日期:2022年2月22日
出处:
黑马程序员SpringBoot2全套视频教程,springboot零基础到项目实战(spring boot2完整版)
黑马程序员SpringBoot2全套视频教程,springboot零基础到项目实战(spring boot2完整版)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
正文
yaml配置文件语法
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进时不允许使用 Tab 键,只允许使用空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,但同级元素必须左侧对齐
- 大小写敏感
- :号和-号后面也必须有空格
yaml支持以下三种数据结构
- 对象:键值对的集合
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值
- 字面量:单个的、不可拆分的值
有关yaml配置文件的细节
1.想要实现读取配置文件的一整块内容
首先,先简单写一个yaml配置文件
datasource: driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc.mysql://localhost/springboot_db username: root password: root123
然后再写一个实体类MyDataSource
需要注意的是这里的两个注解@Component和@ConfigurationProperties
package com.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//1.定义数据模型防撞yaml文件中对应的数据
//2.定义为spring管控的bean
@Component
//3.指定加载的数据
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")
public class MyDataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDateSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
然后在主程序中稍作修改
package com.springboot.controller;
import com.springboot.MyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//Rest模式,是一种书写风格。是设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径(网址)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private MyDataSource myDataSource;
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("springboot is running...");
System.out.println(myDataSource);
return "springboot is running...";
}
}
运行成功!

2.读取yaml数据中不同形式的单一数据
首先,在配置文件中写出各种形式的数据
server:
port: 81
country: China
province: Zhejiang
city: jinhua
user:
name: Jack
age: 20
likes:
- game
- music
- sleep
- hiphop
baseDir: C:\\windows
# 使用${属性名}引用数据
tempDir1: ${baseDir}\temp
# 使用引号包裹的字符出,其中的转义字符可以生效
tempDir2: "${baseDir}\temp"
然后修改主程序进行测试
package com.springboot.controller;
import com.springboot.MyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//Rest模式,是一种书写风格。是设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径(网址)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
//读取yml数据中的单一数据
@Value("${country}")
private String Country;
@Value("${user.age}")
private int Age;
@Value("${likes[2]}")
private String Likes;
@Value("${tempDir1}")
private String temp1;
@Value("${tempDir2}")
private String temp2;
//使用自动装配将所有的数据封装到一个对象Environment中
@Autowired
private Environment env;
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("springboot is running...");
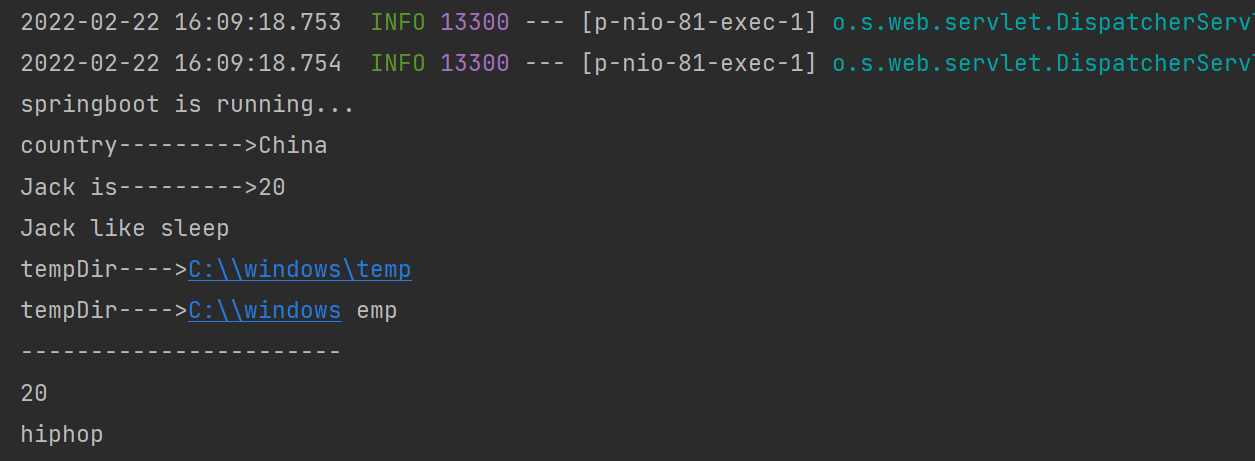
System.out.println("country--------->"+Country);
System.out.println("Jack is--------->"+Age);
System.out.println("Jack like "+Likes);
System.out.println("tempDir---->"+temp1);
System.out.println("tempDir---->"+temp2);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
System.out.println(env.getProperty("user.age"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("likes[3]"));
return "springboot is running...";
}
}
测试结果如图
这里涵盖内容较多需慢慢阅读
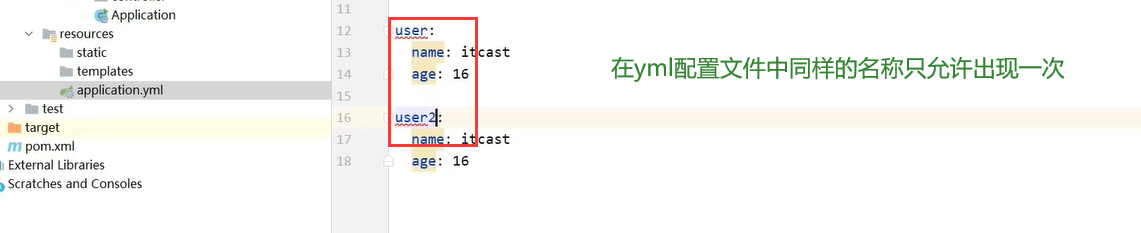
发现问题及解决方案
总结
读取整块配置文件内容用@ConfigurationProperties单个内容用@Value
他们俩的区别与联系:
@Value 和 @ConfigurationProperties 注解都能读取配置文件中的属性值并绑定到 JavaBean 中,但两者存在以下不同。
1. 使用位置不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:标注在 JavaBean 的类名上;
- @Value:标注在 JavaBean 的属性上。
2. 功能不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:用于批量绑定配置文件中的配置;
- @Value:只能一个一个的指定需要绑定的配置。
3. 松散绑定支持不同
@ConfigurationProperties:支持松散绑定(松散语法),例如实体类 Person 中有一个属性为 lastName,那么配置文件中的属性名支持以下写法:
- person.firstName
- person.first-name
- person.first_name
- PERSON_FIRST_NAME
@Vaule:不支持松散绑定。
4. SpEL 支持不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:不支持 SpEL 表达式;
- @Value:支持 SpEL 表达式。
5. 复杂类型封装
- @ConfigurationProperties:支持所有类型数据的封装,例如 Map、List、Set、以及对象等;
- @Value:只支持基本数据类型的封装,例如字符串、布尔值、整数等类型。
6. 应用场景不同
@Value 和 @ConfigurationProperties 两个注解之间,并没有明显的优劣之分,它们只是适合的应用场景不同而已。
- 若只是获取配置文件中的某项值,则推荐使用 @Value 注解;
- 若专门编写了一个 JavaBean 来和配置文件进行映射,则建议使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解。





















 6480
6480











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








