POJ - 1135
Domino Effect
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536KB 64bit IO Format: %lld & %llu
Description
Did you know that you can use domino bones for other things besides playing Dominoes? Take a number of dominoes and build a row by standing them on end with only a small distance in between. If you do it right, you can tip the first domino and cause all others to fall down in succession (this is where the phrase “domino effect” comes from).
While this is somewhat pointless with only a few dominoes, some people went to the opposite extreme in the early Eighties. Using millions of dominoes of different colors and materials to fill whole halls with elaborate patterns of falling dominoes, they created (short-lived) pieces of art. In these constructions, usually not only one but several rows of dominoes were falling at the same time. As you can imagine, timing is an essential factor here.
It is now your task to write a program that, given such a system of rows formed by dominoes, computes when and where the last domino falls. The system consists of several “key dominoes” connected by rows of simple dominoes. When a key domino falls, all rows connected to the domino will also start falling (except for the ones that have already fallen). When the falling rows reach other key dominoes that have not fallen yet, these other key dominoes will fall as well and set off the rows connected to them. Domino rows may start collapsing at either end. It is even possible that a row is collapsing on both ends, in which case the last domino falling in that row is somewhere between its key dominoes. You can assume that rows fall at a uniform rate.
Input
The input file contains descriptions of several domino systems. The first line of each description contains two integers: the number n of key dominoes (1 <= n < 500) and the number m of rows between them. The key dominoes are numbered from 1 to n. There is at most one row between any pair of key dominoes and the domino graph is connected, i.e. there is at least one way to get from a domino to any other domino by following a series of domino rows.
The following m lines each contain three integers a, b, and l, stating that there is a row between key dominoes a and b that takes l seconds to fall down from end to end.
Each system is started by tipping over key domino number 1.
The file ends with an empty system (with n = m = 0), which should not be processed.
Output
For each case output a line stating the number of the case (‘System #1’, ‘System #2’, etc.). Then output a line containing the time when the last domino falls, exact to one digit to the right of the decimal point, and the location of the last domino falling, which is either at a key domino or between two key dominoes(in this case, output the two numbers in ascending order). Adhere to the format shown in the output sample. The test data will ensure there is only one solution. Output a blank line after each system.
Sample Input
2 1
1 2 27
3 3
1 2 5
1 3 5
2 3 5
0 0
Sample Output
System #1
The last domino falls after 27.0 seconds, at key domino 2.
System #2
The last domino falls after 7.5 seconds, between key dominoes 2 and 3.
题目大意:
这里有一些多米诺骨牌,把一些骨牌标记为关键的(key dominoes),在关键的骨牌之间有一些普通的骨牌连成的串。告诉你那些关键骨牌之间有这些骨牌串,并给出这一串骨牌倒下的所需要的时间。首先推倒编号为1的关键骨牌,并且开始计时。要求输出所有骨牌倒下的时间,并且最后倒下的骨牌的编号(如果最后倒下的是关键骨牌,则输出这个关键骨牌的编号;要是最后倒下的是普通骨牌,就输出它所属的这个普通骨牌串是连接哪两个关键骨牌的)。
输入数据:
有多组数据!
首先给出n,m。代表有n个关键骨牌(从1~n编号),有m条普通骨牌串。
接下来是m行,每行包含三个整数x,y,z:
代表x到y之间有一串普通骨牌,倒下所需要的时间是z。
输出数据:
是要输出一句话的!具体看题目描述和英文原题。
注意:时间要求保留1位小数!
Wea!
题解:显然是图论啦!
显然,我们可以把关键骨牌看做点,把那些骨牌串串看做边~
(其实在翻译里就有点暴露了)
然后,我们可以看出是最短路的做法!
要是看不出,不妨把问题做一些简化:只要求出最后倒下的那个关键骨牌就好了。
这样,是不是就很快看出是最短路呢?
其实,我们只要再加上一点修改,就可以完成任务了。
(也就是考虑要是最后倒下的那个骨牌不是关键骨牌的情况)
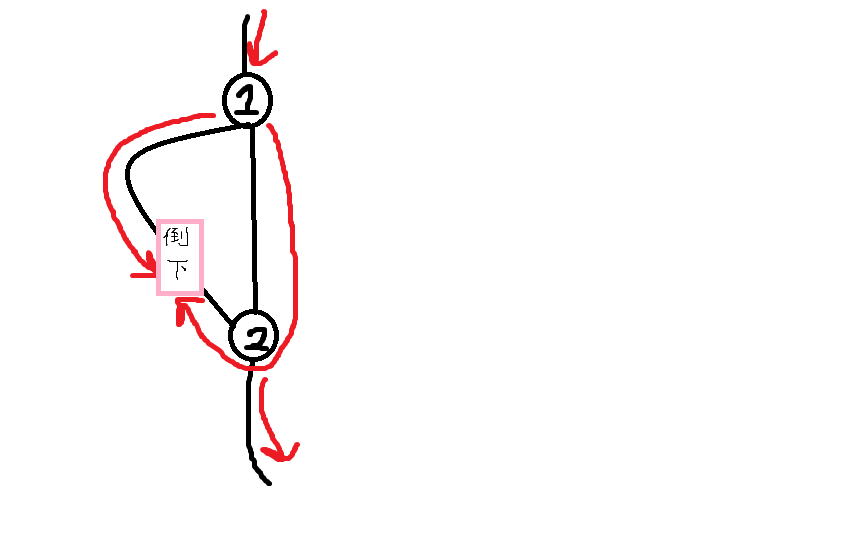
也就是如上情况,红色表示骨牌倒下的方向,黑色的线条表示普通骨牌串。
不妨假设这个骨牌在编号为j的边倒下,这个边全部倒下的时间为w[j],从点1倒到这个骨牌的时间为x,用d[i]表示第i个关键骨牌倒下的时间。
那么,我们可以列出如下方程:
而且,w[j]是已知的,d[2]和d[1]是可以通过裸的最短路算出来的。
那么,x就可以通过如下变形求出来了
是不是很简单呢?
下面贴出我的代码:
/*
*Source Code By Wang_Tao
*2016-09-29
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 510 ;
const int zhf = 10000000 ;
const int maxm = maxn * maxn >> 1 ;
int be[maxn], nxt[maxm], n, m, to[maxm], w[maxm], e ; //使用链式前向星存图
int d[maxn] ; //d[i]表示i点倒下的时间
bool p[maxn] ; //用于dijkstra中判断是否求出最短路
void add ( int x, int y, int z ) {
to[++e] = y ;
nxt[e] = be[x] ;
be[x] = e ;
w[e] = z ;
} // 加边
void init () {
int i, j, k ;
e = 0 ;
for ( i = 1 ; i < maxn ; i ++ )
be[i] = p[i] = 0 ,
d[i] = zhf ;
for ( i = 1 ; i < maxm ; i ++ )
nxt[i] = to[i] = w[i] = 0 ;
} // 记得初始化
int main() {
int i, j, x, y, z, k ;
int Case = 0 ;
while ( scanf ( "%d%d" , &n, &m ) != EOF ) {
if ( !n && !m ) return 0 ;
++ Case ;
init() ;
for ( i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ ) {
scanf ( "%d%d%d" , &x, &y, &z ) ;
add ( x, y, z ) ;
add ( y, x, z ) ;
}
d[1] = 0 ;
for ( i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) { // 就使用O(n^2)的dijkstra,没关系
int minn = zhf ;
for ( j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
if ( !p[j] && d[j] < minn ) {
minn = d[j] ;
k = j ;
}
p[k] = 1 ;
for ( j = be[k] ; j ; j = nxt[j] ) {
int u = to[j] ;
if ( d[u] > d[k] + w[j] ) d[u] = d[k] + w[j] ;
}
}
bool flag = 0 ; // 判断最后倒下的是不是普通骨牌
double ans = 0.0 ; // 存储答案时间
int a = -1, b = -1 ; // 用于存储答案中的两个关键骨牌的编号
for ( i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
for ( j = be[i] ; j ; j = nxt[j] ) {
int u = to[j] ;
int d1 = d[i], d2 = d[u] ;
if ( d1 > d2 ) swap ( d1,d2 );
if ( d2 - d1 >= w[j] ) {
if ( ans < d2 ) {
ans = d2 ;
a = d1 == d[i] ? i : u ;
}
}else {
double Ans ;
double x = ( w[j] + d2 - d1 ) * 1.0 / 2 ;
Ans = x + d1 ;
if ( Ans > ans ) { // 注意这里!
flag = 1 ;
a = i, b = u ; //更新
ans = Ans ;
}
}
}
}
printf ( "System #%d\n", Case ) ;
if ( !flag ) {
a = -1 ;
double maxx = -1 ;
for ( i = 1, a = -1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
if ( d[i] > maxx ) {
maxx = d[i] ;
a = i ;
}
}
printf ( "The last domino falls after %.1f seconds, at key domino %d.\n", ans, a );
}else {
if ( a > b ) swap ( a,b );
printf ( "The last domino falls after %.1f seconds, between key dominoes %d and %d.\n", ans, a, b ) ;
}
puts ("") ;
}
return 0 ;
}嘿嘿嘿,大家都明白了吗?
























 2247
2247

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








