一、静态添加Fragment
新建一个项目FragmentDemo1,
添加一个布局:fragment1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#0078ff"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment1"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>添加另一个布局:fragment2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffff00"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment2"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>新建一个类Fragment1,集成Fragment
package com.example.xm.fragmentdemo1;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* Created by xm on 2016/4/18.
*/
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
/*3个参数
1,Fragment需要加载的布局文件
2,加载layout的父ViewGroup
3,false:不返回父ViewGroup
* */
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1,container,false);
return view;
}
}
Fragment2类:
package com.example.xm.fragmentdemo1;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* Created by xm on 2016/4/18.
*/
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
/*3个参数
1,Fragment需要加载的布局文件
2,加载layout的父ViewGroup
3,false:不返回父ViewGroup
* */
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2,container,false);
return view;
}
}
主Activity的布局文件activity_main.xml,,在里面加入两个Fragment的引用,使用android:name前缀来引用具体的Fragment:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.example.xm.fragmentdemo1.Fragment1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:name="com.example.xm.fragmentdemo1.Fragment2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.example.xm.fragmentdemo1;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
/*
* 此实验是简单的Fragment的静态添加
* */
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
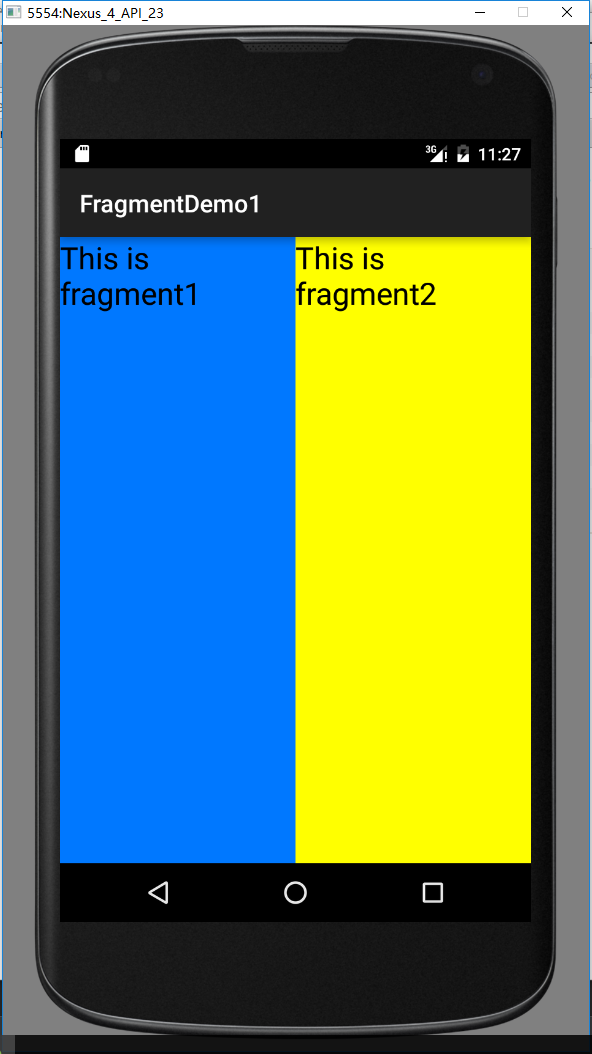
运行效果:
二、动态添加Fragment
动态的添加Fragment,可以使程序的页面就可以定制更加的多样化
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_show_fragment1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="显示Fragment1"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_show_fragment2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="显示Fragment2"
/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fragment_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
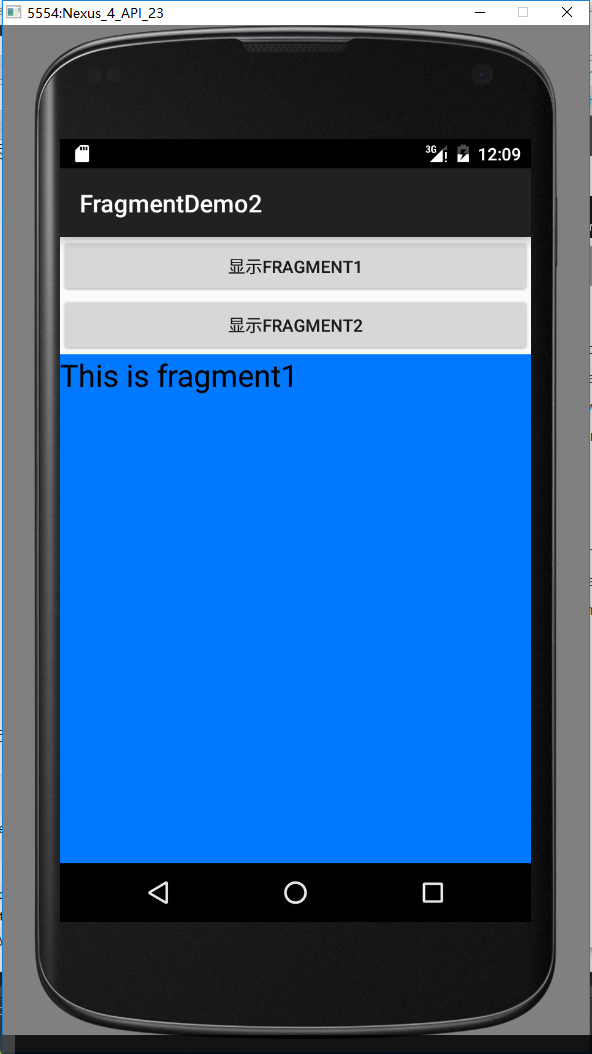
要实现的效果:
在MainActivity.java中:
package com.example.xm.fragmentdemo2;
/*
* 动态的添加Fragment,可以使程序的页面就可以定制更加的多样化
* */
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_show_fragment1);
button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Fragment1 fragment1 = new Fragment1();
//1,获取到FragmentManager,通过getFragmentManager获取
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
//2,开启一个事务,通过调用beginTransaction方法开启
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//3,向容器内加入Fragment,一般使用add或者replace方法实现,需要传入容器的id和Fragment的实例
transaction.add(R.id.fragment_container,fragment1);
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
//4,提交事务,调用的是commit方法提交
transaction.commit();
}
});
Button button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_show_fragment2);
button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Fragment2 fragment2 = new Fragment2();
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.add(R.id.fragment_container,fragment2);
transaction.commit();
}
});
}
}
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








