背景
在ffplay::read_thread执行的线程中,首先会通过avformat_open_input完成对媒体资源的数据读取、格式探查、demuxer匹配等行为:
- 针对媒体资源文件初始化对应的URLProtocol,比如ff_http_protocol,之后还会再生成一个相应的lower protocol,对应http的媒体资源就是ff_tcp_protocol。随后,由URLProtocol完成与服务读写数据的行为。
- 随后,进行探查行为。根据资源后缀名匹配对应的demuxer。例如,mp3资源对应ff_mp3_demuxer解封装器,而它属于AVInputFormat类型的实例。所以,在avformat_open_input的过程中,很重要的一步是生成AVInputFormat。
- 读取id3v2信息。该信息只存在于mp3媒体资源中,用于封装例如专辑album之类的信息
- 读取头部信息
本文主要以mp3媒体资源为例,探究ffmpeg是如何对mp3进行解封装的。
mp3 : 一种音频文件格式,由id3v2+数据部分+id3v1构成,其中数据采用mpeg协议进行压缩
demux : 解封装. 以ffmpeg的视角来看,就是从媒体文件中抽取出AVPacket的过程
mpeg协议 : 在解码之前,mp3的数据部分采用mpeg协议进行压缩,经过ffmpeg解码才会还原为pcm原始音频数据
mp3媒体资源的组成结构

普遍支持的格式是id3v2.3,id3v2.3一般由1个标签头+N*标签帧构成。
函数调用流程图
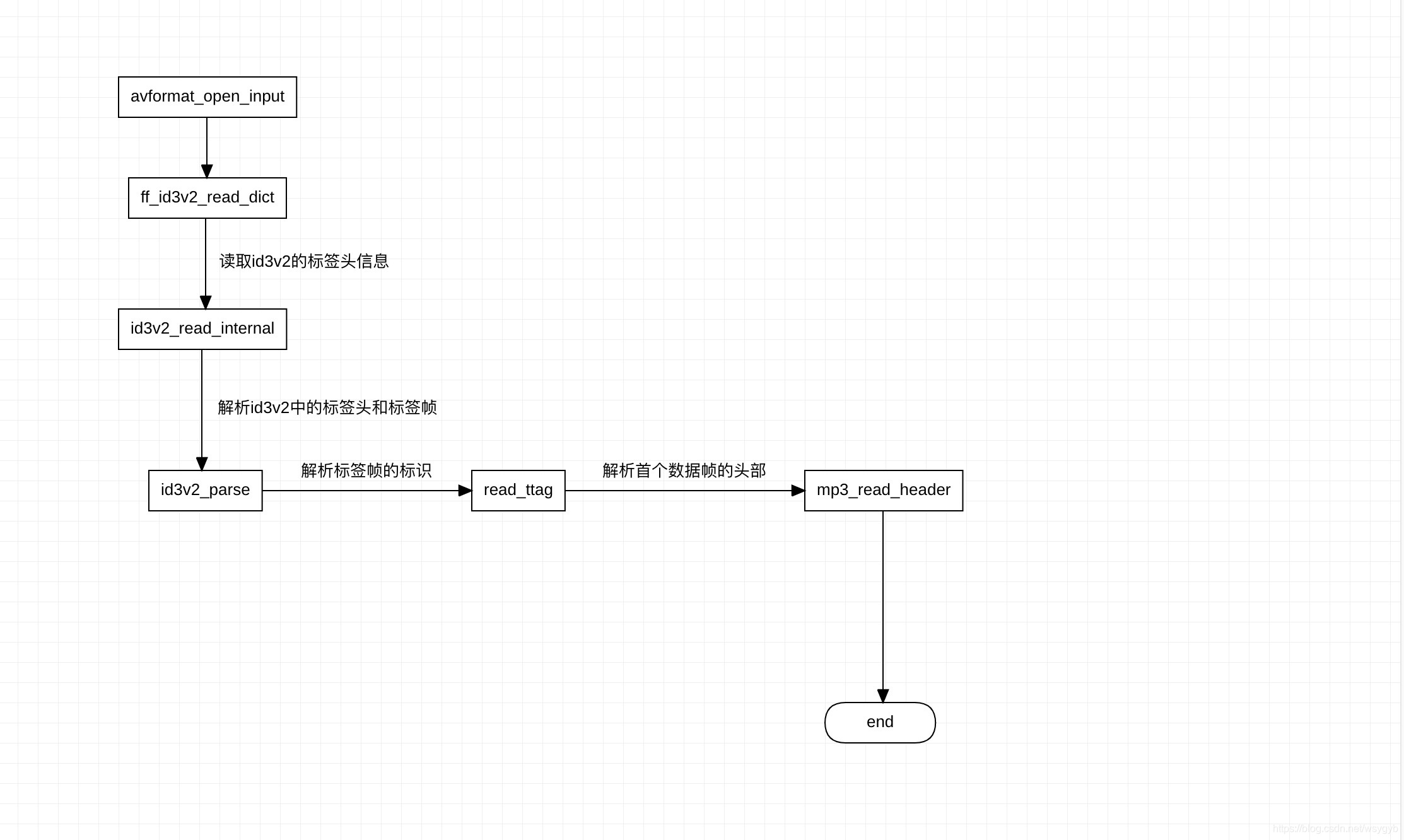
ff_id3v2_read_dict
在avformat_open_input的调用流程中,自匹配完demuxer之后如果媒体资源对应的是mp3音频则通过id3v2_read_internal开始读取id3v2信息,否则在后续的read_header中读取头部信息。id3v2_read_internal函数如下所示:
// ID3v2_DEFAULT_MAGIC-> "ID3"
// max_search_size == 0
static void id3v2_read_internal(AVIOContext *pb, AVDictionary **metadata,
AVFormatContext *s, const char *magic,
ID3v2ExtraMeta **extra_meta, int64_t max_search_size)
{
int len, ret;
//ID3v2_HEADER_SIZE -> 10,标签头的大小
uint8_t buf[ID3v2_HEADER_SIZE];
int found_header;
int64_t start, off;
if (max_search_size && max_search_size < ID3v2_HEADER_SIZE)
return;
start = avio_tell(pb);
do {
/* save the current offset in case there's nothing to read/skip */
off = avio_tell(pb)
//读取mp3文件的标签头, ID3v2_HEADER_SIZE -> 10
ret = avio_read(pb, buf, ID3v2_HEADER_SIZE);
//magic -> "ID3",mp3的ID3V2标签头要求必须是"ID3"开头
found_header = ff_id3v2_match(buf, magic);
//magic 匹配
if (found_header) {
//标签大小
/* parse ID3v2 header */
len = ((buf[6] & 0x7f) << 21) |
((buf[7] & 0x7f) << 14) |
((buf[8] & 0x7f) << 7) |
(buf[9] & 0x7f);
//解析id3v2的标签头+标签帧
id3v2_parse(pb, metadata, s, len, buf[3], buf[5], extra_meta);
} else {
//如果读取到的是数据部分,将指针移动到上一次帧结束的对方
avio_seek(pb, off, SEEK_SET);
}
} while (found_header);//如果一直找到id3v2的header
//设置键值对,把ff_id3v2_34_metadata_conv的kv赋值大奥metadata
ff_metadata_conv(metadata, NULL, ff_id3v2_34_metadata_conv);
ff_metadata_conv(metadata, NULL, id3v2_2_metadata_conv);
ff_metadata_conv(metadata, NULL, ff_id3v2_4_metadata_conv);
merge_date(metadata);
}
- 首先,读取id3v2的标签头,标签头的大小为10字节.起始必须为"ID3".
- 随后,获取标签头的size信息,这个保存在标签头的高四字节中
id3v2的标签头结构
char Header[3]; //必须为“ID3”否则认为标签不存在
char Ver; //版本号ID3V2.3 就记录3
char Revision; //副版本号此版本记录为0
char Flag; //标志字节,只使用高三位,其它位为0
char Size[4]; //标签大小
};
id3v2_parse
id3v2_parse函数主要用于解析id3v2中的标签头和标签帧。在前面的id3v2_read_internal函数调用已经得知了标签头+标签帧的总大小。
static void id3v2_parse(AVIOContext *pb, AVDictionary **metadata,
AVFormatContext *s, int len, uint8_t version,
uint8_t flags, ID3v2ExtraMeta **extra_meta)
{
int isv34, unsync;
unsigned tlen;
char tag[5];
int64_t next, end = avio_tell(pb) + len;
int taghdrlen;
const char *reason = NULL;
AVIOContext pb_local;
AVIOContext *pbx;
unsigned char *buffer = NULL;
int buffer_size = 0;
const ID3v2EMFunc *extra_func = NULL;
unsigned char *uncompressed_buffer = NULL;
av_unused int uncompressed_buffer_size = 0;
const char *comm_frame;
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "id3v2 ver:%d flags:%02X len:%d\n", version, flags, len);
switch (version) {
case 2:
if (flags & 0x40) {
reason = "compression";
goto error;
}
isv34 = 0;
taghdrlen = 6;
comm_frame = "COM";
break;
case 3:
case 4:
isv34 = 1;
taghdrlen = 10;
comm_frame = "COMM";
break;
default:
reason = "version";
goto error;
}
unsync = flags & 0x80;
if (isv34 && flags & 0x40) { /* Extended header present, just skip over it */
int extlen = get_size(pb, 4);
if (version == 4)
/* In v2.4 the length includes the length field we just read. */
extlen -= 4;
if (extlen < 0) {
reason = "invalid extended header length";
goto error;
}
avio_skip(pb, extlen);
len -= extlen + 4;
if (len < 0) {
reason = "extended header too long.";
goto error;
}
}
while (len >= taghdrlen) {
unsigned int tflags = 0;
int tunsync = 0;
int tcomp = 0;
int tencr = 0;
unsigned long av_unused dlen;
if (isv34) {
if (avio_read(pb, tag, 4) < 4)
break;
tag[4] = 0;
if (version == 3) {
tlen = avio_rb32(pb);
} else {
/* some encoders incorrectly uses v3 sizes instead of syncsafe ones
* so check the next tag to see which one to use */
tlen = avio_rb32(pb);
if (tlen > 0x7f) {
if (tlen < len) {
int64_t cur = avio_tell(pb);
if (ffio_ensure_seekback(pb, 2 /* tflags */ + tlen + 4 /* next tag */))
break;
if (check_tag(pb, cur + 2 + size_to_syncsafe(tlen), 4) == 1)
tlen = size_to_syncsafe(tlen);
else if (check_tag(pb, cur + 2 + tlen, 4) != 1)
break;
avio_seek(pb, cur, SEEK_SET);
} else
tlen = size_to_syncsafe(tlen);
}
}
tflags = avio_rb16(pb);
tunsync = tflags & ID3v2_FLAG_UNSYNCH;
} else {
if (avio_read(pb, tag, 3) < 3)
break;
tag[3] = 0;
tlen = avio_rb24(pb);
}
if (tlen > (1<<28))
break;
len -= taghdrlen + tlen;
if (len < 0)
break;
next = avio_tell(pb) + tlen;
if (!tlen) {
if (tag[0])
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Invalid empty frame %s, skipping.\n",
tag);
continue;
}
if (tflags & ID3v2_FLAG_DATALEN) {
if (tlen < 4)
break;
dlen = avio_rb32(pb);
tlen -= 4;
} else
dlen = tlen;
tcomp = tflags & ID3v2_FLAG_COMPRESSION;
tencr = tflags & ID3v2_FLAG_ENCRYPTION;
/* skip encrypted tags and, if no zlib, compressed tags */
if (tencr || (!CONFIG_ZLIB && tcomp)) {
const char *type;
if (!tcomp)
type = "encrypted";
else if (!tencr)
type = "compressed";
else
type = "encrypted and compressed";
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Skipping %s ID3v2 frame %s.\n", type, tag);
avio_skip(pb, tlen);
/* check for text tag or supported special meta tag */
} else if (tag[0] == 'T' ||
!memcmp(tag, "USLT", 4) ||
!strcmp(tag, comm_frame) ||
(extra_meta &&
(extra_func = get_extra_meta_func(tag, isv34)))) {
pbx = pb;
if (unsync || tunsync || tcomp) {
av_fast_malloc(&buffer, &buffer_size, tlen);
if (!buffer) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to alloc %d bytes\n", tlen);
goto seek;
}
}
if (unsync || tunsync) {
int64_t end = avio_tell(pb) + tlen;
uint8_t *b;
b = buffer;
while (avio_tell(pb) < end && b - buffer < tlen && !pb->eof_reached) {
*b++ = avio_r8(pb);
if (*(b - 1) == 0xff && avio_tell(pb) < end - 1 &&
b - buffer < tlen &&
!pb->eof_reached ) {
uint8_t val = avio_r8(pb);
*b++ = val ? val : avio_r8(pb);
}
}
ffio_init_context(&pb_local, buffer, b - buffer, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL,
NULL);
tlen = b - buffer;
pbx = &pb_local; // read from sync buffer
}
if (tag[0] == 'T')
/* parse text tag */
read_ttag(s, pbx, tlen, metadata, tag);
else if (!memcmp(tag, "USLT", 4))
read_uslt(s, pbx, tlen, metadata);
else if (!strcmp(tag, comm_frame))
read_comment(s, pbx, tlen, metadata);
else
/* parse special meta tag */
extra_func->read(s, pbx, tlen, tag, extra_meta, isv34);
} else if (!tag[0]) {
if (tag[1])
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "invalid frame id, assuming padding\n");
avio_skip(pb, tlen);
break;
}
/* Skip to end of tag */
seek:
avio_seek(pb, next, SEEK_SET);
}
/* Footer preset, always 10 bytes, skip over it */
if (version == 4 && flags & 0x10)
end += 10;
error:
if (reason)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_INFO, "ID3v2.%d tag skipped, cannot handle %s\n",
version, reason);
avio_seek(pb, end, SEEK_SET);
av_free(buffer);
av_free(uncompressed_buffer);
return;
}
- 首先,就id3v2的version字段进行判断。这样做的目的是区别是否有带扩展头,当version为3或者4并且flags & 0x40 为真时,带有扩展头。ffmpeg的做法是跳过扩展头。
- 随后,循环读取标签帧,循环结束的条件是
while (len >= taghdrlen).每一次读取都会使len减少当前所遍历到的标签帧大小。 - 标签帧由10字节的枕头和至少一字节的内容构成。ffmpeg读取四字节的标识时,存放在了tag变量。如果tag的第一个字节是【T】,则代表tag是文本类型,随后调用read_ttag进行解析。
id3v2的标签帧结构
char ID[4]; /标识,说明其内容,例如作者/标题等/
char Size[4]; /帧内容的大小,不包括帧头,不得小于1/
char Flags[2]; /标志帧,只定义了6 位/
read_ttag
parse a text tag.代码如下:
static void read_ttag(AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb, int taglen,
AVDictionary **metadata, const char *key)
{
uint8_t *dst;
int encoding, dict_flags = AV_DICT_DONT_OVERWRITE | AV_DICT_DONT_STRDUP_VAL;
unsigned genre;
if (taglen < 1)
return;
encoding = avio_r8(pb);
taglen--; /* account for encoding type byte */
if (decode_str(s, pb, encoding, &dst, &taglen) < 0) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error reading frame %s, skipped\n", key);
return;
}
if (!(strcmp(key, "TCON") && strcmp(key, "TCO")) &&
(sscanf(dst, "(%d)", &genre) == 1 || sscanf(dst, "%d", &genre) == 1) &&
genre <= ID3v1_GENRE_MAX) {
av_freep(&dst);
dst = av_strdup(ff_id3v1_genre_str[genre]);
} else if (!(strcmp(key, "TXXX") && strcmp(key, "TXX"))) {
/* dst now contains the key, need to get value */
key = dst;
if (decode_str(s, pb, encoding, &dst, &taglen) < 0) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error reading frame %s, skipped\n", key);
av_freep(&key);
return;
}
dict_flags |= AV_DICT_DONT_STRDUP_KEY;
} else if (!*dst)
av_freep(&dst);
if (dst)
av_dict_set(metadata, key, dst, dict_flags);
}
- 首先会读取一个字节,如果该字节代表编码格式,则继续读取后续内容直至到达tlen大小
- 如果该字节为【TCON】,则代表类型直接用字符串表示。这时ffmpeg会到类型表中去找到对应的映射,例如Blues、Classic Rock、Country这样的类型。
- 如果该字节对应【TXXX】,则是用户自定义数据。
mp3数据部分的格式解析
mp3的数据并不是由裸的pcm流构成,而是采用mpeg协的压缩数据。数据部分也由多个帧构成,且每个帧都有对应的格式。

在avformat_open_input函数的末尾,会调用iformat->read_header函数进行数据帧帧头的读取。而对应到mp3媒体资源,则是调用mp3_read_header
mp3_read_header
从ffmpeg的角度来说,读取第一个数据帧帧头的行为,在获得mp3媒体资源总时长得一些信息至关重要,特别是对于CBR(固定位率)格式的压缩数据。因为这些数据帧的位率都是一样的,大小也是一样的,因此可以通过每个数据帧的大小、位率求出每帧的时长,从而求出mp3媒体资源的总时长等其它信息。所以ffmpeg在完成demuxer匹配之后,就立马进行了首个数据帧帧头的解析。
static int mp3_read_header(AVFormatContext *s)
{
MP3DecContext *mp3 = s->priv_data;
AVStream *st;
int64_t off;
int ret;
int i;
//事先读取的id3v2信息
s->metadata = s->internal->id3v2_meta;
s->internal->id3v2_meta = NULL;
//todo:
st = avformat_new_stream(s, NULL);
if (!st)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
st->codecpar->codec_type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO;
st->codecpar->codec_id = AV_CODEC_ID_MP3;
st->need_parsing = AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_RAW;
st->start_time = 0;
// lcm of all mp3 sample rates
avpriv_set_pts_info(st, 64, 1, 14112000);
//s->pb: AVIOContext
s->pb->maxsize = -1;
off = avio_tell(s->pb);
if (!av_dict_get(s->metadata, "", NULL, AV_DICT_IGNORE_SUFFIX))
ff_id3v1_read(s);
//fileszie -> 文件大小,可以从例如content-length中获得
if(s->pb->seekable & AVIO_SEEKABLE_NORMAL)
mp3->filesize = avio_size(s->pb);
//vbr格式解析
if (mp3_parse_vbr_tags(s, st, off) < 0)
avio_seek(s->pb, off, SEEK_SET);
ret = ff_replaygain_export(st, s->metadata);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
off = avio_tell(s->pb);
//解析mp3的数据部分
for (i = 0; i < 64 * 1024; i++) {
uint32_t header, header2;
int frame_size;
if (!(i&1023))
ffio_ensure_seekback(s->pb, i + 1024 + 4);
//读取数据帧的枕头, frame_size -> 帧长度,包含帧头的四个字节
frame_size = check(s->pb, off + i, &header);
if (frame_size > 0) {
//重新seek到未读取数据帧的位置
ret = avio_seek(s->pb, off, SEEK_SET);
ffio_ensure_seekback(s->pb, i + 1024 + frame_size + 4);
//去读下一个数据帧的frame sizee
ret = check(s->pb, off + i + frame_size, &header2);
if (ret >= 0 &&
(header & SAME_HEADER_MASK) == (header2 & SAME_HEADER_MASK)) //我也不知道是什么操作
{
av_log(s, i > 0 ? AV_LOG_INFO : AV_LOG_VERBOSE, "Skipping %d bytes of junk at %"PRId64".\n", i, off);
ret = avio_seek(s->pb, off + i, SEEK_SET);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
break;
} else if (ret == CHECK_SEEK_FAILED) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid frame size (%d): Could not seek to %"PRId64".\n", frame_size, off + i + frame_size);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
} else if (frame_size == CHECK_SEEK_FAILED) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed to read frame size: Could not seek to %"PRId64".\n", (int64_t) (i + 1024 + frame_size + 4));
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
ret = avio_seek(s->pb, off, SEEK_SET);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
// the seek index is relative to the end of the xing vbr headers
for (i = 0; i < st->nb_index_entries; i++)
st->index_entries[i].pos += avio_tell(s->pb);
/* the parameters will be extracted from the compressed bitstream */
return 0;
}
- mp3_read_header函数首先调用check进行数据帧帧头的解析,预读四个字节,并调用avpriv_mpegaudio_decode_header获得采样数、采样频率、帧大小等信息。
- 由于mp3的压缩数据可以按照mpeg-1、mpeg-2、mpeg-2.5来压缩,因此也需要从帧头中进行判断,以便后续解码利用。
- 采样频率由采用的mpeg协议版本和layer共同决定。
- 帧的大小的计算公式:a).layer1 ->
((每帧采样数/8*比特率)/采样频率)+填充*4b).layer2、3 ->((每帧采样数/8*比特率)/采样频率)+填充




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








