一、题目
-
题目链接:Head of a Gang (30分)
-
题目说明:
One way that the police finds the head of a gang is to check people’s phone calls. If there is a phone call between A and B, we say that A and B is related. The weight of a relation is defined to be the total time length of all the phone calls made between the two persons. A “Gang” is a cluster of more than 2 persons who are related to each other with total relation weight being greater than a given threshold K. In each gang, the one with maximum total weight is the head. Now given a list of phone calls, you are supposed to find the gangs and the heads.
-
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains two positive numbers N and K (both less than or equal to 1000), the number of phone calls and the weight threthold, respectively. Then N lines follow, each in the following format:
Name1 Name2 Timewhere Name1 and Name2 are the names of people at the two ends of the call, and Time is the length of the call. A name is a string of three capital letters chosen from A-Z. A time length is a positive integer which is no more than 1000 minutes. -
Output Specification:
For each test case, first print in a line the total number of gangs. Then for each gang, print in a line the name of the head and the total number of the members. It is guaranteed that the head is unique for each gang. The output must be sorted according to the alphabetical order of the names of the heads.
-
Sample Input 1:
8 59
AAA BBB 10
BBB AAA 20
AAA CCC 40
DDD EEE 5
EEE DDD 70
FFF GGG 30
GGG HHH 20
HHH FFF 10 -
Sample Output 1:
2
AAA 3
GGG 3 -
Sample Input 2:
8 70
AAA BBB 10
BBB AAA 20
AAA CCC 40
DDD EEE 5
EEE DDD 70
FFF GGG 30
GGG HHH 20
HHH FFF 10 -
Sample Output 2:
0
-
题意说明:给出若干个人之间的通话记录,每条记录可以看做有向边,构成一张图。图可能不连通,而是分成若干组。每个组内各成员间的通话总时长若超过给定阈值K且人数大于2人,则认为这组人是一个“团伙”,而其中和别人通话总时长最多的人是“头目”。现要输出团伙数量、每个团伙的人数和头目姓名
二、三种解法
0. BFS和DFS遍历图
1. 初始思路:邻接表+有向图+DFS
-
初始思路:
- 根据样例可以看出,通话记录是有方向的,A向B的通话总时长和B向A的通话总时长是两条不同的记录,于是可以把每条记录看成一个带权有向边,建立通话关系图。接下来用套DFS或BFS遍历模板,找出所有连通块计算总通话时间
- 邻接表适合存储有向边边权,使用邻接表存图。同时此题中还要存储每个人的通话总时长(用来找头目),可以单独设置一个数组存点权。在输入记录时,每条记录都把通话双方的点权同时增大
- 最后输出要求按头目名称字母顺序排列,可以用
map<string,int>自动排序
-
满分代码
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> #include<string> using namespace std; typedef struct NODE { int v; //端点 int w; //边权 NODE(int _v,int _w):v(_v),w(_w){} }NODE; const int MAXN = 2010; //通话记录1000条,人数最多可能2000 bool vis[MAXN] = {false}; //访问标记 int weight[MAXN] = {0}; //每个人的权重(点权) vector<NODE> Adj[MAXN]; //邻接表 map<string,int> mp; //人名 -> 邻接表下标 string int2string[MAXN]; //邻接表下标 -> 人名 int N,K,personNum = 0; //记录数、权重阈值、总人数 map<string,int> gang; //找出的团伙头目和人数,map自动按string字母有序 //把人名转换为Adj邻接表下标返回 int string2int(string str) { //如果是新人,分配一个下标 if(mp.find(str) == mp.end()) { mp[str] = personNum; int2string[personNum] = str; personNum++; } return mp[str]; } //DFS遍历nowVisit所在的连通块,计算总权重、人数、头目 void DFS(int nowVisit,int &head,int &gangMember,int &totalWeight) { gangMember++; vis[nowVisit] = true; if(weight[nowVisit] > weight[head]) head = nowVisit; //找到和nowVisit通话的所有人,继续DFS for(int i=0;i<Adj[nowVisit].size();i++) { totalWeight+=Adj[nowVisit][i].w; //cout<<"cheak:"<<int2string[nowVisit]<<" "<<int2string[Adj[nowVisit][i].v]<<" "<<totalWeight<<'\n'; if(!vis[Adj[nowVisit][i].v]) DFS(Adj[nowVisit][i].v,head,gangMember,totalWeight); } } //访问所有连通块,每块是一个可能的gang void DFSTrave() { for(int i=0;i<personNum;i++) { if(!vis[i]) { int head = i,gangMember = 0,totalWeight=0; DFS(i,head,gangMember,totalWeight); if(gangMember>2 && totalWeight>K) gang[int2string[head]] = gangMember; } } } int main() { cin>>N>>K; string personA,personB; int a,b,time; //遍历N条通话记录,初始化邻接表和权重表 for(int i=0;i<N;i++) { //personA向personB打了time分钟电话 cin>>personA>>personB>>time; a = string2int(personA); b = string2int(personB); weight[a] += time; weight[b] += time; Adj[a].push_back(NODE(b,time)); //在邻接表中记录一条有向边 } //DFS遍历所有联通块,找出所有gang DFSTrave(); //输出gang信息 cout<<gang.size()<<endl; for(map<string,int>::iterator it = gang.begin();it!=gang.end();it++) cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; return 0; } /* 8 59 AAA BBB 10 BBB AAA 20 AAA CCC 40 DDD EEE 5 EEE DDD 70 FFF GGG 30 GGG HHH 20 HHH FFF 10 */
2. 修改思路:邻接矩阵+无向图+DFS
-
上面的代码虽然满分了,但是有一个潜在问题!!我把每条通话记录看做有向边,因此建立出来图的每个部分不一定是强连通分量,不能保证从任意点出发都能DFS搜索到整个连通块。举例来说,示例1中AAA为头目的团伙通话网络图如下,从AAA或BBB出发都DFS能搜索到所有结点,但是从CCC出发DFS就不能搜索到AAA和BBB,这将导致
DFSTrave函数把CCC看做一个单独的团伙,之后从AAA或BBB搜索时,由于CCC已做过访问标记,AAA和BBB会被看做另一个单独的团伙。

-
因此,上面能AC完全是因为运气好,DFS过程正好是从能访问整个团伙成员的点开始的
-
为了保证每个团伙都是有向图中的一个强连通分量,就不得不为每条通话记录建两条有向边,这样就很麻烦了。所以还不如改成无向图用邻接矩阵存储,修改后满分代码如下
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<map> #include<string> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 2010; //通话记录1000条,人数最多可能2000 bool vis[MAXN] = {false}; //访问标记 int weight[MAXN] = {0}; //每个人的权重 int G[MAXN][MAXN] = {0}; //邻接矩阵 map<string,int> mp; //人名 -> 邻接表下标 string int2string[MAXN]; //邻接表下标 -> 人名 int N,K,personNum = 0; //记录数、权重阈值、总人数 map<string,int> gang; //找出的团伙头目和人数,map自动按string字母有序 //把人名转换为邻接矩阵下标返回 int string2int(string str) { //如果是新人,分配一个下标 if(mp.find(str) == mp.end()) { mp[str] = personNum; int2string[personNum] = str; personNum++; } return mp[str]; } //DFS遍历一个连通块,计算总权重、人数、头目 void DFS(int nowVisit,int &head,int &gangMember,int &totalWeight) { gangMember++; vis[nowVisit] = true; if(weight[nowVisit] > weight[head]) head = nowVisit; for(int i=0;i<personNum;i++) { if(G[nowVisit][i] > 0) //从nowVisit可以到达i { totalWeight += G[nowVisit][i]; G[nowVisit][i] = G[i][nowVisit] = 0; //删除这条边,避免回头 //cout<<"cheak:"<<int2string[nowVisit]<<" "<<int2string[i]<<" "<<totalWeight<<'\n'; if(!vis[i]) DFS(i,head,gangMember,totalWeight); } } } //访问所有连通块,每块是一个可能的gang void DFSTrave() { for(int i=0;i<personNum;i++) { if(!vis[i]) { int head = i,gangMember = 0,totalWeight=0; DFS(i,head,gangMember,totalWeight); if(gangMember>2 && totalWeight>K) gang[int2string[head]] = gangMember; } } } int main() { cin>>N>>K; string personA,personB; int a,b,time; //遍历N条通话记录,初始化邻接表和权重表 for(int i=0;i<N;i++) { //personA向personB打了time分钟电话 cin>>personA>>personB>>time; a = string2int(personA); b = string2int(personB); weight[a] += time; weight[b] += time; G[a][b] += time; G[b][a] += time; } //DFS遍历所有联通块,找出所有gang DFSTrave(); //输出gang信息 cout<<gang.size()<<endl; for(map<string,int>::iterator it = gang.begin();it!=gang.end();it++) cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; return 0; } -
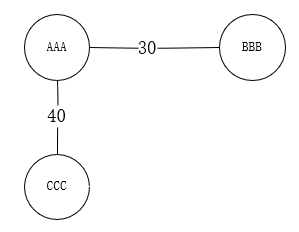
改用邻接表存无向图后,AAA头目的团伙示意图如下,注意一下
G[nowVisit][i] = G[i][nowVisit] = 0;这句,这是为了避免从AAA开始DFS计算了AAA->BBB的边权后,在从BBB开始DFS搜索时又重复计算BBB->AAA
3. 试试广度优先:邻接矩阵+无向图+BFS
-
套广度优先模板,稍微改一下就行了
-
满分代码
#include<iostream> #include <queue> #include<map> #include<string> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 2010; //通话记录1000条,人数最多可能2000 bool inqueue[MAXN] = {false}; //访问标记 int weight[MAXN] = {0}; //每个人的权重 int G[MAXN][MAXN] = {0}; //邻接矩阵 map<string,int> mp; //人名 -> 邻接表下标 string int2string[MAXN]; //邻接表下标 -> 人名 int N,K,personNum = 0; //记录数、权重阈值、总人数 map<string,int> gang; //找出的团伙头目和人数,map自动按string字母有序 //把人名转换为邻接矩阵下标返回 int string2int(string str) { //如果是新人,分配一个下标 if(mp.find(str) == mp.end()) { mp[str] = personNum; int2string[personNum] = str; personNum++; } return mp[str]; } //BFS遍历一个连通块,计算总权重、人数、头目 void BFS(int s,int &head,int &gangMember,int &totalWeight) { queue<int> q; q.push(s); inqueue[s] = true; while(!q.empty()) { int top = q.front(); q.pop(); gangMember++; if(weight[top]>weight[head]) head = top; for(int i=0;i<personNum;i++) { if(G[top][i] > 0) //从nowVisit可以到达i { totalWeight += G[top][i]; G[top][i] = G[i][top] = 0; //删除这条边,避免回头 //cout<<"cheak:"<<int2string[nowVisit]<<" "<<int2string[i]<<" "<<totalWeight<<'\n'; if(!inqueue[i]) { q.push(i); inqueue[i] = true; } } } } } //访问所有连通块,每块是一个可能的gang void BFSTrave() { for(int i=0;i<personNum;i++) { if(!inqueue[i]) { int head = i,gangMember = 0,totalWeight=0; BFS(i,head,gangMember,totalWeight); if(gangMember>2 && totalWeight>K) gang[int2string[head]] = gangMember; } } } int main() { cin>>N>>K; string personA,personB; int a,b,time; //遍历N条通话记录,初始化邻接表和权重表 for(int i=0;i<N;i++) { //personA向personB打了time分钟电话 cin>>personA>>personB>>time; a = string2int(personA); b = string2int(personB); weight[a] += time; weight[b] += time; G[a][b] += time; G[b][a] += time; } //BFS遍历所有联通块,找出所有gang BFSTrave(); //输出gang信息 cout<<gang.size()<<endl; for(map<string,int>::iterator it = gang.begin();it!=gang.end();it++) cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl; return 0; }






















 119
119











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










