif s == (1, 3):
r = -1
is_terminal = True
else:
r = 0
s_ = (s[0], np.clip(s[1]-1, 0, 3))
elif action_name == 'down':
if s == (2, 0) or s == (1, 1):
r = -1
is_terminal = True
else:
r = 0
s_ = (s[0], np.clip(s[1]+1, 0, 3))
elif action_name == 'left':
if s == (3, 1):
r = -1
is_terminal = True
elif s == (3, 2):
r = 1
is_terminal = True
else:
r = 0
s_ = (np.clip(s[0]-1, 0, 3), s[1])
else:
if s == (1, 1) or s == (0, 2):
r = -1
is_terminal = True
else:
r = 0
s_ = (np.clip(s[0]+1, 0, 3), s[1])
return r, s_, is_terminal
def update_Q_table(self, s, a, r, s_, is_terminal):
if is_terminal is False:
self.check_status_exist(s_)
q_new = r + self.gamma * self.Q_table.loc[self.id_status[s_], :].max()
else:
q_new = r
q_old = self.Q_table.loc[self.id_status[s], a]
self.Q_table.loc[self.id_status[s], a] = (1 - self.alpha) * q_old + self.alpha * q_new
def check_status_exist(self, status):
if status not in self.id_status.keys():
id = len(self.id_status)
self.id_status[status] = id
self.Q_table = self.Q_table.append(pd.Series([0]*len(self.actions), index=self.actions, name=id))
def RL_Q_learning(self):
# 使用yield函数实现同步绘图
for episode in range(self.max_episode):
s = (0, 0)
self.status = s
yield
is_terminal = False
while is_terminal is False:
a = self.choose_action_by_epsilon_greedy(s)
r, s_, is_terminal = self.get_environment_feedback(s, a)
self.update_Q_table(s, a, r, s_, is_terminal)
s = s_
self.status = s
yield
print(self.Q_table)
print(self.id_status)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = wx.App()
Maze(None)
app.MainLoop()








 本文通过两个实例介绍强化学习中的Q学习算法。实例一:在一维环境中寻找目标位置T,运用ε-greedy策略和Q-learning算法进行学习,最终得到Q表。实例二:在一个迷宫环境中寻找宝藏并避开陷阱,采用wxPython实现强化学习过程的可视化。
本文通过两个实例介绍强化学习中的Q学习算法。实例一:在一维环境中寻找目标位置T,运用ε-greedy策略和Q-learning算法进行学习,最终得到Q表。实例二:在一个迷宫环境中寻找宝藏并避开陷阱,采用wxPython实现强化学习过程的可视化。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








