参考文献:
http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6575988
http://www.androidmi.com/Androidkaifa/rumen/201005/633.html
1 什么是JNI
JNI是Java Native Interface的缩写,即Java本地接口.从Java1.1开始,JNI标准成为Java平台的一部分,它允许java代码和用其它语言编写的代码进行交互.JNI是本地编程接口,它使得在Java虚拟机(VM)内部运行的Java代码能够与用其他编程语言(如C,C++和汇编语言)的应用程序和库进行交互操作.
在Android中提供的JNI的方式,让Java程序可以调用C语言程序。Android中很多Java类都具有native接口,这些native接口就是同本地实现,然后注册到系统中的.
JNI在Android层次结构中的作用如下图所示:
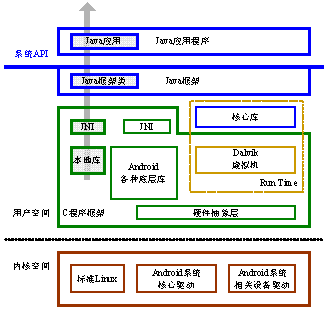
在Android中,主要的JNI代码在以下的路径中:
Android源码根目录/frameworks/base/core/jni/
这个路径中的内容将被编译成库libandroid_runtime.so,这就是一个普通的动态库,被放置在目标系统的/system/lib目录中.
除此之外,Android还包含其他的JNI库,例如,媒体部分的JNI目录frameworks/base/media/jni/中,被编译成库libmedia_jni.so.
JNI中的各个文件实际上就是C++的普通文件,其命名一般和支持的Java类有对应关系。这种关系是习惯上的写法,而不是强制的。
在Android中实现的JNI库,需要连接动态库libnativehelper.so.
2 注册JNI方法
在Android源码根目录/frameworks/base/services/jni/目录下有一个onload.cpp文件,其内容如下:
- /*
- * Copyright (C) 2009 The Android Open Source Project
- *
- * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
- * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
- * You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- */
- #include "JNIHelp.h"
- #include "jni.h"
- #include "utils/Log.h"
- #include "utils/misc.h"
- namespace android {
- int register_android_server_AlarmManagerService(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_BatteryService(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_InputApplicationHandle(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_InputWindowHandle(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_InputManager(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_LightsService(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_PowerManagerService(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_UsbDeviceManager(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_UsbHostManager(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_VibratorService(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_SystemServer(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_location_GpsLocationProvider(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_connectivity_Vpn(JNIEnv* env);
- int register_android_server_HelloService(JNIEnv *env);
- };
- using namespace android;
- extern "C" jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved)
- {
- JNIEnv* env = NULL;
- jint result = -1;
- if (vm->GetEnv((void**) &env, JNI_VERSION_1_4) != JNI_OK) {
- LOGE("GetEnv failed!");
- return result;
- }
- LOG_ASSERT(env, "Could not retrieve the env!");
- register_android_server_PowerManagerService(env);
- register_android_server_InputApplicationHandle(env);
- register_android_server_InputWindowHandle(env);
- register_android_server_InputManager(env);
- register_android_server_LightsService(env);
- register_android_server_AlarmManagerService(env);
- register_android_server_BatteryService(env);
- register_android_server_UsbDeviceManager(env);
- register_android_server_UsbHostManager(env);
- register_android_server_VibratorService(env);
- register_android_server_SystemServer(env);
- register_android_server_location_GpsLocationProvider(env);
- register_android_server_connectivity_Vpn(env);
- register_android_server_HelloService(env);
- return JNI_VERSION_1_4;
- }
onload.cpp文件上部分为注册函数的声明,下部分为调用各种注册函数,而 这些注册函数就是JNI方法的注册函数! 正有通过这些注册函数,上层才有可能调用注册的JNI方法.
这些注册函数是由同目录下的其他.cpp文件中实现,如上面的register_android_server_HelloService(env)这个函数是在com_android_service_HelloService.cpp文件中实现的.那么编译器又是如何知道这点的呢? 答案当然是Android.mk这个文件,打开这个文件,其内容如下:
- LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
- include $(CLEAR_VARS)
- LOCAL_SRC_FILES:= \
- com_android_server_AlarmManagerService.cpp \
- com_android_server_BatteryService.cpp \
- com_android_server_InputApplicationHandle.cpp \
- com_android_server_InputManager.cpp \
- com_android_server_InputWindowHandle.cpp \
- com_android_server_LightsService.cpp \
- com_android_server_PowerManagerService.cpp \
- com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp \
- com_android_server_UsbDeviceManager.cpp \
- com_android_server_UsbHostManager.cpp \
- com_android_server_VibratorService.cpp \
- com_android_server_location_GpsLocationProvider.cpp \
- com_android_server_connectivity_Vpn.cpp \
- com_android_server_HelloService.cpp \
- onload.cpp
- LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += \
- $(JNI_H_INCLUDE) \
- frameworks/base/services \
- frameworks/base/core/jni \
- external/skia/include/core
- LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := \
- libandroid_runtime \
- libcutils \
- libhardware \
- libhardware_legacy \
- libnativehelper \
- libsystem_server \
- libutils \
- libui \
- libinput \
- libskia \
- libgui \
- libusbhost
- ifeq ($(WITH_MALLOC_LEAK_CHECK),true)
- LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DMALLOC_LEAK_CHECK
- endif
- LOCAL_MODULE:= libandroid_servers
- include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
接下来让我们来看看其中一个注册函数的具体实现过程是如何的,比如:register_android_server_HelloService(env),打开com_android_service_HelloService.cpp文件,其下有注册函数的实现代码,如下:
- int register_android_server_HelloService(JNIEnv *env) {
- return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/server/HelloService", method_table, NELEM(method_table));
- }
- /*JNI方法表*/
- static const JNINativeMethod method_table[] = {
- {"init_native", "()Z", (void*)hello_init},
- {"setVal_native", "(I)V", (void*)hello_setVal},
- {"getVal_native", "()I", (void*)hello_getVal},
- };
如hello_setVal函数的实现:
- /*通过硬件抽象层定义的硬件访问接口设置硬件寄存器val的值*/
- static void hello_setVal(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jint value) {
- int val = value;
- LOGI("Hello JNI: set value %d to device.", val);
- if(!hello_device) {
- LOGI("Hello JNI: device is not open.");
- return;
- }
- hello_device->set_val(hello_device, val);
- }
- /*通过硬件抽象层定义的硬件模块打开接口打开硬件设备*/
- static inline int hello_device_open(const hw_module_t* module, struct hello_device_t** device) {
- return module->methods->open(module, HELLO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, (struct hw_device_t**)device);
- }
- /*通过硬件模块ID来加载指定的硬件抽象层模块并打开硬件*/
- static jboolean hello_init(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz) {
- hello_module_t* module;
- LOGI("Hello JNI: initializing......");
- if(hw_get_module(HELLO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, (const struct hw_module_t**)&module) == 0) {
- LOGI("Hello JNI: hello Stub found.");
- if(hello_device_open(&(module->common), &hello_device) == 0) {
- LOGI("Hello JNI: hello device is open.");
- return 0;
- }
- LOGE("Hello JNI: failed to open hello device.");
- return -1;
- }
- LOGE("Hello JNI: failed to get hello stub module.");
- return -1;
- }
3 方法列表说明
关于static const JNINativeMethod method_table[]方法列表的原型如下:
- typedef struct {
- const char* name;
- const char* signature;
- void* fnPtr;
- } JNINativeMethod;
第一个变量name是Java中函数的名字。第二个变量signature,用字符串是描述了函数的参数和返回值.第三个变量fnPtr是函数指针,指向C函数。
其中比较难以理解的是第二个参数,例如:"()V"
"(II)V"
"(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V"
实际上这些字符是与函数的参数类型一一对应的。"()" 中的字符表示参数,后面的则代表返回值。例如"()V" 就表示void Func();
"(II)V" 表示 void Func(int, int);
具体的每一个字符的对应关系如下
字符 Java类型 C类型
V void void
Z jboolean boolean
I jint int
J jlong long
D jdouble double
F jfloat float
B jbyte byte
C jchar char
S jshort short
数组则以"["开始,用两个字符表示
[I jintArray int[]
[F jfloatArray float[]
[B jbyteArray byte[]
[C jcharArray char[]
[S jshortArray short[]
[D jdoubleArray double[]
[J jlongArray long[]
[Z jbooleanArray boolean[]
上面的都是基本类型。如果Java函数的参数是class,则以"L"开头,以";"结尾.中间是用"/" 隔开的包及类名。而其对应的C函数名的参数则为jobject. 一个例外是String类,其对应的类为jstring
Ljava/lang/String; String jstring
Ljava/net/Socket; Socket jobject
如果JAVA函数位于一个嵌入类,则用$作为类名间的分隔符。
例如 "(Ljava/lang/String;Landroid/os/FileUtils$FileStatus;)Z"






















 654
654

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








