一、SQL
一、数据库环境搭建:
官网:http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/windows/
1.安装mysql-installer-community-5.6.26.0.msi:
期间设置密码
注:可能需要先安装.NET(LINGZHUO21-3_dotNetFx40_Full_x86_x64.exe)
2、使用界面操作,需安装MySQL-Front_V5.3.4.214_Setup.1435658094.exe:
一直next即可。
详细见:http://pan.baidu.com/disk/home#path=%252F%25E9%25A2%2586%25E5%258D%2593%25E5%259F%25B9%25E8%25AE%25AD%252FJAVA%252F%25E9%259C%2580%25E8%25A6%2581%25E7%259A%2584%25E8%25BD%25AF%25E4%25BB%25B6%25E5%258C%2585%252FSQL
二、结构:
DATABASE 数据库
TABLE 表
字段 属性 主键(一个TABLE中不能重复,唯一标示一条记录)
外键(一个表中数据持有的别的表的主键)
auto_increment(自增长)
注:Mysql忽略大小写。
四、语句
字符varchar(多少位)
BINARY 区别大小写,必须写在not null前面,
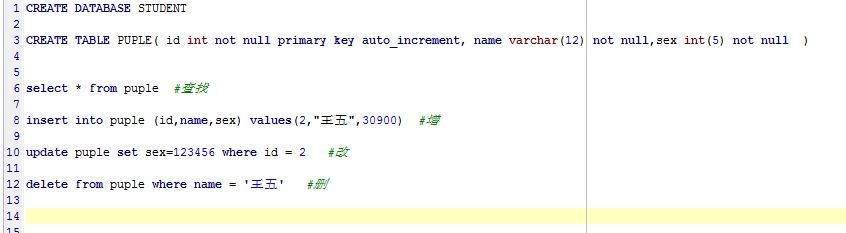
select * from user where binary name=’”+name+”’ and password = ‘”+password+”’”); //区分大小写
二、单例模式:
1.定义
单例设计模式:(只能有一个对象)
1.将构造器私有化
2.利用公开、静态的方法来获得构造器。(加锁)
3.私有的静态属性。
范例1:用户注册与登录:
//连接数据库的类:
步骤:
1)加载JDBC-ODBC桥驱动程序: Class.forName(“完整类名”);
2)连接数据库 :
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(“jdbc:odbc:数据库完整名称,用户,密码”);
3)创建SQL语句实例对象:
Statement state = con.creatStatement();
/*单例模式:
*
*
* */
public class SqlManager {
private Statement state; //需要获得的就state
public Statement getState() {//获得state的方法
return state;
}
private static SqlManager manager;//3.静态方法需要调用静态属性,所以manager必须是静态的
public static synchronized SqlManager Instance(){ //2.获得构造器方法<1>.避免多线程时创建多个对象,使用同步锁,仅一个线程进入<2>.静态化使类直接调用此方法
if(manager==null){
manager = new SqlManager(); //对manager初始化
}
return manager;
}
private SqlManager(){ //1.构造器私有化,使其他类不能直接访问它
String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; //在加载的包里,找好路径
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student"; //注:连接数据库表的名称是student(连接的是数据库的名称)
String user = "root";
String password = "3649962";
//1.加载驱动
try {
Class.forName(driver);
//2.与数据库建立连接(注:一定导入的是java.sql包)
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
if(!conn.isClosed()){
//3.数据库操作类
System.out.println("连接成功!");
state = conn.createStatement(); //将其改为成员变量
//仅此需要改:创建一个用户表
String creatTable = "create table if not exists user(id int not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20) not null,password varchar(30) not null)";
state.execute(creatTable);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}注册类:
public class Register extends JFrame {
private JPanel contentPane;
private JTextArea textAreausername;//1.将text变为成员变量,方便获得其中数据
private JTextArea textAreapassword;
private String username;
private String password;
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
Register frame = new Register();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame.
*/
public Register() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100, 100, 477, 323);
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
textAreausername = new JTextArea();
textAreausername.setBounds(138, 31, 180, 50);
contentPane.add(textAreausername);
textAreapassword = new JTextArea();
textAreapassword.setBounds(138, 104, 188, 57);
contentPane.add(textAreapassword);
JButton btnNewButton = new JButton("确定");
btnNewButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { //2.点击事件
String name = textAreausername.getText();
textAreausername.setText("");
String word = textAreapassword.getText();
textAreapassword.setText("");
if(isRegex(name,"\\w{1,}")&isRegex(word,"\\w{6,}")){
username = name;
password = word;
Statement state = SqlManager.Instance().getState();//获得实例
System.out.println("获得实例");
//先判断是否有这个用户
/*方法二:String sql = "select * from user where name='"+username+"' ";
* ResultSet set = state.executeQuery(sql);//查找和username相同的name执行
* set.last();//1.将游标放最后
int num = set.getRow();//判断这行是第几行,
*
* */
String sql = "select count(*) from user where name='"+username+"' ";
try {
ResultSet set = state.executeQuery(sql);//执行
set.first();//1.将游标放第一
int num = set.getInt(1);//用上面介绍的getRow()方法
if(num>0){
System.out.println("用户已存在");
}else{//插入
String insert = "insert into user(name,password) values('"+username+"','"+password+"')";
state.execute(insert);
System.out.println("注册成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
System.out.println("不符合规则,请重新输入!");
}
}
});
btnNewButton.setBounds(262, 203, 64, 57);
contentPane.add(btnNewButton);
JLabel label = new JLabel("\u7528\u6237\u540D\uFF1A");
label.setBounds(38, 49, 78, 25);
contentPane.add(label);
JLabel label_1 = new JLabel("\u5BC6\u7801\uFF1A");
label_1.setBounds(38, 123, 78, 25);
contentPane.add(label_1);
}
public boolean isRegex(String str,String regex){ //正则表达式
return str.matches(regex);
}
}登录类:
public class SignIn extends JFrame {
private JPanel contentPane;
private JTextArea textAreausername;//1.变成成员变量
private JTextArea textAreapassword;
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
SignIn frame = new SignIn();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame.
*/
public SignIn() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100, 100, 500, 364);
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
textAreausername = new JTextArea();
textAreausername.setBounds(133, 21, 216, 58);
contentPane.add(textAreausername);
textAreapassword = new JTextArea();
textAreapassword.setBounds(133, 113, 221, 58);
contentPane.add(textAreapassword);
JButton btnNewButton = new JButton("登录");
btnNewButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String user_name = textAreausername.getText();//2获取信息
String password = textAreapassword.getText();
Statement state = SqlManager.Instance().getState(); //3.获得数据库对象
try {
ResultSet set = state.executeQuery("select * from user where name='"+user_name+"' and password = '"+password+"'");
set.last();
int num = set.getRow();//判断是否有符合条件的记录
System.out.println(num);
if(num==1){
System.out.println("恭喜您,已经登录!");
textAreausername.setText("");
textAreapassword.setText("");
}else if(num==0){
System.out.println("请先注册!");
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
btnNewButton.setBounds(243, 217, 82, 70);
contentPane.add(btnNewButton);
JLabel lblNewLabel = new JLabel("\u7528\u6237\u540D\uFF1A");
lblNewLabel.setBounds(10, 39, 90, 30);
contentPane.add(lblNewLabel);
JLabel lblNewLabel_1 = new JLabel("\u5BC6\u7801\uFF1A");
lblNewLabel_1.setBounds(10, 128, 90, 30);
contentPane.add(lblNewLabel_1);
}
}三、prepareStatement 预编译
SQL语句被预编译并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。然后可以使用此对象多次高效地执行该语句。
步骤:
1.建立连接后,有了Connection
2.con.con.prepareStatement(“select * from user where name = ? and password = ?”);
3.使用2中返回的prepareStatement的类型,用其getString方法,添加值,1代表第一个?,依次类推
4.执行:state.executeQuery();
注:若要增加用户还需要判断num值,进行select操作。
Connection con = SqlManager.Instance().getConn();//获得实例
System.out.println("获得实例");
try {
if(!con.isClosed()){
PreparedStatement state = (PreparedStatement) con.prepareStatement("select * from user where name = ? and password = ?");
state.setString(1,username );//设置第一个?的参数是username
state.setString(2, password);//设置第二个参数为password
ResultSet set = state.executeQuery();
set.last();
int num = set.getRow();
System.out.println(num);
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}相比Statement而言,使登录时避免了 or ,的混乱登录。
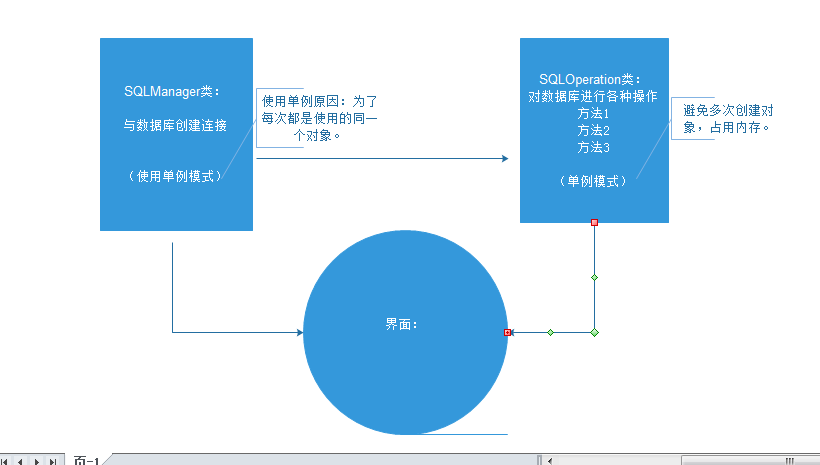
四、MVC模式:
使用的几种模式:mvc模式,单例模式,工厂模式。
MVC模式:将所有的操作方法写到一个类中,使用时进行调用即可:
范例:这里仅在类中写了登录的方法:
public class SQLOperation {
private static SQLOperation operation;
/**获得实例的方法
*
* */
public static synchronized SQLOperation Instance(){
if(operation == null){
operation = new SQLOperation();
}
return operation;
}
private SQLOperation(){
}
/**是否登录的方法
* 登录成功则返回true
*
*
* */
boolean isSignIn (String user_name,String password){
int num = 0;
Statement state = SqlManager.Instance().getState(); //3.获得数据库对象
try {
ResultSet set = state.executeQuery("select * from user where name='"+user_name+"' and password = '"+password+"'");
set.last();
num = set.getRow();//判断是否有符合条件的记录
System.out.println(num);
if(num==1){
System.out.println("恭喜您,已经登录!");
}else if(num==0){
System.out.println("请先注册!");
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return num == 1;
}
}//使用时,创建类对象直接调用。判断是否登录成功。
boolean issignIn = SQLOperation.Instance().isSignIn(user_name, password);图解:
五、补充:
1.数据库的种类:
ORACLE(甲骨文)、DB2、SQL Server、Sybase、Informix、MySQL、VF、 Access等。
2.mysql的优势:
快速,轻量级,易于扩展,开源免费,跨平台。
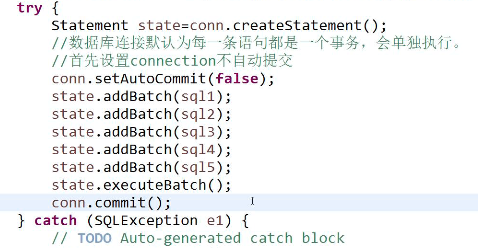
六、事务:
事务:一组不可拆分的操作。
con.setAutoCommit(false);//设置不自动提交,是Connection接口中的方法
con.commit();该方法表示:提交
范例:
public class Test_Commit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = SqlManager.Instance().getConn();
try {
Statement state = con.createStatement();
con.setAutoCommit(false);
state.execute("insert into user (name,password) values('zhangsan3','12434344')");
state.execute("insert into user (name,password) values('lisi2','1244344')");
state.execute("insert into user (name,password) values('wangwu1','12434344')");
state.execute("insert into user (name,password) values('zhshikan2','987344')");
state.execute("insert into user (name,password) values('zhousan3','12439844')");
con.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}解释:当execute中有一条有错误时,其他的execute都不能执行。
七、addBatch方法
1.使用:void addBatch(String sql)
throws SQLException
将给定的 SQL 命令添加到此 Statement 对象的当前命令列表中。通过调用方法 executeBatch 可以批量执行此列表中的命令。
2.优点:
批量执行,效率更高
3、范例:





















 3072
3072











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








