Vanya wants to minimize a tree. He can perform the following operation multiple times: choose a vertex v, and two disjoint (except for v) paths of equal length a0 = v, a1, ..., ak, and b0 = v, b1, ..., bk. Additionally, vertices a1, ..., ak, b1, ..., bk must not have any neighbours in the tree other than adjacent vertices of corresponding paths. After that, one of the paths may be merged into the other, that is, the verticesb1, ..., bk can be effectively erased:
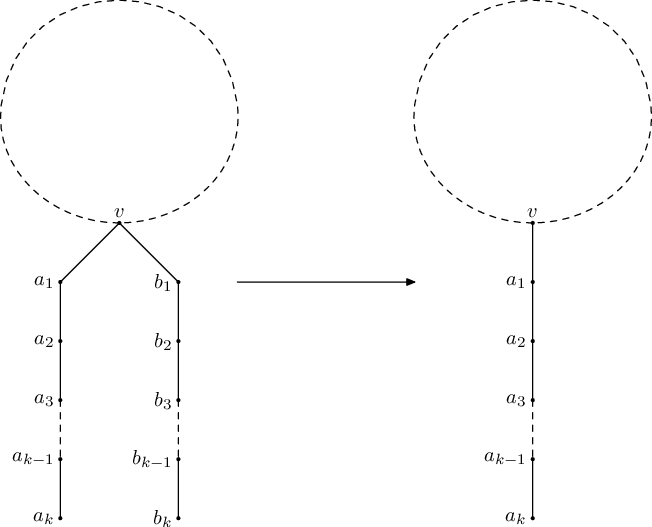
Help Vanya determine if it possible to make the tree into a path via a sequence of described operations, and if the answer is positive, also determine the shortest length of such path.
The first line of input contains the number of vertices n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105).
Next n - 1 lines describe edges of the tree. Each of these lines contains two space-separated integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v) — indices of endpoints of the corresponding edge. It is guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
If it is impossible to obtain a path, print -1. Otherwise, print the minimum number of edges in a possible path.
6 1 2 2 3 2 4 4 5 1 6
3
7 1 2 1 3 3 4 1 5 5 6 6 7
-1
In the first sample case, a path of three edges is obtained after merging paths 2 - 1 - 6 and 2 - 4 - 5.
It is impossible to perform any operation in the second sample case. For example, it is impossible to merge paths 1 - 3 - 4 and 1 - 5 - 6, since vertex 6 additionally has a neighbour 7 that is not present in the corresponding path.
题意:给一棵树,如果两条链,像上面一样,a[i]和b[i]都没有邻居,就可以合并它们,问最后能不能合并成一条链,
且要求链长度最小
题解:如果我们知道根是什么我们很好做
但是,如果可行,那么根一定可以取直径中点,为什么自己画一画就明白了
YJQ好假还给我讲DFS2遍DP2遍的鬼畜做法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 200020;
struct edge
{
int to, nxt;
}e[MAXN << 1];
int n, d[MAXN], dl[MAXN], dr[MAXN], head[MAXN], cnt, ans, l, r, rt;
inline void add(int x, int y) { e[ ++cnt ].to = y; e[ cnt ].nxt = head[ x ]; head[ x ] = cnt; }
inline void addedge(int x, int y) { add( x, y ); add( y, x ); }
inline int dfs(int x, int fa, int dep, int *d)
{
d[ x ] = dep;
for( int i = head[ x ] ; i ; i = e[ i ].nxt )
if( e[ i ].to ^ fa )
dfs( e[ i ].to, x, dep + 1, d );
}
inline int solve(int x, int fa)
{
vector < int > v;
for( int i = head[ x ] ; i ; i = e[ i ].nxt )
if( e[ i ].to ^ fa )
v.push_back( solve( e[ i ].to, x ) );
sort( v.begin(), v.end() );
v.resize( unique( v.begin(), v.end() ) - v.begin() );
if( x ^ fa )
{
if( v.size() > 1 )
puts( "-1" ), exit( 0 );
if( v.empty() ) return 1;
return v[ 0 ] + 1;
}
if( v.size() > 2 ) return -1;
return v[ 0 ] + v[ v.size() - 1 ];
}
int main()
{
scanf( "%d", &n );
for( int i = 1 ; i < n ; i++ )
{
int u, v;
scanf( "%d%d", &u, &v );
addedge( u, v );
}
dfs( 1, 0, 0, d );
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ ) if( d[ i ] > d[ l ] ) l = i;
dfs( l, 0, 0, dl );
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ ) if( dl[ i ] > dl[ r ] ) r = i;
dfs( r, 0, 0, dr );
rt = l;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ )
if( dl[ i ] + dr[ i ] == dl[ r ] && min( dl[ i ], dr[ i ] ) > min( dl[ rt ], dr[ rt ] ) ) rt = i;
ans = solve( rt, rt );
while( ans && !( ans & 1 ) ) ans >>= 1;
cout << ans << endl;
}




















 426
426

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








