为了分析Input场景下ANR发生的原因,特意找了对Input系统全面介绍的一篇文章,如果系统对于Input Event超过预定时间(5s)没有响应,则会弹出ANR提示用户继续等待或者选择FC。通过下面文章对Input事件传递流程的分析,在InputDispatcher.cpp里面会对持有分发锁有一个超时时间(3s),在WMS中才是对事件真正开始计时。
- InputDispatching Timeout: 输入事件分发超时5s,包括按键和触摸事件。
一. 概述
先简单总结和回顾以下前几篇文章的内容:
- Input系统—InputReader线程:通过EventHub从/dev/input节点获取事件,转换成EventEntry事件加入到InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue。
- Input系统—InputDispatcher线程:从mInboundQueue队列取出事件,转换成DispatchEntry事件加入到connection的outboundQueue队列。再然后开始处理分发事件,取出outbound队列,放入waitQueue.
- Input系统—UI线程:创建socket pair,分别位于”InputDispatcher”线程和focused窗口所在进程的UI主线程,可相互通信。
- UI主线程:通过setFdEvents(), 监听socket客户端,收到消息后回调NativeInputEventReceiver();【见小节2.1】
- “InputDispatcher”线程: 通过IMS.registerInputChannel(),监听socket服务端,收到消息后回调handleReceiveCallback;【见小节3.1】
接下来,以按键事件为例,说一说一次事件处理过程是如何完成。按键事件经过InputReader,再到InputDispatcher的startDispatchCycleLocked()过程会调用publishKeyEvent(),从该方法说起。
二. InputDispatcher线程
2.1 InputPublisher.publishKeyEvent
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputPublisher::publishKeyEvent(...) {
if (!seq) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_KEY;
msg.body.key.seq = seq;
msg.body.key.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.key.source = source;
msg.body.key.action = action;
msg.body.key.flags = flags;
msg.body.key.keyCode = keyCode;
msg.body.key.scanCode = scanCode;
msg.body.key.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.key.repeatCount = repeatCount;
msg.body.key.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.key.eventTime = eventTime;
//通过InputChannel来发送消息
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
2.2 InputChannel.sendMessage
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
size_t msgLength = msg->size();
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
//向目标mFd写入消息,采用异步非阻塞方式
nWrite = ::send(mFd, msg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
if (nWrite < 0) {
int error = errno;
if (error == EAGAIN || error == EWOULDBLOCK) {
return WOULD_BLOCK;
}
if (error == EPIPE || error == ENOTCONN || error == ECONNREFUSED || error == ECONNRESET) {
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
return -error;
}
if (size_t(nWrite) != msgLength) {
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
return OK;
}
Input系统—UI线程讲解了会创建socket pair,用于两个进程的线程间相互通信。当mFd写入消息后,此时会唤醒处于epoll_wait状态的应用进程的UI线程,见下文。
另外,当写入失败,则返回值为WOULD_BLOCK或者DEAD_OBJECT。
三. UI主线程
当收到消息的处理过程,Android消息机制在获取下一条消息的时候,会调用lnativePollOnce(),最终进入到Looper::pollInner()过程,如下:
3.1 Looper::pollInner
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
...
int result = POLL_WAKE;
mResponses.clear();
mResponseIndex = 0;
mPolling = true; //即将处于idle状态
struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS]; //fd最大个数为16
//等待事件发生或者超时,在nativeWake()方法,向管道写端写入字符;
int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
mPolling = false; //不再处于idle状态
mLock.lock(); //请求锁
...
//循环遍历,处理所有的事件
for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {
int fd = eventItems[i].data.fd;
uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;
if (fd == mWakeEventFd) {
if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {
awoken(); //已唤醒则读取并清空管道数据
}
} else {
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex >= 0) {
int events = 0;
if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) events |= EVENT_INPUT;
if (epollEvents & EPOLLOUT) events |= EVENT_OUTPUT;
if (epollEvents & EPOLLERR) events |= EVENT_ERROR;
if (epollEvents & EPOLLHUP) events |= EVENT_HANGUP;
//处理request,生成对应的reponse对象,push到mResponses数组
pushResponse(events, mRequests.valueAt(requestIndex));
}
}
}
Done: ;
//再处理Native的Message,调用相应回调方法
while (mMessageEnvelopes.size() != 0) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
//取出消息
const MessageEnvelope& messageEnvelope = mMessageEnvelopes.itemAt(0);
if (messageEnvelope.uptime <= now) {
sp<MessageHandler> handler = messageEnvelope.handler;
Message message = messageEnvelope.message;
mMessageEnvelopes.removeAt(0); //移除该消息
mLock.unlock();
handler->handleMessage(message); // 处理消息事件
}
mLock.lock();
...
}
mLock.unlock(); //释放锁
//处理带有Callback()方法的Response事件,执行Reponse相应的回调方法
for (size_t i = 0; i < mResponses.size(); i++) {
Response& response = mResponses.editItemAt(i);
if (response.request.ident == POLL_CALLBACK) {
int fd = response.request.fd;
int events = response.events;
void* data = response.request.data;
// 处理请求的回调方法【见小节3.2】
int callbackResult = response.request.callback->handleEvent(fd, events, data);
if (callbackResult == 0) {
removeFd(fd, response.request.seq); //移除fd
}
response.request.callback.clear(); //清除reponse引用的回调方法
result = POLL_CALLBACK; // 发生回调
}
}
return result;
}
此处response.request.callback是指NativeInputEventReceiver,接下来便是执行NativeInputEventReceiver.handleEvent();
3.2 handleEvent
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
int NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent(int receiveFd, int events, void* data) {
if (events & (ALOOPER_EVENT_ERROR | ALOOPER_EVENT_HANGUP)) {
return 0; //移除窗口或者IME对话框, 则移除该事件
}
if (events & ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT) {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
//【见小节3.3】
status_t status = consumeEvents(env, false /*consumeBatches*/, -1, NULL);
mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "handleReceiveCallback");
return status == OK || status == NO_MEMORY ? 1 : 0;
}
if (events & ALOOPER_EVENT_OUTPUT) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < mFinishQueue.size(); i++) {
const Finish& finish = mFinishQueue.itemAt(i);
//【见小节3.4】
status_t status = mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal(finish.seq, finish.handled);
if (status) {
mFinishQueue.removeItemsAt(0, i);
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
return 1; //保留callback,稍后重试
}
if (status != DEAD_OBJECT) {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
String8 message;
message.appendFormat("Failed to finish input event. status=%d", status);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.string());
mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "finishInputEvent");
}
return 0; //移除callback
}
}
mFinishQueue.clear();
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT);
return 1;
}
return 1;
}
UI线程收到Key事件后,开始处理该事件。
3.3 NativeInputEventReceiver.consumeEvents
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
...
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> receiverObj(env, NULL);
bool skipCallbacks = false;
for (;;) {
uint32_t seq;
InputEvent* inputEvent;
//【见小节3.3.1】
status_t status = mInputConsumer.consume(&mInputEventFactory,
consumeBatches, frameTime, &seq, &inputEvent);
if (status) {
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
...
return OK; //消费完成
}
return status; //消失失败
}
if (!skipCallbacks) {
if (!receiverObj.get()) {
receiverObj.reset(jniGetReferent(env, mReceiverWeakGlobal));
if (!receiverObj.get()) {
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
}
jobject inputEventObj;
switch (inputEvent->getType()) {
case AINPUT_EVENT_TYPE_KEY:
//由Native的inputEvent来生成Java层的事件
inputEventObj = android_view_KeyEvent_fromNative(env,
static_cast<KeyEvent*>(inputEvent));
break;
...
}
if (inputEventObj) {
//执行Java层的InputEventReceiver.dispachInputEvent【见小节3.3.3】
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
skipCallbacks = true; //分发过程发生异常
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputEventObj);
} else {
skipCallbacks = true;
}
}
if (skipCallbacks) {
//发生异常,则直接向InputDispatcher线程发送完成信号。
mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal(seq, false);
}
}
}
3.3.1 InputConsumer.consume
[->InputTransport.cpp ::InputConsumer]
status_t InputConsumer::consume(InputEventFactoryInterface* factory,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, uint32_t* outSeq, InputEvent** outEvent) {
*outSeq = 0;
*outEvent = NULL;
//循环遍历所有的Event
while (!*outEvent) {
if (mMsgDeferred) {
mMsgDeferred = false; //上一次没有处理的消息
} else {
//收到新消息【见小节3.3.2】
status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&mMsg);
if (result) {
if (consumeBatches || result != WOULD_BLOCK) {
result = consumeBatch(factory, frameTime, outSeq, outEvent);
if (*outEvent) {
break;
}
}
return result;
}
}
switch (mMsg.header.type) {
case InputMessage::TYPE_KEY: {
//从mKeyEventPool池中取出KeyEvent
KeyEvent* keyEvent = factory->createKeyEvent();
if (!keyEvent) return NO_MEMORY;
//将msg封装成KeyEvent
initializeKeyEvent(keyEvent, &mMsg);
*outSeq = mMsg.body.key.seq;
*outEvent = keyEvent;
break;
}
...
}
}
return OK;
}
3.3.2 InputChannel.receiveMessage
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputChannel::receiveMessage(InputMessage* msg) {
ssize_t nRead;
do {
//读取InputDispatcher发送过来的消息
nRead = ::recv(mFd, msg, sizeof(InputMessage), MSG_DONTWAIT);
} while (nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR);
if (nRead < 0) {
int error = errno;
if (error == EAGAIN || error == EWOULDBLOCK) {
return WOULD_BLOCK;
}
if (error == EPIPE || error == ENOTCONN || error == ECONNREFUSED) {
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
return -error;
}
if (nRead == 0) {
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
if (!msg->isValid(nRead)) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
return OK;
}
3.3.3 InputEventReceiver.dispachInputEvent
[-> InputEventReceiver.java]
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
onInputEvent(event); //[见小节3.3.4]
}
3.3.4 onInputEvent
[-> ViewRootImpl.java ::WindowInputEventReceiver]
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
public void onInputEvent(InputEvent event) {
enqueueInputEvent(event, this, 0, true); //【见小节3.3.5】
}
...
}
3.3.5 enqueueInputEvent
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
void enqueueInputEvent(InputEvent event,
InputEventReceiver receiver, int flags, boolean processImmediately) {
adjustInputEventForCompatibility(event);
QueuedInputEvent q = obtainQueuedInputEvent(event, receiver, flags);
QueuedInputEvent last = mPendingInputEventTail;
if (last == null) {
mPendingInputEventHead = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
} else {
last.mNext = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
}
mPendingInputEventCount += 1;
if (processImmediately) {
doProcessInputEvents(); //【见小节3.3.6】
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
}
3.3.6 doProcessInputEvents
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
void doProcessInputEvents() {
while (mPendingInputEventHead != null) {
QueuedInputEvent q = mPendingInputEventHead;
mPendingInputEventHead = q.mNext;
if (mPendingInputEventHead == null) {
mPendingInputEventTail = null;
}
q.mNext = null;
mPendingInputEventCount -= 1;
long eventTime = q.mEvent.getEventTimeNano();
long oldestEventTime = eventTime;
...
mChoreographer.mFrameInfo.updateInputEventTime(eventTime, oldestEventTime);
//[见小节3.3.7]
deliverInputEvent(q);
}
if (mProcessInputEventsScheduled) {
mProcessInputEventsScheduled = false;
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG_PROCESS_INPUT_EVENTS);
}
}
3.3.7 事件分发
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
private void deliverInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onInputEvent(q.mEvent, 0);
}
InputStage stage;
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
if (stage != null) {
stage.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q); //[见小节3.4]
}
}
经过一系列的InputStage调用, 最终会分发到真正需要处理该时间的窗口. 当处理完后会调用finishInputEvent(), 见小节3.4
3.4 finishInputEvent
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
private void finishInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mReceiver != null) {
boolean handled = (q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED_HANDLED) != 0;
//[见小节3.4.1]
q.mReceiver.finishInputEvent(q.mEvent, handled);
} else {
q.mEvent.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();
}
recycleQueuedInputEvent(q);
}
3.4.1 mReceiver.finishInputEvent
public final void finishInputEvent(InputEvent event, boolean handled) {
if (mReceiverPtr == 0) {
...
} else {
int index = mSeqMap.indexOfKey(event.getSequenceNumber());
if (index < 0) {
...
} else {
int seq = mSeqMap.valueAt(index);
mSeqMap.removeAt(index);
//经过层层调用,见[小节3.5]
nativeFinishInputEvent(mReceiverPtr, seq, handled);
}
}
event.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();
}
3.5 sendFinishedSignal
[-> InputTransport.cpp ::InputConsumer]
status_t InputConsumer::sendFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
...
size_t seqChainCount = mSeqChains.size();
if (seqChainCount) {
uint32_t currentSeq = seq;
uint32_t chainSeqs[seqChainCount];
size_t chainIndex = 0;
for (size_t i = seqChainCount; i-- > 0; ) {
const SeqChain& seqChain = mSeqChains.itemAt(i);
if (seqChain.seq == currentSeq) {
currentSeq = seqChain.chain;
chainSeqs[chainIndex++] = currentSeq;
mSeqChains.removeAt(i);
}
}
status_t status = OK;
while (!status && chainIndex-- > 0) {
//[见小节3.5.1]
status = sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(chainSeqs[chainIndex], handled);
}
if (status) {
// An error occurred so at least one signal was not sent, reconstruct the chain.
do {
SeqChain seqChain;
seqChain.seq = chainIndex != 0 ? chainSeqs[chainIndex - 1] : seq;
seqChain.chain = chainSeqs[chainIndex];
mSeqChains.push(seqChain);
} while (chainIndex-- > 0);
return status;
}
}
return sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(seq, handled);
}
3.5.1 sendUnchainedFinishedSignal
[-> InputTransport.cpp ::InputConsumer]
status_t InputConsumer::sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_FINISHED;
msg.body.finished.seq = seq;
msg.body.finished.handled = handled;
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
通过InputChannel->sendMessage,将TYPE_FINISHED类型的消息,发送回InputDispatcher线程。
四. InputDispatcher线程
4.1 Looper::pollInner
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
...
Done:
...
for (size_t i = 0; i < mResponses.size(); i++) {
Response& response = mResponses.editItemAt(i);
if (response.request.ident == POLL_CALLBACK) {
int fd = response.request.fd;
int events = response.events;
void* data = response.request.data;
// 处理请求的回调方法【见小节4.2】
int callbackResult = response.request.callback->handleEvent(fd, events, data);
...
}
}
return result;
}
此处response.request.callback是指SimpleLooperCallback。接下来调用SimpleLooperCallback.handleEvent(). 执行后的返回值callbackResult=0则移除该fd,否则稍后重新尝试。
4.2 handleEvent
[-> Looper.cpp ::SimpleLooperCallback]
SimpleLooperCallback::SimpleLooperCallback(Looper_callbackFunc callback) :
mCallback(callback) {
}
int SimpleLooperCallback::handleEvent(int fd, int events, void* data) {
//handleReceiveCallback()【见小节4.3】
return mCallback(fd, events, data);
}
IMS.registerInputChannel()过程,会调用Looper.addFd()完成的赋值操作,mCallback等于handleReceiveCallback()方法。
4.3 handleReceiveCallback
[-> InputDispatcher]
int InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback(int fd, int events, void* data) {
InputDispatcher* d = static_cast<InputDispatcher*>(data);
{
AutoMutex _l(d->mLock);
ssize_t connectionIndex = d->mConnectionsByFd.indexOfKey(fd);
bool notify;
sp<Connection> connection = d->mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (!(events & (ALOOPER_EVENT_ERROR | ALOOPER_EVENT_HANGUP))) {
...
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
bool gotOne = false;
status_t status;
for (;;) {
uint32_t seq;
bool handled;
//【见小节4.4】
status = connection->inputPublisher.receiveFinishedSignal(&seq, &handled);
if (status) {
break;
}
//【见小节4.5】
d->finishDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, seq, handled);
gotOne = true;
}
if (gotOne) {
d->runCommandsLockedInterruptible(); //执行命令【见小节4.6】
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
return 1;
}
}
notify = status != DEAD_OBJECT || !connection->monitor;
} else {
...
//input channel被关闭或者发生错误
}
//取消注册channel
d->unregisterInputChannelLocked(connection->inputChannel, notify);
return 0;
}
}
4.4 InputPublisher.receiveFinishedSignal
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputPublisher::receiveFinishedSignal(uint32_t* outSeq, bool* outHandled) {
InputMessage msg;
//接收消息
status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&msg);
if (result) {
*outSeq = 0;
*outHandled = false;
return result;
}
if (msg.header.type != InputMessage::TYPE_FINISHED) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR; //发生错误
}
*outSeq = msg.body.finished.seq;
*outHandled = msg.body.finished.handled;
return OK;
}
4.5 finishDispatchCycleLocked
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::finishDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
connection->inputPublisherBlocked = false;
if (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_BROKEN
|| connection->status == Connection::STATUS_ZOMBIE) {
return;
}
//通知系统准备启动下一次分发流程【见小节4.5.1】
onDispatchCycleFinishedLocked(currentTime, connection, seq, handled);
}
4.5.1 onDispatchCycleFinishedLocked
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::onDispatchCycleFinishedLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
//向mCommandQueue添加命令
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
& InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible);
commandEntry->connection = connection;
commandEntry->eventTime = currentTime;
commandEntry->seq = seq;
commandEntry->handled = handled;
}
4.6 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptible() {
if (mCommandQueue.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
do {
//从mCommandQueue队列的头部取出第一个元素【见小节4.6.1】
CommandEntry* commandEntry = mCommandQueue.dequeueAtHead();
Command command = commandEntry->command;
//此处调用的命令隐式地包含'LockedInterruptible'
(this->*command)(commandEntry);
commandEntry->connection.clear();
delete commandEntry;
} while (! mCommandQueue.isEmpty());
return true;
}
由【小节4.5】,可以队列中的元素至少有doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible。
4.6.1 doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible(
CommandEntry* commandEntry) {
sp<Connection> connection = commandEntry->connection;
nsecs_t finishTime = commandEntry->eventTime;
uint32_t seq = commandEntry->seq;
bool handled = commandEntry->handled;
//获取分发事件
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->findWaitQueueEntry(seq);
if (dispatchEntry) {
nsecs_t eventDuration = finishTime - dispatchEntry->deliveryTime;
//打印出所有分发时间超过2s的事件
if (eventDuration > SLOW_EVENT_PROCESSING_WARNING_TIMEOUT) {
String8 msg;
msg.appendFormat("Window '%s' spent %0.1fms processing the last input event: ",
connection->getWindowName(), eventDuration * 0.000001f);
dispatchEntry->eventEntry->appendDescription(msg);
ALOGI("%s", msg.string());
}
bool restartEvent;
if (dispatchEntry->eventEntry->type == EventEntry::TYPE_KEY) {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
restartEvent = afterKeyEventLockedInterruptible(connection,
dispatchEntry, keyEntry, handled);
} else if (dispatchEntry->eventEntry->type == EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION) {
...
} else {
...
}
if (dispatchEntry == connection->findWaitQueueEntry(seq)) {
//将dispatchEntry事件从等待队列(waitQueue)中移除
connection->waitQueue.dequeue(dispatchEntry);
if (restartEvent && connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
connection->outboundQueue.enqueueAtHead(dispatchEntry);
} else {
releaseDispatchEntryLocked(dispatchEntry);
}
}
//启动下一个事件处理循环。
startDispatchCycleLocked(now(), connection);
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 打印出所有分发时间超过2s的事件;
- 将dispatchEntry事件从等待队列(waitQueue)中移除;
- 启动下一个事件处理循环。
五. 总结
5.1 整体框架图
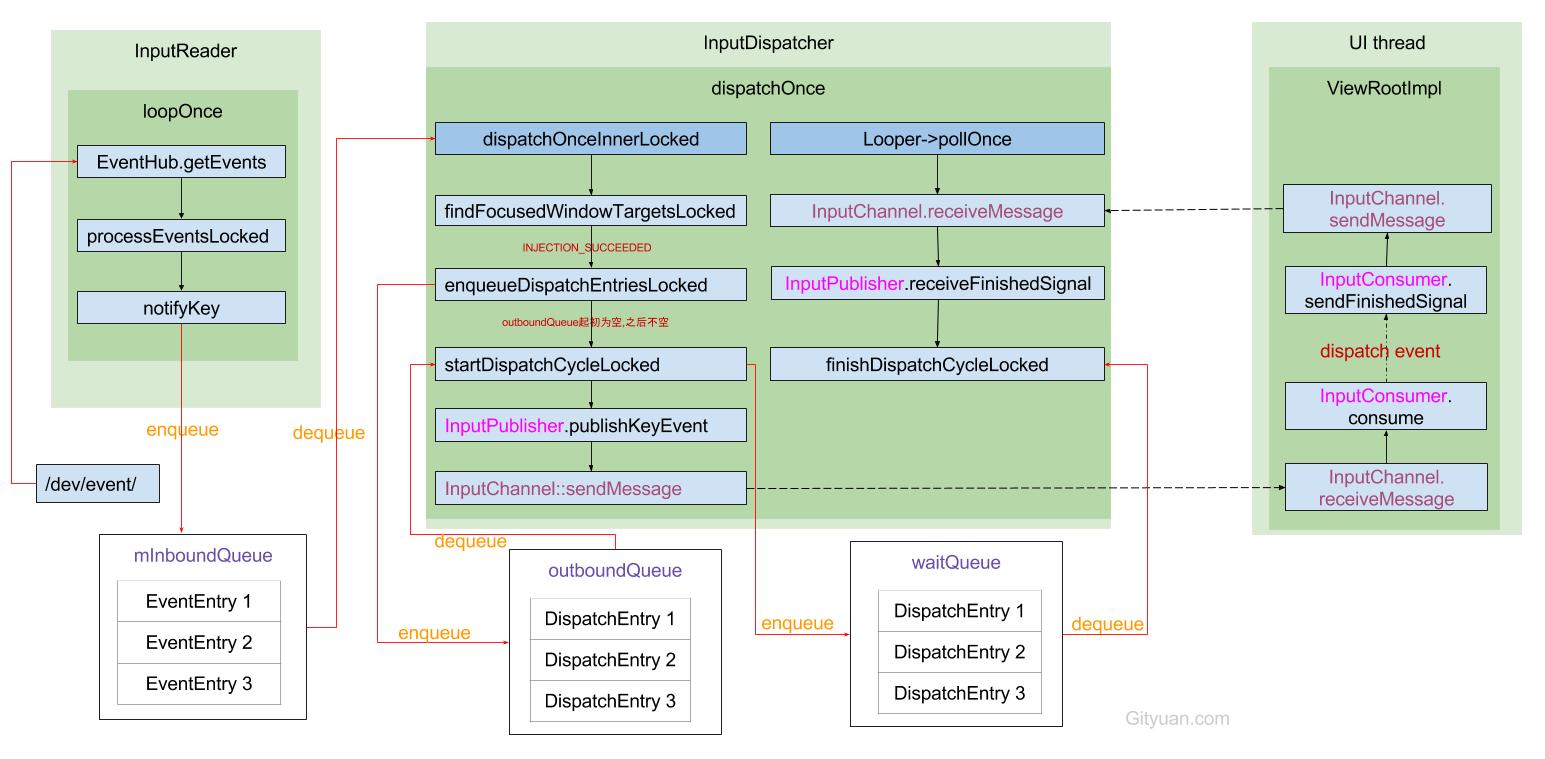
5.2 交互过程
用一张图来总结交互过程,主要是通过一对socket方式来通信。 当input时间分发到app端, 那么便进入来了InputEventReceiver.dispatchInputEvent()过程.
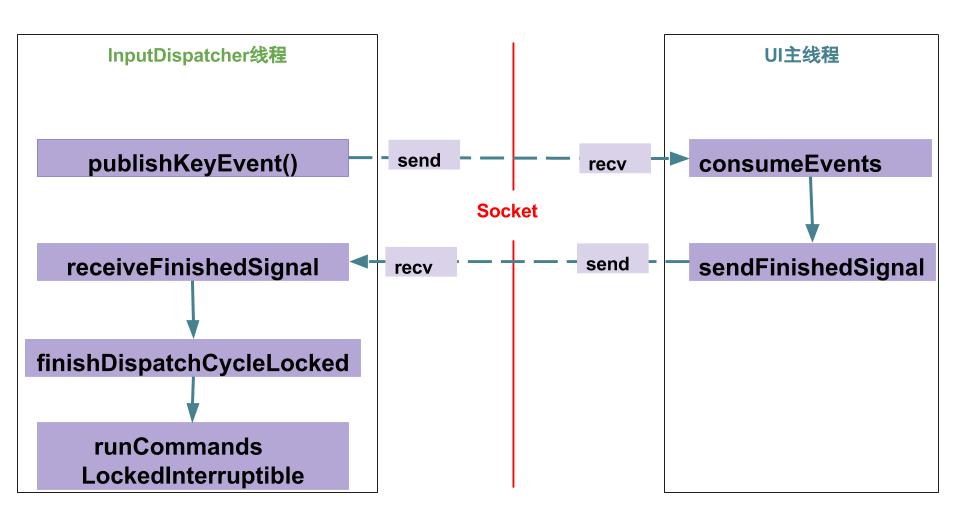
图解:
- InputDispatcher线程调用InputPublisher的publishKeyEvent向UI主线程发送input事件;
- UI主线程接收到该事件后,调用InputConsumer的consumeEvents来处理该事件, 一路执行到ViewRootImpl.deliverInputEvent()方法;
- UI主线程经过一系列的InputStage来处理, 当事件分发完成,则会执行finishInputEvent()方法.再进一步调用InputConsumer::sendFinishedSignal 告知InputDispatcher线程该时事件已处理完成.
- InputDispatcher线程收到该事件后, 执行InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback();最终会调用doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible()方法 ,将dispatchEntry事件从等待队列(waitQueue)中移除.
基于Android 6.0源码, 分析InputManagerService的启动过程
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/
- InputDispatcher.cpp
- InputReader.cpp
- InputManager.cpp
- EventHub.cpp
- InputListener.cpp
frameworks/native/libs/input/
- InputTransport.cpp
- Input.cpp
- InputDevice.cpp
- Keyboard.cpp
- KeyCharacterMap.cpp
- IInputFlinger.cpp
frameworks/base/services/core/
- java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
- jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
一. 概述
当用户触摸屏幕或者按键操作,首次触发的是硬件驱动,驱动收到事件后,将该相应事件写入到输入设备节点, 这便产生了最原生态的内核事件。接着,输入系统取出原生态的事件,经过层层封装后成为KeyEvent或者MotionEvent ;最后,交付给相应的目标窗口(Window)来消费该输入事件。可见,输入系统在整个过程起到承上启下的衔接作用。
Input模块的主要组成:
- Native层的InputReader负责从EventHub取出事件并处理,再交给InputDispatcher;
- Native层的InputDispatcher接收来自InputReader的输入事件,并记录WMS的窗口信息,用于派发事件到合适的窗口;
- Java层的InputManagerService跟WMS交互,WMS记录所有窗口信息,并同步更新到IMS,为InputDispatcher正确派发事件到ViewRootImpl提供保障;
Input相关的动态库:
- libinputflinger.so:frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/
- libinputservice.so:frameworks/base/libs/input/
- libinput.so: frameworks/native/libs/input/
1.1 整体框架类图
InputManagerService作为system_server中的重要服务,继承于IInputManager.Stub, 作为Binder服务端,那么Client位于InputManager的内部通过IInputManager.Stub.asInterface() 获取Binder代理端,C/S两端通信的协议是由IInputManager.aidl来定义的。
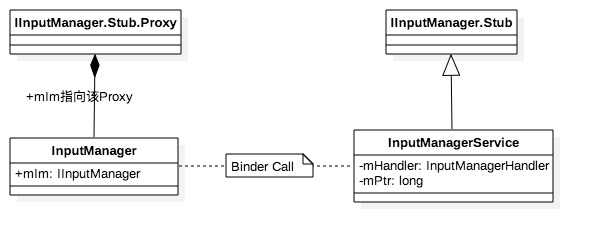
Input模块所涉及的重要类的关系如下:
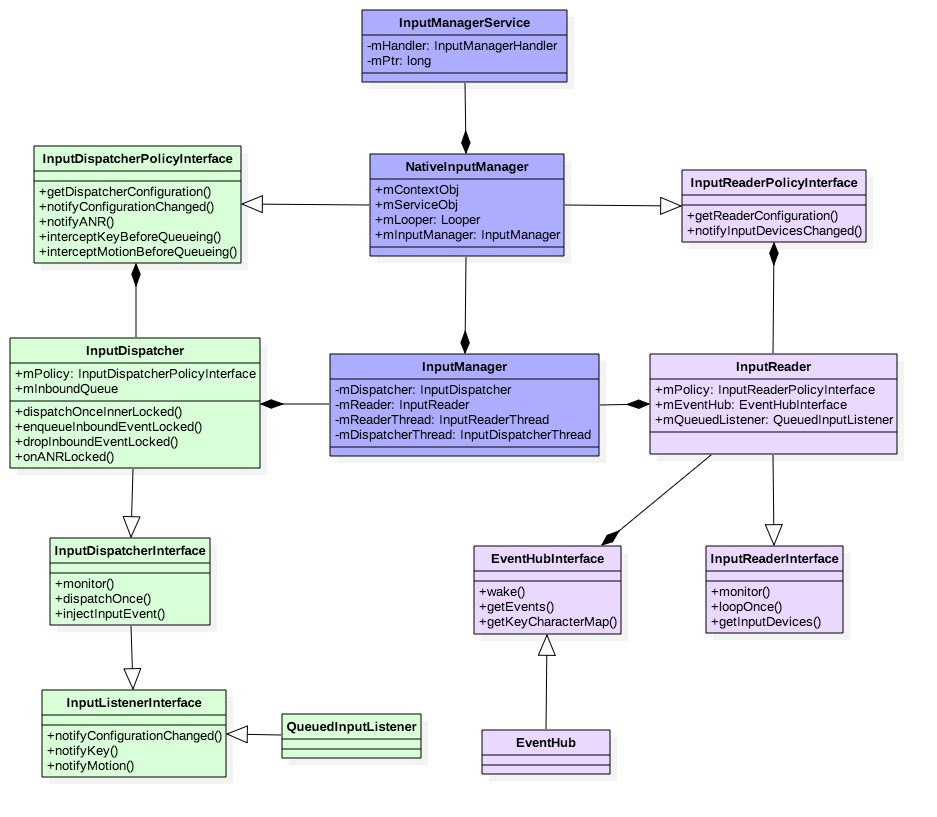
图解:
- InputManagerService位于Java层的InputManagerService.java文件;
- 其成员
mPtr指向Native层的NativeInputManager对象;
- 其成员
- NativeInputManager位于Native层的com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp文件;
- 其成员
mServiceObj指向Java层的IMS对象; - 其成员
mLooper是指“android.display”线程的Looper;
- 其成员
- InputManager位于libinputflinger中的InputManager.cpp文件;
- InputDispatcher和InputReader的成员变量
mPolicy都是指NativeInputManager对象; - InputReader的成员
mQueuedListener,数据类型为QueuedInputListener;通过其内部成员变量mInnerListener指向InputDispatcher对象; 这便是InputReader跟InputDispatcher交互的中间枢纽。
- InputDispatcher和InputReader的成员变量
1.2 启动调用栈
IMS服务是伴随着system_server进程的启动而启动,整个调用过程:
InputManagerService(初始化)
nativeInit
NativeInputManager
EventHub
InputManager
InputDispatcher
Looper
InputReader
QueuedInputListener
InputReaderThread
InputDispatcherThread
IMS.start(启动)
nativeStart
InputManager.start
InputReaderThread->run
InputDispatcherThread->run
整个过程首先创建如下对象:NativeInputManager,EventHub,InputManager, InputDispatcher,InputReader,InputReaderThread,InputDispatcherThread。 接着便是启动两个工作线程InputReader,InputDispatcher。
二. 启动过程
private void startOtherServices() {
//初始化IMS对象【见小节2.1】
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager);
...
//将InputMonitor对象保持到IMS对象
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputMonitor());
//[见小节2.9]
inputManager.start();
}
2.1 InputManagerService
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;
// 运行在线程"android.display"
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());
...
//初始化native对象【见小节2.2】
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());
LocalServices.addService(InputManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
}
2.2 nativeInit
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
//获取native消息队列
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
...
//创建Native的InputManager【见小节2.3】
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,
messageQueue->getLooper());
im->incStrong(0);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im); //返回Native对象的指针
}
2.3 NativeInputManager
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject contextObj,
jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper) :
mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
mContextObj = env->NewGlobalRef(contextObj); //上层IMS的context
mServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(serviceObj); //上层IMS对象
...
sp<EventHub> eventHub = new EventHub(); // 创建EventHub对象【见小节2.4】
mInputManager = new InputManager(eventHub, this, this); // 创建InputManager对象【见小节2.5】
}
此处的mLooper是指“android.display”线程的Looper; libinputservice.so库中PointerController和SpriteController对象都继承于于MessageHandler, 这两个Handler采用的便是该mLooper.
2.4 EventHub
[-> EventHub.cpp]
EventHub::EventHub(void) :
mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD), mNextDeviceId(1), mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(0), mClosingDevices(0),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false), mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0), mPendingEventIndex(0), mPendingINotify(false) {
acquire_wake_lock(PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, WAKE_LOCK_ID);
//创建epoll
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
mINotifyFd = inotify_init();
//此处DEVICE_PATH为"/dev/input",监听该设备路径
int result = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY;
//添加INotify到epoll实例
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);
int wakeFds[2];
result = pipe(wakeFds); //创建管道
mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
//将pipe的读和写都设置为非阻塞方式
result = fcntl(mWakeReadPipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
result = fcntl(mWakeWritePipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_WAKE;
//添加管道的读端到epoll实例
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, &eventItem);
...
}
该方法主要功能:
- 初始化INotify(监听”/dev/input”),并添加到epoll实例
- 创建非阻塞模式的管道,并添加到epoll;
2.5 InputManager
[-> InputManager.cpp]
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
//创建InputDispatcher对象【见小节2.6】
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
//创建InputReader对象【见小节2.7】
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);
initialize();//【见小节2.8】
}
InputDispatcher和InputReader的mPolicy成员变量都是指NativeInputManager对象。
2.6 InputDispatcher
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) :
mPolicy(policy),
mPendingEvent(NULL), mLastDropReason(DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false), mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(NULL),
mDispatchEnabled(false), mDispatchFrozen(false), mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mInputTargetWaitCause(INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE) {
//创建Looper对象
mLooper = new Looper(false);
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = NULL;
//获取分发超时参数
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);
}
该方法主要工作:
- 创建属于自己线程的Looper对象;
- 超时参数来自于IMS,参数默认值keyRepeatTimeout = 500,keyRepeatDelay = 50。
2.7 InputReader
[-> InputReader.cpp]
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1),
mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0) {
// 创建输入监听对象
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
refreshConfigurationLocked(0);
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();
}
}
此处mQueuedListener的成员变量mInnerListener便是InputDispatcher对象。 前面【小节2.5】InputManager创建完InputDispatcher和InputReader对象, 接下里便是调用initialize初始化。
2.8 initialize
[-> InputManager.cpp]
void InputManager::initialize() {
//创建线程“InputReader”
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);
//创建线程”InputDispatcher“
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);
}
InputReaderThread::InputReaderThread(const sp<InputReaderInterface>& reader) :
Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mReader(reader) {
}
InputDispatcherThread::InputDispatcherThread(const sp<InputDispatcherInterface>& dispatcher) :
Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mDispatcher(dispatcher) {
}
初始化的主要工作就是创建两个能访问Java代码的native线程。
- 创建线程“InputReader”
- 创建线程”InputDispatcher“
到此[2.1-2.8]整个的InputManagerService对象初始化过程并完成,接下来便是调用其start方法。
2.9 IMS.start
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public void start() {
// 启动native对象[见小节2.10]
nativeStart(mPtr);
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
//注册触摸点速度和是否显示功能的观察者
registerPointerSpeedSettingObserver();
registerShowTouchesSettingObserver();
mContext.registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings();
updateShowTouchesFromSettings();
}
}, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED), null, mHandler);
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings(); //更新触摸点的速度
updateShowTouchesFromSettings(); //是否在屏幕上显示触摸点
}
2.10 nativeStart
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr) {
//此处ptr记录的便是NativeInputManager
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
// [见小节2.11]
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();
...
}
2.11 InputManager.start
[InputManager.cpp]
status_t InputManager::start() {
result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
...
return OK;
}
该方法的主要功能是启动两个线程:
- 启动线程“InputReader”
- 启动线程”InputDispatcher“
三. 总结
分层视角:
- Java层InputManagerService:采用android.display线程处理Message.
- JNI的NativeInputManager:采用android.display线程处理Message,以及创建EventHub。
- Native的InputManager:创建InputReaderThread和InputDispatcherThread两个线程
主要功能:
- IMS服务中的成员变量mPtr记录Native层的NativeInputManager对象;
- IMS对象的初始化过程的重点在于native初始化,分别创建了以下对象:
- NativeInputManager;
- EventHub, InputManager;
- InputReader,InputDispatcher;
- InputReaderThread,InputDispatcherThread
- IMS启动过程的主要功能是启动以下两个线程:
- InputReader:从EventHub取出事件并处理,再交给InputDispatcher
- InputDispatcher:接收来自InputReader的输入事件,并派发事件到合适的窗口。
从整个启动过程,可知有system_server进程中有3个线程跟Input输入系统息息相关,分别是android.display, InputReader,InputDispatcher。
- InputDispatcher线程:属于Looper线程,会创建属于自己的Looper,循环分发消息;
- InputReader线程:通过getEvents()调用EventHub读取输入事件,循环读取消息;
- android.display线程:属于Looper线程,用于处理Java层的IMS.InputManagerHandler和JNI层的NativeInputManager中指定的MessageHandler消息;
Input事件流程:Linux Kernel -> IMS(InputReader -> InputDispatcher) -> WMS -> ViewRootImpl, 后续再进一步介绍。
四. 附录
最后在列举整个input处理流程中常见的重要对象或结构体,后续input系列文章直接使用以上结构体,可回过来查看。
4.1 InputReader.h
4.1.1 InputDevice
class InputDevice {
...
private:
InputReaderContext* mContext;
int32_t mId;
int32_t mGeneration;
int32_t mControllerNumber;
InputDeviceIdentifier mIdentifier;
String8 mAlias;
uint32_t mClasses;
Vector<InputMapper*> mMappers;
uint32_t mSources;
bool mIsExternal;
bool mHasMic;
bool mDropUntilNextSync;
typedef int32_t (InputMapper::*GetStateFunc)(uint32_t sourceMask, int32_t code);
int32_t getState(uint32_t sourceMask, int32_t code, GetStateFunc getStateFunc);
PropertyMap mConfiguration;
};
4.2 InputDispatcher.h
4.2.1 DropReason
enum DropReason {
DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED = 0, //不丢弃
DROP_REASON_POLICY = 1, //策略
DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH = 2, //应用切换
DROP_REASON_DISABLED = 3, //disable
DROP_REASON_BLOCKED = 4, //阻塞
DROP_REASON_STALE = 5, //过时
};
enum InputTargetWaitCause {
INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE,
INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY, //系统没有准备就绪
INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY, //应用没有准备就绪
};
EventEntry* mPendingEvent;
Queue<EventEntry> mInboundQueue; //需要InputDispatcher分发的事件队列
Queue<EventEntry> mRecentQueue;
Queue<CommandEntry> mCommandQueue;
Vector<sp<InputWindowHandle> > mWindowHandles;
sp<InputWindowHandle> mFocusedWindowHandle; //聚焦窗口
sp<InputApplicationHandle> mFocusedApplicationHandle; //聚焦应用
String8 mLastANRState; //上一次ANR时的分发状态
InputTargetWaitCause mInputTargetWaitCause;
nsecs_t mInputTargetWaitStartTime;
nsecs_t mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime;
bool mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired;
//目标等待的应用
sp<InputApplicationHandle> mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle;
4.2.2 Connection
class Connection : public RefBase {
enum Status {
STATUS_NORMAL, //正常状态
STATUS_BROKEN, //发生无法恢复的错误
STATUS_ZOMBIE //input channel被注销掉
};
Status status; //状态
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel; //永不为空
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle; //可能为空
bool monitor;
InputPublisher inputPublisher;
InputState inputState;
//当socket占满的同时,应用消费某些输入事件之前无法发布事件,则值为true.
bool inputPublisherBlocked;
//需要被发布到connection的事件队列
Queue<DispatchEntry> outboundQueue;
//已发布到connection,但还没有收到来自应用的“finished”响应的事件队列
Queue<DispatchEntry> waitQueue;
}
4.2.3 EventEntry
struct EventEntry : Link<EventEntry> {
mutable int32_t refCount;
int32_t type; //时间类型
nsecs_t eventTime; //事件时间
uint32_t policyFlags;
InjectionState* injectionState;
bool dispatchInProgress; //初始值为false, 分发过程则设置成true
};
此处type的可取值为:
- TYPE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED
- TYPE_DEVICE_RESET
- TYPE_KEY: 按键事件
- TYPE_MOTION: 触摸时间
4.2.4 INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION
enum {
// 内部使用, 正在执行注入操作
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING = -1,
// 事件注入成功
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED = 0,
// 事件注入失败, 由于injector没有权限将聚焦的input事件注入到应用
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED = 1,
// 事件注入失败, 由于没有可用的input target
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED = 2,
// 事件注入失败, 由于超时
INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_TIMED_OUT = 3
};
4.3 InputTransport.h
4.3.1 InputChannel
class InputChannel : public RefBase {
// 创建一对input channels
static status_t openInputChannelPair(const String8& name,
sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel);
status_t sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg); //发送消息
status_t receiveMessage(InputMessage* msg); //接收消息
//获取InputChannel的fd的拷贝
sp<InputChannel> dup() const;
private:
String8 mName;
int mFd;
};
sendMessage的返回值:
- OK: 代表成功;
- WOULD_BLOCK: 代表Channel已满;
- DEAD_OBJECT: 代表Channel已关闭;
receiveMessage的返回值:
- OK: 代表成功;
- WOULD_BLOCK: 代表Channel为空;
- DEAD_OBJECT: 代表Channel已关闭;
4.3.2 InputTarget
struct InputTarget {
enum {
FLAG_FOREGROUND = 1 << 0, //事件分发到前台app
FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED = 1 << 1,
FLAG_SPLIT = 1 << 2, //MotionEvent被拆分成多窗口
FLAG_ZERO_COORDS = 1 << 3,
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS = 1 << 8, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE = 1 << 9, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER = 1 << 10, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT = 1 << 11, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT = 1 << 12, //
FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER = 1 << 13, //
FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED = 1 << 14,
//所有分发模式的掩码
FLAG_DISPATCH_MASK = FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT
| FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER,
};
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel; //目标的inputChannel
int32_t flags;
float xOffset, yOffset; //用于MotionEvent
float scaleFactor; //用于MotionEvent
BitSet32 pointerIds;
};
4.3.3 InputPublisher
class InputPublisher {
public:
//获取输入通道
inline sp<InputChannel> getChannel() { return mChannel; }
status_t publishKeyEvent(...); //将key event发送到input channel
status_t publishMotionEvent(...); //将motion event发送到input channel
//接收来自InputConsumer发送的完成信号
status_t receiveFinishedSignal(uint32_t* outSeq, bool* outHandled);
private:
sp<InputChannel> mChannel;
};
4.3.4 InputConsumer
class InputConsumer {
public:
inline sp<InputChannel> getChannel() { return mChannel; }
status_t consume(...); //消费input channel的事件
//向InputPublisher发送完成信号
status_t sendFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled);
bool hasDeferredEvent() const;
bool hasPendingBatch() const;
private:
sp<InputChannel> mChannel;
InputMessage mMsg; //当前input消息
bool mMsgDeferred;
Vector<Batch> mBatches; //input批量消息
Vector<TouchState> mTouchStates;
Vector<SeqChain> mSeqChains;
status_t consumeBatch(...);
status_t consumeSamples(...);
static void initializeKeyEvent(KeyEvent* event, const InputMessage* msg);
static void initializeMotionEvent(MotionEvent* event, const InputMessage* msg);
}
4.4 input.h
4.4.1 KeyEvent
class KeyEvent : public InputEvent {
...
protected:
int32_t mAction;
int32_t mFlags;
int32_t mKeyCode;
int32_t mScanCode;
int32_t mMetaState;
int32_t mRepeatCount;
nsecs_t mDownTime; //专指按下时间
nsecs_t mEventTime; //事件发生时间(包括down/up等事件)
}
4.4.2 MotionEvent
class MotionEvent : public InputEvent {
...
protected:
int32_t mAction;
int32_t mActionButton;
int32_t mFlags;
int32_t mEdgeFlags;
int32_t mMetaState;
int32_t mButtonState;
float mXOffset;
float mYOffset;
float mXPrecision;
float mYPrecision;
nsecs_t mDownTime; //按下时间
Vector<PointerProperties> mPointerProperties;
Vector<nsecs_t> mSampleEventTimes;
Vector<PointerCoords> mSamplePointerCoords;
};
}
4.5 InputListener.h
4.5.1 NotifyKeyArgs
struct NotifyKeyArgs : public NotifyArgs {
nsecs_t eventTime; //事件发生时间
int32_t deviceId;
uint32_t source;
uint32_t policyFlags;
int32_t action;
int32_t flags;
int32_t keyCode;
int32_t scanCode;
int32_t metaState;
nsecs_t downTime; //按下时间
...
};一. InputReader起点
上一篇文章Input系统—启动篇,介绍IMS服务的启动过程会创建两个native线程,分别是InputReader,InputDispatcher. 接下来从InputReader线程的执行过程从threadLoop为起点开始分析。
1.1 threadLoop
[-> InputReader.cpp]
bool InputReaderThread::threadLoop() {
mReader->loopOnce(); //【见小节1.2】
return true;
}
threadLoop返回值true代表的是会不断地循环调用loopOnce()。另外,如果当返回值为false则会 退出循环。整个过程是不断循环的地调用InputReader的loopOnce()方法,先来回顾一下InputReader对象构造方法。
1.2 loopOnce
[-> InputReader.cpp]
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
...
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
uint32_t changes = mConfigurationChangesToRefresh;
if (changes) {
timeoutMillis = 0;
...
} else if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextTimeout);
}
}
//从EventHub读取事件,其中EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE = 256【见小节2.1】
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) { //处理事件【见小节3.1】
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {
inputDevicesChanged = true;
getInputDevicesLocked(inputDevices);
}
...
} // release lock
if (inputDevicesChanged) { //输入设备发生改变
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);
}
//发送事件到nputDispatcher【见小节4.1】
mQueuedListener->flush();
}
二. EventHub
2.1 getEvents
[-> EventHub.cpp]
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
AutoMutex _l(mLock); //加锁
struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];
RawEvent* event = buffer; //原始事件
size_t capacity = bufferSize; //容量大小为256
bool awoken = false;
for (;;) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
...
if (mNeedToScanDevices) {
mNeedToScanDevices = false;
scanDevicesLocked(); //扫描设备【见小节2.2】
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
}
while (mOpeningDevices != NULL) {
Device* device = mOpeningDevices;
mOpeningDevices = device->next;
event->when = now;
event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
event->type = DEVICE_ADDED; //添加设备的事件
event += 1;
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
...
bool deviceChanged = false;
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {
//从mPendingEventItems读取事件项
const struct epoll_event& eventItem = mPendingEventItems[mPendingEventIndex++];
...
//获取设备ID所对应的device
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(eventItem.data.u32);
Device* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
//从设备不断读取事件,放入到readBuffer
int32_t readSize = read(device->fd, readBuffer,
sizeof(struct input_event) * capacity);
if (readSize == 0 || (readSize < 0 && errno == ENODEV)) {
deviceChanged = true;
closeDeviceLocked(device);//设备已被移除则执行关闭操作
} else if (readSize < 0) {
...
} else if ((readSize % sizeof(struct input_event)) != 0) {
...
} else {
int32_t deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
size_t count = size_t(readSize) / sizeof(struct input_event);
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//获取readBuffer的数据
struct input_event& iev = readBuffer[i];
//将input_event信息, 封装成RawEvent
event->when = nsecs_t(iev.time.tv_sec) * 1000000000LL
+ nsecs_t(iev.time.tv_usec) * 1000LL;
event->deviceId = deviceId;
event->type = iev.type;
event->code = iev.code;
event->value = iev.value;
event += 1;
capacity -= 1;
}
if (capacity == 0) {
mPendingEventIndex -= 1;
break;
}
}
}
...
}
...
mLock.unlock(); //poll之前先释放锁
//等待input事件的到来
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
...
mLock.lock(); //poll之后再次请求锁
if (pollResult < 0) { //出现错误
mPendingEventCount = 0;
if (errno != EINTR) {
usleep(100000); //系统发生错误则休眠1s
}
} else {
mPendingEventCount = size_t(pollResult);
}
}
return event - buffer; //返回所读取的事件个数
}
EventHub采用INotify + epoll机制实现监听目录/dev/input下的设备节点,经过EventHub将input_event结构体 + deviceId 转换成RawEvent结构体,如下:
2.1.1 RawEvent
[-> InputEventReader.h]
struct input_event {
struct timeval time; //事件发生的时间点
__u16 type;
__u16 code;
__s32 value;
};
struct RawEvent {
nsecs_t when; //事件发生的时间店
int32_t deviceId; //产生事件的设备Id
int32_t type; // 事件类型
int32_t code;
int32_t value;
};
此处事件类型:
- DEVICE_ADDED(添加)
- DEVICE_REMOVED(删除)
- FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN(扫描完成)
- type<FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT(其他事件)
getEvents()已完成转换事件转换工作, 接下来,顺便看看设备扫描过程.
2.2 设备扫描
2.2.1 scanDevicesLocked
void EventHub::scanDevicesLocked() {
//此处DEVICE_PATH="/dev/input"【见小节2.3】
status_t res = scanDirLocked(DEVICE_PATH);
...
}
2.2.2 scanDirLocked
status_t EventHub::scanDirLocked(const char *dirname)
{
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char *filename;
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *de;
dir = opendir(dirname);
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
//读取/dev/input/目录下所有的设备节点
while((de = readdir(dir))) {
if(de->d_name[0] == '.' &&
(de->d_name[1] == '\0' ||
(de->d_name[1] == '.' && de->d_name[2] == '\0')))
continue;
strcpy(filename, de->d_name);
//打开相应的设备节点【2.2.3】
openDeviceLocked(devname);
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
2.2.3 openDeviceLocked
status_t EventHub::openDeviceLocked(const char *devicePath) {
char buffer[80];
//打开设备文件
int fd = open(devicePath, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;
//获取设备名
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGNAME(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1){
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.name.setTo(buffer);
}
identifier.bus = inputId.bustype;
identifier.product = inputId.product;
identifier.vendor = inputId.vendor;
identifier.version = inputId.version;
//获取设备物理地址
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPHYS(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.location.setTo(buffer);
}
//获取设备唯一ID
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGUNIQ(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.uniqueId.setTo(buffer);
}
//将identifier信息填充到fd
assignDescriptorLocked(identifier);
//设置fd为非阻塞方式
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
//获取设备ID,分配设备对象内存
int32_t deviceId = mNextDeviceId++;
Device* device = new Device(fd, deviceId, String8(devicePath), identifier);
...
//注册epoll
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
if (mUsingEpollWakeup) {
eventItem.events |= EPOLLWAKEUP;
}
eventItem.data.u32 = deviceId;
if (epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &eventItem)) {
delete device; //添加失败则删除该设备
return -1;
}
...
//【见小节2.2.4】
addDeviceLocked(device);
}
2.2.4 addDeviceLocked
void EventHub::addDeviceLocked(Device* device) {
mDevices.add(device->id, device); //添加到mDevices队列
device->next = mOpeningDevices;
mOpeningDevices = device;
}
介绍了EventHub从设备节点获取事件的流程,当收到事件后接下里便开始处理事件。
三. InputReader
3.1 processEventsLocked
[-> InputReader.cpp]
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {
int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;
while (batchSize < count) {
if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT
|| rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {
break;
}
batchSize += 1; //同一设备的事件打包处理
}
//数据事件的处理【见小节3.3】
processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);
} else {
switch (rawEvent->type) {
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED:
//设备添加【见小节3.2】
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED:
//设备移除
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN:
//设备扫描完成
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);
break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false);//不会发生
break;
}
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}
事件处理总共有下几类类型:
- DEVICE_ADDED(设备增加), [见小节3.2]
- DEVICE_REMOVED(设备移除)
- FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN(设备扫描完成)
- 数据事件[见小节3.4]
先来说说DEVICE_ADDED设备增加的过程。
3.2 设备增加
3.2.1 addDeviceLocked
void InputReader::addDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t deviceId) {
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
if (deviceIndex >= 0) {
return; //已添加的相同设备则不再添加
}
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier = mEventHub->getDeviceIdentifier(deviceId);
uint32_t classes = mEventHub->getDeviceClasses(deviceId);
int32_t controllerNumber = mEventHub->getDeviceControllerNumber(deviceId);
//【见小节3.2.2】
InputDevice* device = createDeviceLocked(deviceId, controllerNumber, identifier, classes);
device->configure(when, &mConfig, 0);
device->reset(when);
mDevices.add(deviceId, device); //添加设备到mDevices
...
}
3.2.2 createDeviceLocked
InputDevice* InputReader::createDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId, int32_t controllerNumber,
const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, uint32_t classes) {
//创建InputDevice对象
InputDevice* device = new InputDevice(&mContext, deviceId, bumpGenerationLocked(),
controllerNumber, identifier, classes);
...
//获取键盘源类型
uint32_t keyboardSource = 0;
int32_t keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NON_ALPHABETIC;
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_KEYBOARD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY) {
keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD) {
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_DPAD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD) {
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_GAMEPAD;
}
//添加键盘类设备InputMapper
if (keyboardSource != 0) {
device->addMapper(new KeyboardInputMapper(device, keyboardSource, keyboardType));
}
//添加鼠标类设备InputMapper
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR) {
device->addMapper(new CursorInputMapper(device));
}
//添加触摸屏设备InputMapper
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT) {
device->addMapper(new MultiTouchInputMapper(device));
} else if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH) {
device->addMapper(new SingleTouchInputMapper(device));
}
...
return device;
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建InputDevice对象,将InputReader的mContext赋给InputDevice对象所对应的变量
- 根据设备类型来创建并添加相对应的InputMapper,同时设置mContext.
input设备类型有很多种,以上代码只列举部分常见的设备以及相应的InputMapper:
- 键盘类设备:KeyboardInputMapper
- 触摸屏设备:MultiTouchInputMapper或SingleTouchInputMapper
- 鼠标类设备:CursorInputMapper
介绍完设备增加过程,继续回到[小节3.1]除了设备的增删,更常见事件便是数据事件,那么接下来介绍数据事件的 处理过程。
3.3 事件处理
3.3.1 processEventsForDeviceLocked
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId,
const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
...
InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
if (device->isIgnored()) {
return; //可忽略则直接返回
}
//【见小节3.3.2】
device->process(rawEvents, count);
}
3.3.2 InputDevice.process
void InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count--; rawEvent++) {
if (mDropUntilNextSync) {
if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
mDropUntilNextSync = false;
}
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_DROPPED) {
mDropUntilNextSync = true;
reset(rawEvent->when);
} else {
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
//调用具体mapper来处理【见小节3.4】
mapper->process(rawEvent);
}
}
}
}
小节[3.2]createDeviceLocked创建设备并添加InputMapper,提到会有多种InputMapper。 这里以KeyboardInputMapper(按键事件)为例来展开说明
3.4 按键事件处理
3.4.1 KeyboardInputMapper.process
[-> InputReader.cpp ::KeyboardInputMapper]
void KeyboardInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
switch (rawEvent->type) {
case EV_KEY: {
int32_t scanCode = rawEvent->code;
int32_t usageCode = mCurrentHidUsage;
mCurrentHidUsage = 0;
if (isKeyboardOrGamepadKey(scanCode)) {
int32_t keyCode;
//获取所对应的KeyCode【见小节3.4.2】
if (getEventHub()->mapKey(getDeviceId(), scanCode, usageCode, &keyCode, &flags)) {
keyCode = AKEYCODE_UNKNOWN;
flags = 0;
}
//【见小节3.4.4】
processKey(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->value != 0, keyCode, scanCode, flags);
}
break;
}
case EV_MSC: ...
case EV_SYN: ...
}
}
3.4.2 EventHub::mapKey
[-> EventHub.cpp]
status_t EventHub::mapKey(int32_t deviceId,
int32_t scanCode, int32_t usageCode, int32_t metaState,
int32_t* outKeycode, int32_t* outMetaState, uint32_t* outFlags) const {
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Device* device = getDeviceLocked(deviceId); //获取设备对象
status_t status = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
if (device) {
sp<KeyCharacterMap> kcm = device->getKeyCharacterMap();
if (kcm != NULL) {
//根据scanCode找到keyCode【见小节3.4.3】
if (!kcm->mapKey(scanCode, usageCode, outKeycode)) {
*outFlags = 0;
status = NO_ERROR;
}
}
}
...
return status;
}
将事件的扫描码(scanCode)转换成键盘码(Keycode)
3.4.3 KeyCharacterMap::mapKey
[-> KeyCharacterMap.cpp]
status_t KeyCharacterMap::mapKey(int32_t scanCode, int32_t usageCode, int32_t* outKeyCode) const {
...
if (scanCode) {
ssize_t index = mKeysByScanCode.indexOfKey(scanCode);
if (index >= 0) {
//根据scanCode找到keyCode
*outKeyCode = mKeysByScanCode.valueAt(index);
return OK;
}
}
*outKeyCode = AKEYCODE_UNKNOWN;
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
再回到[3.4.1],接下来进入如下过程:
3.4.4 InputMapper.processKey
[-> InputReader.cpp]
void KeyboardInputMapper::processKey(nsecs_t when, bool down, int32_t keyCode,
int32_t scanCode, uint32_t policyFlags) {
if (down) {
if (mParameters.orientationAware && mParameters.hasAssociatedDisplay) {
keyCode = rotateKeyCode(keyCode, mOrientation);
}
ssize_t keyDownIndex = findKeyDown(scanCode);
if (keyDownIndex >= 0) {
//mKeyDowns记录着所有按下的键
keyCode = mKeyDowns.itemAt(keyDownIndex).keyCode;
} else {
...
mKeyDowns.push(); //压入栈顶
KeyDown& keyDown = mKeyDowns.editTop();
keyDown.keyCode = keyCode;
keyDown.scanCode = scanCode;
}
mDownTime = when; //记录按下时间点
} else {
ssize_t keyDownIndex = findKeyDown(scanCode);
if (keyDownIndex >= 0) {
//键抬起操作,则移除按下事件
keyCode = mKeyDowns.itemAt(keyDownIndex).keyCode;
mKeyDowns.removeAt(size_t(keyDownIndex));
} else {
return; //键盘没有按下操作,则直接忽略抬起操作
}
}
nsecs_t downTime = mDownTime;
...
//创建NotifyKeyArgs对象, when记录eventTime, downTime记录按下时间;
NotifyKeyArgs args(when, getDeviceId(), mSource, policyFlags,
down ? AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN : AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP,
AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_FROM_SYSTEM, keyCode, scanCode, newMetaState, downTime);
//通知key事件【见小节3.4.5】
getListener()->notifyKey(&args);
}
参数说明:
- mKeyDowns记录着所有按下的键;
- mDownTime记录按下时间点;
- 此处KeyboardInputMapper的mContext指向InputReader,getListener()获取的便是mQueuedListener。 接下来调用该对象的notifyKey.
3.4.5 QueuedInputListener.notifyKey
[-> InputListener.cpp]
void QueuedInputListener::notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args) {
mArgsQueue.push(new NotifyKeyArgs(*args));
}
mArgsQueue的数据类型为Vector<NotifyArgs*>,将该key事件压人该栈顶。 到此,整个事件加工完成, 再然后就是将事件发送给InputDispatcher线程.
四. QueuedListener
4.1 QueuedInputListener.flush
[-> InputListener.cpp]
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
//【见小节4.2】
args->notify(mInnerListener);
delete args;
}
mArgsQueue.clear();
}
从InputManager对象初始化的过程可知,mInnerListener便是InputDispatcher对象。
4.2 NotifyKeyArgs.notify
[-> InputListener.cpp]
void NotifyKeyArgs::notify(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) const {
listener->notifyKey(this); // this是指NotifyKeyArgs【见小节4.3】
}
4.3 InputDispatcher.notifyKey
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args) {
if (!validateKeyEvent(args->action)) {
return;
}
...
int32_t keyCode = args->keyCode;
if (keyCode == AKEYCODE_HOME) {
if (args->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) {
property_set("sys.domekey.down", "1");
} else if (args->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP) {
property_set("sys.domekey.down", "0");
}
}
if (metaState & AMETA_META_ON && args->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) {
...
} else if (args->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP) {
...
}
KeyEvent event; //初始化KeyEvent对象
event.initialize(args->deviceId, args->source, args->action,
flags, keyCode, args->scanCode, metaState, 0,
args->downTime, args->eventTime);
//mPolicy是指NativeInputManager对象。【小节4.3.1】
mPolicy->interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(&event, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
bool needWake;
{
mLock.lock();
if (shouldSendKeyToInputFilterLocked(args)) {
mLock.unlock();
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_FILTERED;
//当inputEventObj不为空, 则事件被filter所拦截【见小节4.3.2】
if (!mPolicy->filterInputEvent(&event, policyFlags)) {
return;
}
mLock.lock();
}
int32_t repeatCount = 0;
//创建KeyEntry对象
KeyEntry* newEntry = new KeyEntry(args->eventTime,
args->deviceId, args->source, policyFlags,
args->action, flags, keyCode, args->scanCode,
metaState, repeatCount, args->downTime);
//将KeyEntry放入队列【见小节4.3.3】
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry);
mLock.unlock();
}
if (needWake) {
//唤醒InputDispatcher线程【见小节4.3.5】
mLooper->wake();
}
}
该方法的主要功能:
- 调用NativeInputManager.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing,加入队列前执行拦截动作,但并不改变流程,调用链:
- IMS.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing
- InputMonitor.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing (继承IMS.WindowManagerCallbacks)
- PhoneWindowManager.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing (继承WindowManagerPolicy)
- 当mInputFilterEnabled=true(该值默认为false,可通过setInputFilterEnabled设置),则调用NativeInputManager.filterInputEvent过滤输入事件;
- 当返回值为false则过滤该事件,不再往下分发;
- 生成KeyEvent,并调用enqueueInboundEventLocked,将该事件加入到InputDispatcherd的成员变量mInboundQueue。
4.3.1 interceptKeyBeforeQueueing
void NativeInputManager::interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(const KeyEvent* keyEvent,
uint32_t& policyFlags) {
...
if ((policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED)) {
nsecs_t when = keyEvent->getEventTime(); //时间
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
jobject keyEventObj = android_view_KeyEvent_fromNative(env, keyEvent);
if (keyEventObj) {
// 调用Java层的IMS.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing
wmActions = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing,
keyEventObj, policyFlags);
...
} else {
...
}
handleInterceptActions(wmActions, when, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
} else {
...
}
}
该方法会调用Java层的InputManagerService的interceptKeyBeforeQueueing()方法。
4.3.2 filterInputEvent
bool NativeInputManager::filterInputEvent(const InputEvent* inputEvent, uint32_t policyFlags) {
jobject inputEventObj;
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
switch (inputEvent->getType()) {
case AINPUT_EVENT_TYPE_KEY:
inputEventObj = android_view_KeyEvent_fromNative(env,
static_cast<const KeyEvent*>(inputEvent));
break;
case AINPUT_EVENT_TYPE_MOTION:
inputEventObj = android_view_MotionEvent_obtainAsCopy(env,
static_cast<const MotionEvent*>(inputEvent));
break;
default:
return true; // 走事件正常的分发流程
}
if (!inputEventObj) {
return true; // 当inputEventObj为空, 则走事件正常的分发流程
}
//当inputEventObj不为空,则调用Java层的IMS.filterInputEvent()
jboolean pass = env->CallBooleanMethod(mServiceObj, gServiceClassInfo.filterInputEvent,
inputEventObj, policyFlags);
if (checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "filterInputEvent")) {
pass = true; //出现Exception,则走事件正常的分发流程
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputEventObj);
return pass;
}
当inputEventObj不为空,则调用Java层的IMS.filterInputEvent(). 经过层层调用后, 最终会再调用InputDispatcher.injectInputEvent(),该基本等效于该方法的后半段:
- enqueueInboundEventLocked
- wakeup
4.3.3 enqueueInboundEventLocked
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
bool needWake = mInboundQueue.isEmpty();
mInboundQueue.enqueueAtTail(entry); //将该事件放入mInboundQueue队列尾部
switch (entry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(entry);
if (isAppSwitchKeyEventLocked(keyEntry)) {
if (keyEntry->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) {
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown = true; //按下事件
} else if (keyEntry->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP) {
if (mAppSwitchSawKeyDown) {
//其中APP_SWITCH_TIMEOUT=500ms
mAppSwitchDueTime = keyEntry->eventTime + APP_SWITCH_TIMEOUT;
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown = false;
needWake = true;
}
}
}
break;
}
case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
//当前App无响应且用户希望切换到其他应用窗口,则drop该窗口事件,并处理其他窗口事件
MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(entry);
if (motionEntry->action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN
&& (motionEntry->source & AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER)
&& mInputTargetWaitCause == INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY
&& mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle != NULL) {
int32_t displayId = motionEntry->displayId;
int32_t x = int32_t(motionEntry->pointerCoords[0].
getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_X));
int32_t y = int32_t(motionEntry->pointerCoords[0].
getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_Y));
//查询可触摸的窗口【见小节4.3.4】
sp<InputWindowHandle> touchedWindowHandle = findTouchedWindowAtLocked(displayId, x, y);
if (touchedWindowHandle != NULL
&& touchedWindowHandle->inputApplicationHandle
!= mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle) {
mNextUnblockedEvent = motionEntry;
needWake = true;
}
}
break;
}
}
return needWake;
}
AppSwitchKeyEvent是指keyCode等于以下值:
- AKEYCODE_HOME
- AKEYCODE_ENDCALL
- AKEYCODE_APP_SWITCH
4.3.4 findTouchedWindowAtLocked
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
sp<InputWindowHandle> InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked(int32_t displayId,
int32_t x, int32_t y) {
//从前台到后台来遍历查询可触摸的窗口
size_t numWindows = mWindowHandles.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numWindows; i++) {
sp<InputWindowHandle> windowHandle = mWindowHandles.itemAt(i);
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
if (windowInfo->displayId == displayId) {
int32_t flags = windowInfo->layoutParamsFlags;
if (windowInfo->visible) {
if (!(flags & InputWindowInfo::FLAG_NOT_TOUCHABLE)) {
bool isTouchModal = (flags & (InputWindowInfo::FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
| InputWindowInfo::FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL)) == 0;
if (isTouchModal || windowInfo->touchableRegionContainsPoint(x, y)) {
return windowHandle; //找到目标窗口
}
}
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
此处mWindowHandles的赋值过程是由Java层的InputMonitor.setInputWindows(),经过JNI调用后进入InputDispatcher::setInputWindows()方法完成. 进一步说, 就是WMS执行addWindow()过程或许UI改变等场景,都会触发该方法的修改.
4.3.5 Looper.wake
[-> system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp]
void Looper::wake() {
uint64_t inc = 1;
ssize_t nWrite = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(write(mWakeEventFd, &inc, sizeof(uint64_t)));
if (nWrite != sizeof(uint64_t)) {
if (errno != EAGAIN) {
ALOGW("Could not write wake signal, errno=%d", errno);
}
}
}
[小节4.3]的过程会调用enqueueInboundEventLocked()方法来决定是否需要将数字1写入句柄mWakeEventFd来唤醒InputDispatcher线程. 满足唤醒的条件:
- 执行enqueueInboundEventLocked方法前,mInboundQueue队列为空,执行完必然不再为空,则需要唤醒分发线程;
- 当事件类型为key事件,且发生一对按下和抬起操作,则需要唤醒;
- 当事件类型为motion事件,且当前可触摸的窗口属于另一个应用,则需要唤醒.
五. 总结
5.1 核心工作
InputReader整个过程涉及多次事件封装转换,其主要工作核心是以下三大步骤:
- getEvents:通过EventHub(监听目录/dev/input)读取事件放入mEventBuffer,而mEventBuffer是一个大小为256的数组, 再将事件input_event转换为RawEvent; [见小节2.1]
- processEventsLocked: 对事件进行加工, 转换RawEvent -> NotifyKeyArgs(NotifyArgs) [见小节3.1]
- QueuedListener->flush:将事件发送到InputDispatcher线程, 转换NotifyKeyArgs -> KeyEntry(EventEntry) [见小节4.1]
InputReader线程不断循环地执行InputReader.loopOnce(), 每次处理完生成的是EventEntry(比如KeyEntry, MotionEntry), 接下来的工作就交给InputDispatcher线程。
5.2 流程图
点击查看大图:
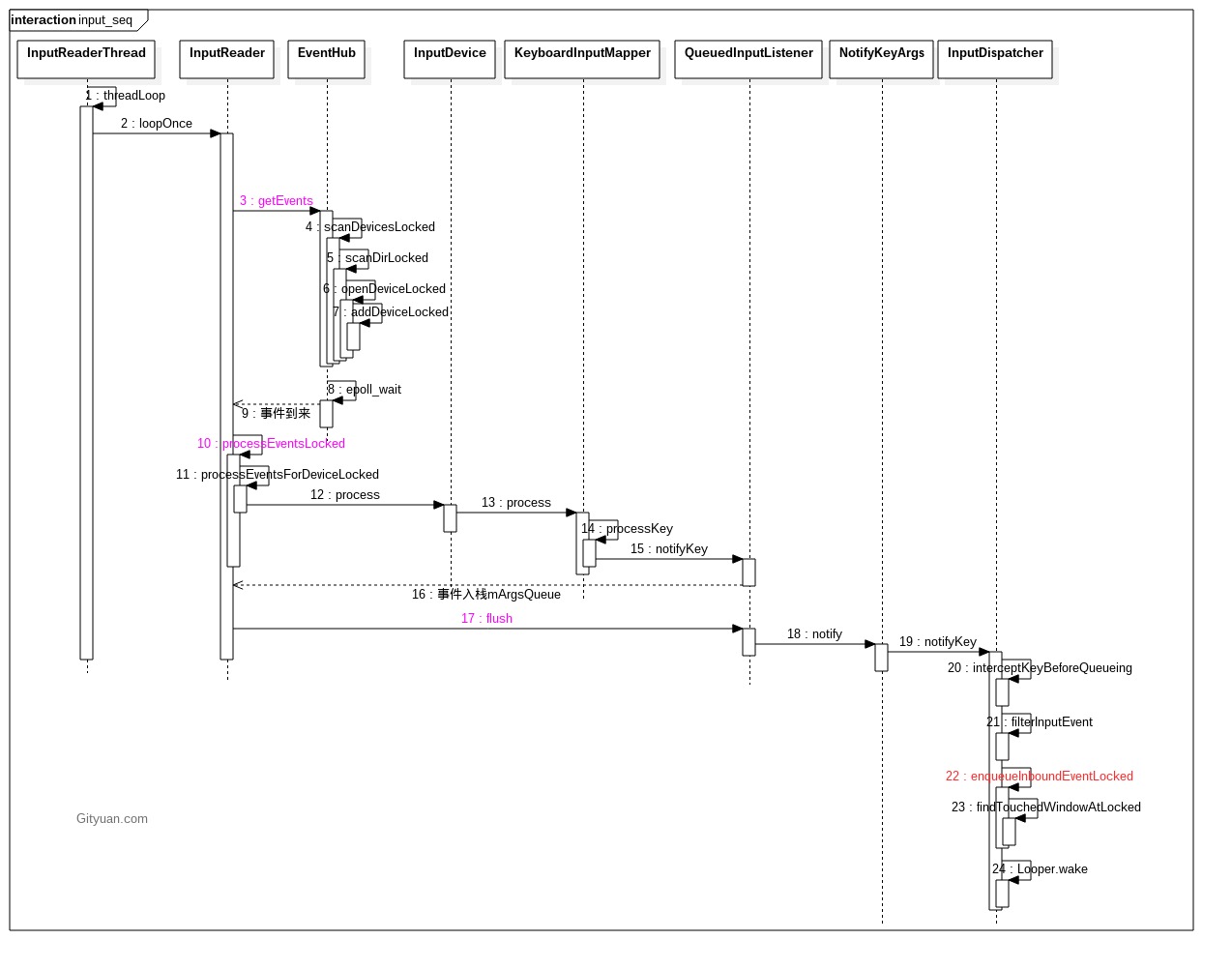
InputReader的核心工作就是从EventHub获取数据后生成EventEntry事件,加入到InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue队列,再唤醒InputDispatcher线程。
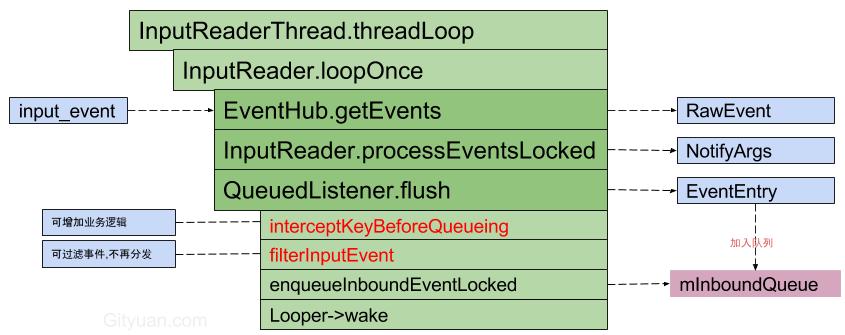
说明:
- IMS.filterInputEvent可以过滤无需上报的事件,当该方法返回值为false则代表是需要被过滤掉的事件,无机会交给InputDispatcher来分发。
- 节点/dev/input的event事件所对应的输入设备信息位于
/proc/bus/input/devices,也可以通过getevent来获取事件. 不同的input事件所对应的物理input节点,比如常见的情形:- 屏幕触摸和(MENU,HOME,BACK)3按键:对应同一个input设备节点;
- POWER和音量(下)键:对应同一个input设备节点;
- 音量(上)键:对应同一个input设备节点;
一. InputDispatcher起点
上篇文章输入系统之InputReader线程,介绍InputReader利用EventHub获取数据后生成EventEntry事件,加入到InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue队列,再唤醒InputDispatcher线程。本文将介绍InputDispatcher,同样从threadLoop为起点开始分析。
1.1 threadLoop
先来回顾一下InputDispatcher对象的初始化过程:
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) :
mPolicy(policy),
mPendingEvent(NULL), mLastDropReason(DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false), mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(NULL),
mDispatchEnabled(false), mDispatchFrozen(false), mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mInputTargetWaitCause(INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE) {
//创建Looper对象
mLooper = new Looper(false);
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = NULL;
//获取分发超时参数
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);
}
该方法主要工作:
- 创建属于自己线程的Looper对象;
- 超时参数来自于IMS,参数默认值keyRepeatTimeout = 500,keyRepeatDelay = 50。
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
bool InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop() {
mDispatcher->dispatchOnce(); //【见小节1.2】
return true;
}
整个过程不断循环地调用InputDispatcher的dispatchOnce()来分发事件
1.2 dispatchOnce
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
//唤醒等待线程,monitor()用于监控dispatcher是否发生死锁
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
//当mCommandQueue不为空时处理【见小节2.1】
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
//【见小节3.1】
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis); //进入epoll_wait
}
线程执行Looper->pollOnce,进入epoll_wait等待状态,当发生以下任一情况则退出等待状态:
- callback:通过回调方法来唤醒;
- timeout:到达nextWakeupTime时间,超时唤醒;
- wake: 主动调用Looper的wake()方法;
二. InputDispatcher
2.1 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now(); //当前时间
if (!mDispatchEnabled) { //默认值为false
resetKeyRepeatLocked(); //重置操作
}
if (mDispatchFrozen) { //默认值为false
return; //当分发被冻结,则不再处理超时和分发事件的工作,直接返回
}
//优化app切换延迟,当切换超时,则抢占分发,丢弃其他所有即将要处理的事件。
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;
...
if (!mPendingEvent) {
if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
if (!mPendingEvent) {
return; //没有事件需要处理,则直接返回
}
} else {
//从mInboundQueue取出头部的事件
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.dequeueAtHead();
}
...
resetANRTimeoutsLocked(); //重置ANR信息[见小节2.1.1]
}
bool done = false;
DropReason dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED;
if (!(mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_POLICY;
} else if (!mDispatchEnabled) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_DISABLED;
}
...
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* typedEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
if (isAppSwitchDue) {
if (isAppSwitchKeyEventLocked(typedEntry)) {
resetPendingAppSwitchLocked(true);
isAppSwitchDue = false;
} else if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH;
}
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED
&& isStaleEventLocked(currentTime, typedEntry)) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_BLOCKED;
}
// 分发按键事件[见小节2.2]
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, typedEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
...
}
...
//分发操作完成,则进入该分支
if (done) {
if (dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
//[见小节2.1.2]
dropInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent, dropReason);
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
releasePendingEventLocked(); //释放pending事件见小节2.10]
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; //强制立刻执行轮询
}
}
在enqueueInboundEventLocked()的过程中已设置mAppSwitchDueTime等于eventTime加上500ms:
mAppSwitchDueTime = keyEntry->eventTime + APP_SWITCH_TIMEOUT;
该方法主要功能:
- mDispatchFrozen用于决定是否冻结事件分发工作不再往下执行;
- 当事件分发的时间点距离该事件加入mInboundQueue的时间超过500ms,则认为app切换过期,即isAppSwitchDue=true;
- mInboundQueue不为空,则取出头部的事件,放入mPendingEvent变量;并重置ANR时间;
- 根据EventEntry的type类型分别处理,比如按键调用dispatchKeyLocked分发事件;再根据分发结果来决定是否进入done;
- 执行完成(done)的处理:
- 根据dropReason(默认NOT_DROPPED不处理)来决定是否丢失事件; dropInboundEventLocked
- 释放当前正在处理的事件(即mPendingEvent); releasePendingEventLocked
关于dispatchKeyLocked分发事件,
- 不会执行done过情况:
- 当前Event时间小于唤醒时间;
- 让policy有机会执行拦截操作;
- 调用findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked方法的返回结果是INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING, 即targets没有处于Ready状态;
- 会执行done的情况:
- 该事件需要丢弃, 即dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED;
- findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked的返回结果不是INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING(没有正在处理的事件);
接下来以按键为例来展开说明, 则进入[小节2.2] dispatchKeyLocked.
2.1.1 resetANRTimeoutsLocked
void InputDispatcher::resetANRTimeoutsLocked() {
// 重置等待超时cause和handle
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
}
2.1.2 dropInboundEventLocked
void InputDispatcher::dropInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry, DropReason dropReason) {
const char* reason;
switch (dropReason) {
case DROP_REASON_POLICY:
reason = "inbound event was dropped because the policy consumed it";
break;
case DROP_REASON_DISABLED:
if (mLastDropReason != DROP_REASON_DISABLED) {
ALOGI("Dropped event because input dispatch is disabled.");
}
reason = "inbound event was dropped because input dispatch is disabled";
break;
case DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH:
ALOGI("Dropped event because of pending overdue app switch.");
reason = "inbound event was dropped because of pending overdue app switch";
break;
case DROP_REASON_BLOCKED:
ALOGI("Dropped event because the current application is not responding and the user "
"has started interacting with a different application.");
reason = "inbound event was dropped because the current application is not responding "
"and the user has started interacting with a different application";
break;
case DROP_REASON_STALE:
ALOGI("Dropped event because it is stale.");
reason = "inbound event was dropped because it is stale";
break;
default:
return;
}
switch (entry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
CancelationOptions options(CancelationOptions::CANCEL_NON_POINTER_EVENTS, reason);
synthesizeCancelationEventsForAllConnectionsLocked(options);
break;
}
...
}
}
2.2 dispatchKeyLocked
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchKeyLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, KeyEntry* entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
...
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_TRY_AGAIN_LATER) {
// case1: 当前时间小于唤醒时间,则进入等待状态。
if (currentTime < entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime) {
if (entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime;
}
return false; //直接返回
}
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_UNKNOWN;
entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime = 0;
}
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_UNKNOWN) {
//case2: 让policy有机会执行拦截操作
if (entry->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
& InputDispatcher::doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingLockedInterruptible);
if (mFocusedWindowHandle != NULL) {
commandEntry->inputWindowHandle = mFocusedWindowHandle;
}
commandEntry->keyEntry = entry;
entry->refCount += 1;
return false; //直接返回
} else {
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_CONTINUE;
}
} else if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_SKIP) {
if (*dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
*dropReason = DROP_REASON_POLICY;
}
}
//case3: 如果需要丢弃该事件,则执行清理操作
if (*dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
setInjectionResultLocked(entry, *dropReason == DROP_REASON_POLICY
? INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED : INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED);
return true; //直接返回
}
Vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
//case4: 寻找焦点 【见小节2.3】
int32_t injectionResult = findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
if (injectionResult == INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING) {
return false; //直接返回
}
setInjectionResultLocked(entry, injectionResult);
if (injectionResult != INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED) {
return true; //直接返回
}
addMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets);
//只有injectionResult是成功,才有机会执行分发事件【见小节2.5】
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
在以下场景下,有可能无法分发事件:
- 当前时间小于唤醒时间(nextWakeupTime)的情况;
- policy需要提前拦截事件的情况;
- 需要drop事件的情况;
- 寻找聚焦窗口失败的情况;
如果成功跳过以上所有情况,则会进入执行事件分发的过程。
2.3 findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked
int32_t InputDispatcher::findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const EventEntry* entry, Vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
int32_t injectionResult;
String8 reason;
if (mFocusedWindowHandle == NULL) {
if (mFocusedApplicationHandle != NULL) {
//【见小节2.3.2】
injectionResult = handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(currentTime, entry,
mFocusedApplicationHandle, NULL, nextWakeupTime,
"Waiting because no window has focus but there is a "
"focused application that may eventually add a window "
"when it finishes starting up.");
goto Unresponsive;
}
ALOGI("Dropping event because there is no focused window or focused application.");
injectionResult = INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED;
goto Failed;
}
//权限检查
if (! checkInjectionPermission(mFocusedWindowHandle, entry->injectionState)) {
injectionResult = INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED;
goto Failed;
}
//检测窗口是否为更多的输入操作而准备就绪【见小节2.3.1】
reason = checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked(currentTime,
mFocusedWindowHandle, entry, "focused");
if (!reason.isEmpty()) {
//【见小节2.3.2】
injectionResult = handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(currentTime, entry,
mFocusedApplicationHandle, mFocusedWindowHandle, nextWakeupTime, reason.string());
goto Unresponsive;
}
injectionResult = INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED;
//成功找到目标窗口,添加到目标窗口 [见小节2.3.3]
addWindowTargetLocked(mFocusedWindowHandle,
InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS, BitSet32(0),
inputTargets);
Failed:
Unresponsive:
//TODO: 统计等待时长信息,目前没有实现,这个方法还是很值得去改造
nsecs_t timeSpentWaitingForApplication = getTimeSpentWaitingForApplicationLocked(currentTime);
updateDispatchStatisticsLocked(currentTime, entry,
injectionResult, timeSpentWaitingForApplication);
return injectionResult;
}
此处mFocusedWindowHandle是何处赋值呢?是在InputDispatcher.setInputWindows()方法,具体见下一篇文章Input系统—UI线程.
寻找聚焦窗口失败的情况:
- 无窗口,无应用:Dropping event because there is no focused window or focused application.(这并不导致ANR的情况,因为没有机会调用handleTargetsNotReadyLocked)
- 无窗口, 有应用:Waiting because no window has focus but there is a focused application that may eventually add a window when it finishes starting up.
另外,还有更多多的失败场景见checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked的过程,如下:
2.3.1 checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked
String8 InputDispatcher::checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle, const EventEntry* eventEntry,
const char* targetType) {
//当窗口暂停的情况,则保持等待
if (windowHandle->getInfo()->paused) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window is paused.", targetType);
}
//当窗口连接未注册,则保持等待
ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(windowHandle->getInputChannel());
if (connectionIndex < 0) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window's input channel is not "
"registered with the input dispatcher. The window may be in the process "
"of being removed.", targetType);
}
//当窗口连接已死亡,则保持等待
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window's input connection is %s."
"The window may be in the process of being removed.", targetType,
connection->getStatusLabel());
}
// 当窗口连接已满,则保持等待
if (connection->inputPublisherBlocked) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window's input channel is full. "
"Outbound queue length: %d. Wait queue length: %d.",
targetType, connection->outboundQueue.count(), connection->waitQueue.count());
}
if (eventEntry->type == EventEntry::TYPE_KEY) {
// 按键事件,输出队列或事件等待队列不为空
if (!connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty() || !connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()) {
return String8::format("Waiting to send key event because the %s window has not "
"finished processing all of the input events that were previously "
"delivered to it. Outbound queue length: %d. Wait queue length: %d.",
targetType, connection->outboundQueue.count(), connection->waitQueue.count());
}
} else {
// 非按键事件,事件等待队列不为空且头事件分发超时500ms
if (!connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()
&& currentTime >= connection->waitQueue.head->deliveryTime
+ STREAM_AHEAD_EVENT_TIMEOUT) {
return String8::format("Waiting to send non-key event because the %s window has not "
"finished processing certain input events that were delivered to it over "
"%0.1fms ago. Wait queue length: %d. Wait queue head age: %0.1fms.",
targetType, STREAM_AHEAD_EVENT_TIMEOUT * 0.000001f,
connection->waitQueue.count(),
(currentTime - connection->waitQueue.head->deliveryTime) * 0.000001f);
}
}
return String8::empty();
}
2.3.2 handleTargetsNotReadyLocked
int32_t InputDispatcher::handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const EventEntry* entry,
const sp<InputApplicationHandle>& applicationHandle,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,
nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime, const char* reason) {
if (applicationHandle == NULL && windowHandle == NULL) {
if (mInputTargetWaitCause != INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY) {
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY;
mInputTargetWaitStartTime = currentTime; //当前时间
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired = false;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
}
} else {
if (mInputTargetWaitCause != INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY) {
nsecs_t timeout;
if (windowHandle != NULL) {
timeout = windowHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
} else if (applicationHandle != NULL) {
timeout = applicationHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
} else {
timeout = DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT; // 5s
}
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY;
mInputTargetWaitStartTime = currentTime; //当前时间
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = currentTime + timeout;
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired = false;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
if (windowHandle != NULL) {
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle = windowHandle->inputApplicationHandle;
}
if (mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle == NULL && applicationHandle != NULL) {
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle = applicationHandle;
}
}
}
if (mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired) {
return INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_TIMED_OUT; //等待超时已过期,则直接返回
}
//当超时5s则进入ANR流程
if (currentTime >= mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime) {
onANRLocked(currentTime, applicationHandle, windowHandle,
entry->eventTime, mInputTargetWaitStartTime, reason);
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; //强制立刻执行轮询来执行ANR策略
return INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING;
} else {
if (mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime; //当触发超时则强制执行轮询
}
return INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING;
}
}
此处mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime是由当前时间戳+5s, 并设置mInputTargetWaitCause等于INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY. 也就是说ANR时间段是指input等待理由处于INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY(应用没有准备就绪)的时间长达5s的场景.而前面resetANRTimeoutsLocked() 过程是唯一用于重置等待理由的地方.
那么, ANR时间区间是指当前这次的事件dispatch过程中执行findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked()方法到下一次执行resetANRTimeoutsLocked()的时间区间.
- 当applicationHandle和windowHandle同时为空, 且system准备就绪的情况下
- 设置等待理由 INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY;
- 设置超时等待时长为无限大;
- 设置TimeoutExpired= false
- 清空等待队列;
- 当applicationHandle和windowHandle至少一个不为空, 且application准备就绪的情况下:
- 设置等待理由 INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY;
- 设置超时等待时长为5s;
- 设置TimeoutExpired= false
- 清空等待队列;
继续回到[小节2.3]findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked,如果没有发生ANR,则addWindowTargetLocked()将该事件添加到inputTargets。
2.3.3 addWindowTargetLocked
void InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked(const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,
int32_t targetFlags, BitSet32 pointerIds, Vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
inputTargets.push();
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
InputTarget& target = inputTargets.editTop();
target.inputChannel = windowInfo->inputChannel;
target.flags = targetFlags;
target.xOffset = - windowInfo->frameLeft;
target.yOffset = - windowInfo->frameTop;
target.scaleFactor = windowInfo->scaleFactor;
target.pointerIds = pointerIds;
}
将当前聚焦窗口mFocusedWindowHandle的inputChannel传递到inputTargets。
2.4 dispatchEventLocked
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
EventEntry* eventEntry, const Vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
//【见小节2.4.1】向mCommandQueue队列添加doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible命令
pokeUserActivityLocked(eventEntry);
for (size_t i = 0; i < inputTargets.size(); i++) {
const InputTarget& inputTarget = inputTargets.itemAt(i);
//[见小节2.4.3]
ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel);
if (connectionIndex >= 0) {
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
//找到目标连接[见小节2.5]
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, &inputTarget);
}
}
}
该方法主要功能是将eventEntry发送到目标inputTargets.
其中pokeUserActivityLocked(eventEntry)方法最终会调用到Java层的PowerManagerService.java中的userActivityFromNative()方法. 这也是PMS中唯一的native call方法.
2.4.1 pokeUserActivityLocked
void InputDispatcher::pokeUserActivityLocked(const EventEntry* eventEntry) {
if (mFocusedWindowHandle != NULL) {
const InputWindowInfo* info = mFocusedWindowHandle->getInfo();
if (info->inputFeatures & InputWindowInfo::INPUT_FEATURE_DISABLE_USER_ACTIVITY) {
return;
}
}
...
//【见小节2.4.2】
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
& InputDispatcher::doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible);
commandEntry->eventTime = eventEntry->eventTime;
commandEntry->userActivityEventType = eventType;
}
2.4.2 postCommandLocked
InputDispatcher::CommandEntry* InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command command) {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = new CommandEntry(command);
// 将命令加入mCommandQueue队尾
mCommandQueue.enqueueAtTail(commandEntry);
return commandEntry;
}
2.4.3 getConnectionIndexLocked
ssize_t InputDispatcher::getConnectionIndexLocked(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
ssize_t connectionIndex = mConnectionsByFd.indexOfKey(inputChannel->getFd());
if (connectionIndex >= 0) {
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (connection->inputChannel.get() == inputChannel.get()) {
return connectionIndex;
}
}
return -1;
}
根据inputChannel的fd从mConnectionsByFd队列中查询目标connection.
2.5 prepareDispatchCycleLocked
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget) {
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
return; //当连接已破坏,则直接返回
}
...
//[见小节2.6]
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
当connection状态不正确,则直接返回。
2.6 enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget) {
bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty();
//[见小节2.7]
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER);
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
//当原先的outbound队列为空, 且当前outbound不为空的情况执行.[见小节2.8]
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 根据dispatchMode来分别执行DispatchEntry事件加入队列的操作。
- 当起初connection.outboundQueue等于空, 经enqueueDispatchEntryLocked处理后, outboundQueue不等于空情况下, 则执行startDispatchCycleLocked()方法.
2.7 enqueueDispatchEntryLocked
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(
const sp<Connection>& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget,
int32_t dispatchMode) {
int32_t inputTargetFlags = inputTarget->flags;
if (!(inputTargetFlags & dispatchMode)) {
return; //分发模式不匹配,则直接返回
}
inputTargetFlags = (inputTargetFlags & ~InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_MASK) | dispatchMode;
//生成新的事件, 加入connection的outbound队列
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = new DispatchEntry(eventEntry,
inputTargetFlags, inputTarget->xOffset, inputTarget->yOffset,
inputTarget->scaleFactor);
switch (eventEntry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = keyEntry->action;
dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags = keyEntry->flags;
if (!connection->inputState.trackKey(keyEntry,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags)) {
delete dispatchEntry;
return; //忽略不连续的事件
}
break;
}
...
}
...
//添加到outboundQueue队尾
connection->outboundQueue.enqueueAtTail(dispatchEntry);
}
该方法主要功能:
- 根据dispatchMode来决定是否需要加入outboundQueue队列;
- 根据EventEntry,来生成DispatchEntry事件;
- 将dispatchEntry加入到connection的outbound队列.
执行到这里,其实等于由做了一次搬运的工作,将InputDispatcher中mInboundQueue中的事件取出后, 找到目标window后,封装dispatchEntry加入到connection的outbound队列.
2.8 startDispatchCycleLocked
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
//当Connection状态正常,且outboundQueue不为空
while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL
&& !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.head;
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime; //设置deliveryTime时间
status_t status;
EventEntry* eventEntry = dispatchEntry->eventEntry;
switch (eventEntry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
//发布Key事件 [见小节2.9]
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
keyEntry->deviceId, keyEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
keyEntry->keyCode, keyEntry->scanCode,
keyEntry->metaState, keyEntry->repeatCount, keyEntry->downTime,
keyEntry->eventTime);
break;
}
...
}
if (status) { //publishKeyEvent失败情况
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
if (connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()) {
//pipe已满,但waitQueue为空. 不正常的行为
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
} else {
// 处于阻塞状态
connection->inputPublisherBlocked = true;
}
} else {
//不不正常的行为
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
}
return;
}
//从outboundQueue中取出事件,重新放入waitQueue队列
connection->outboundQueue.dequeue(dispatchEntry);
connection->waitQueue.enqueueAtTail(dispatchEntry);
}
}
startDispatchCycleLocked的主要功能: 从outboundQueue中取出事件,重新放入waitQueue队列
- startDispatchCycleLocked触发时机:当起初connection.outboundQueue等于空, 经enqueueDispatchEntryLocked处理后, outboundQueue不等于空。
- startDispatchCycleLocked主要功能: 从outboundQueue中取出事件,重新放入waitQueue队列
- publishKeyEvent执行结果status不等于OK的情况下:
- WOULD_BLOCK,且waitQueue等于空,则调用abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(),该方法最终会调用到Java层的IMS.notifyInputChannelBroken().
- WOULD_BLOCK,且waitQueue不等于空,则处于阻塞状态,即inputPublisherBlocked=true
- 其他情况,则调用abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked
- abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked()方法最终会调用到Java层的IMS.notifyInputChannelBroken().
2.9 inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputPublisher::publishKeyEvent(...) {
if (!seq) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_KEY;
msg.body.key.seq = seq;
msg.body.key.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.key.source = source;
msg.body.key.action = action;
msg.body.key.flags = flags;
msg.body.key.keyCode = keyCode;
msg.body.key.scanCode = scanCode;
msg.body.key.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.key.repeatCount = repeatCount;
msg.body.key.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.key.eventTime = eventTime;
//通过InputChannel来发送消息
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
InputChannel通过socket向远端的socket发送消息。socket通道是如何建立的呢? InputDispatcher又是如何与前台的window通信的呢? 见下一篇文章Input系统—进程交互, 从文章的小节2.1开始继续往下说.
2.10 releasePendingEventLocked
void InputDispatcher::releasePendingEventLocked() {
if (mPendingEvent) {
resetANRTimeoutsLocked(); //重置ANR超时时间
releaseInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent); //释放mPendingEvent对象,并记录到mRecentQueue队列
mPendingEvent = NULL; //置空mPendingEvent变量.
}
}
三. 处理Comand
3.1 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptible() {
if (mCommandQueue.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
do {
//从mCommandQueue队列的头部取出第一个元素
CommandEntry* commandEntry = mCommandQueue.dequeueAtHead();
Command command = commandEntry->command;
//此处调用的命令隐式地包含'LockedInterruptible'
(this->*command)(commandEntry);
commandEntry->connection.clear();
delete commandEntry;
} while (! mCommandQueue.isEmpty());
return true;
}
通过循环方式处理完mCommandQueue队列的所有命令,处理过程从mCommandQueue中取出CommandEntry.
typedef void (InputDispatcher::*Command)(CommandEntry* commandEntry);
struct CommandEntry : Link<CommandEntry> {
CommandEntry(Command command);
Command command;
sp<Connection> connection;
nsecs_t eventTime;
KeyEntry* keyEntry;
sp<InputApplicationHandle> inputApplicationHandle;
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle;
String8 reason;
int32_t userActivityEventType;
uint32_t seq;
bool handled;
};
前面小节【2.4.1】添加的doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible命令. 接下来进入该方法:
3.2 doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible
[-> InputDispatcher]
void InputDispatcher::doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible(CommandEntry* commandEntry) {
mLock.unlock();
//【见小节4.3】
mPolicy->pokeUserActivity(commandEntry->eventTime, commandEntry->userActivityEventType);
mLock.lock();
}
3.3 pokeUserActivity
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
void NativeInputManager::pokeUserActivity(nsecs_t eventTime, int32_t eventType) {
//[见小节4.4]
android_server_PowerManagerService_userActivity(eventTime, eventType);
}
3.4 android_server_PowerManagerService_userActivity
[-> com_android_server_power_PowerManagerService.cpp]
void android_server_PowerManagerService_userActivity(nsecs_t eventTime, int32_t eventType) {
// Tell the power HAL when user activity occurs.
if (gPowerModule && gPowerModule->powerHint) {
gPowerModule->powerHint(gPowerModule, POWER_HINT_INTERACTION, NULL);
}
if (gPowerManagerServiceObj) {
...
//[见小节4.5]
env->CallVoidMethod(gPowerManagerServiceObj,
gPowerManagerServiceClassInfo.userActivityFromNative,
nanoseconds_to_milliseconds(eventTime), eventType, 0);
}
}
3.5 PMS.userActivityFromNative
[-> PowerManagerService.java]
private void userActivityFromNative(long eventTime, int event, int flags) {
userActivityInternal(eventTime, event, flags, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
}
private void userActivityInternal(long eventTime, int event, int flags, int uid) {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (userActivityNoUpdateLocked(eventTime, event, flags, uid)) {
updatePowerStateLocked();
}
}
}
runCommandsLockedInterruptible是不断地从mCommandQueue队列取出命令,然后执行直到全部执行完成。 除了doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible,还有其他如下命令:
- doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible
- doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingLockedInterruptible
- doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible
- doNotifyInputChannelBrokenLockedInterruptible
- doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible
四. 总结
4.1 流程图
点击查看大图:
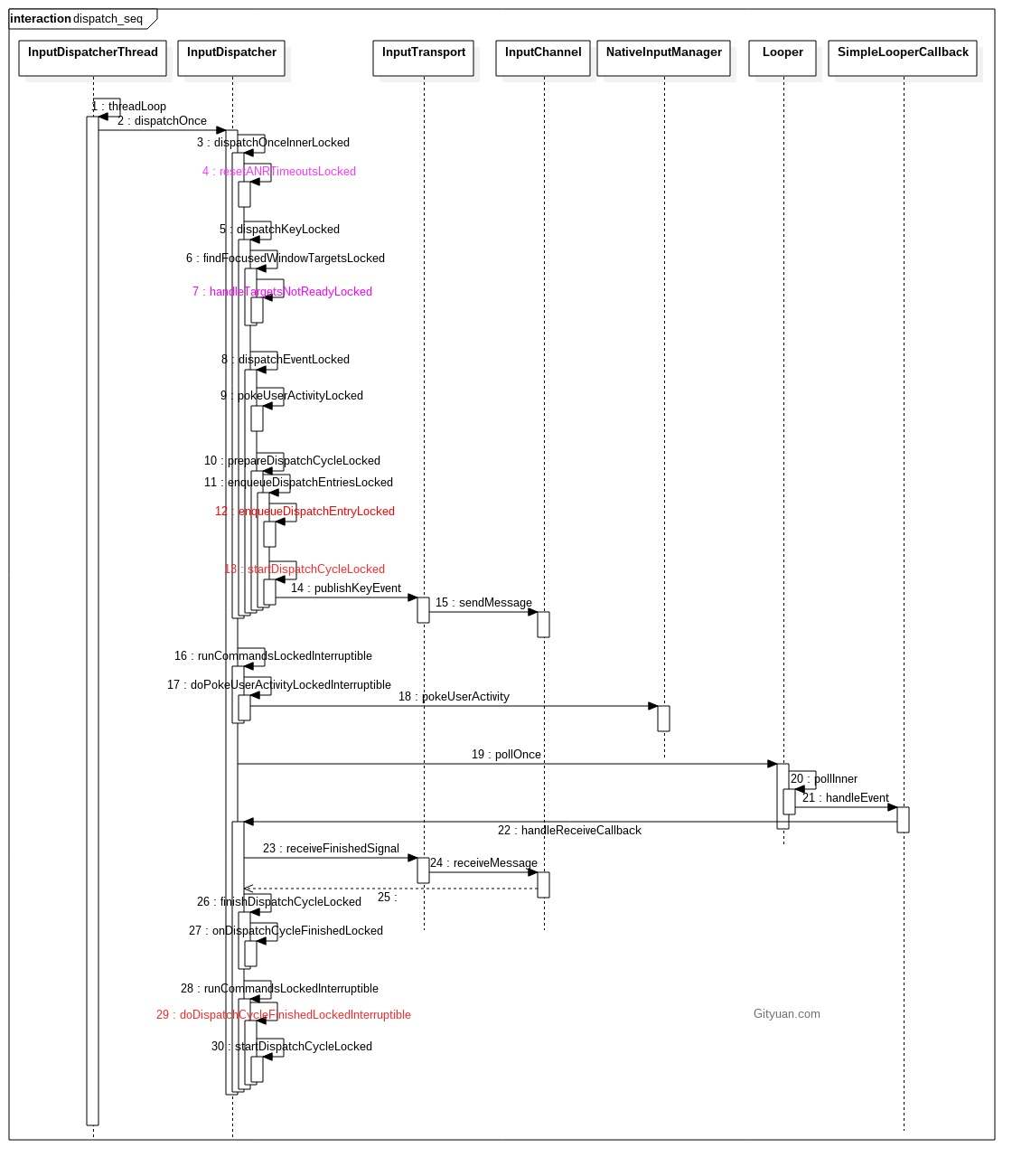
4.2 核心方法
用一张图来整体概况InputDispatcher线程的主要工作:
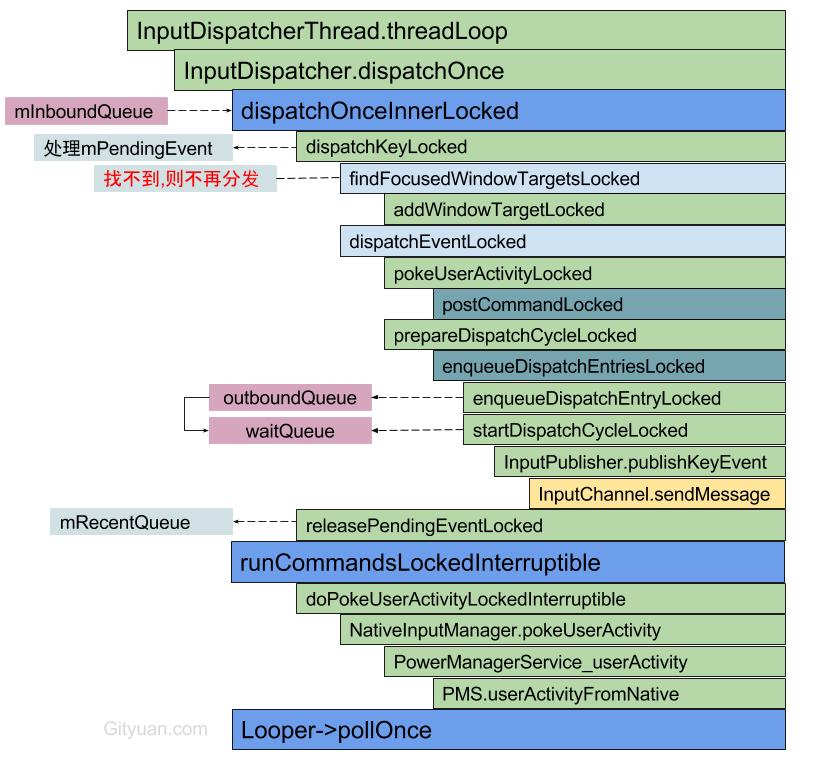
图解:
- dispatchOnceInnerLocked(): 从InputDispatcher的
mInboundQueue队列,取出事件EventEntry。另外该方法开始执行的时间点(currentTime)便是后续事件dispatchEntry的分发时间(deliveryTime) - dispatchKeyLocked():满足一定条件时会添加命令doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingLockedInterruptible;
- enqueueDispatchEntryLocked():生成事件DispatchEntry并加入connection的
outbound队列 - startDispatchCycleLocked():从outboundQueue中取出事件DispatchEntry, 重新放入connection的
waitQueue队列; - InputChannel.sendMessage通过socket方式将消息发送给远程进程;
- runCommandsLockedInterruptible():通过循环遍历地方式,依次处理mCommandQueue队列中的所有命令。而mCommandQueue队列中的命令是通过postCommandLocked()方式向该队列添加的。
一. 概述
前面文章都是介绍了两个线程InputReader和InputDispatcher的工作过程。在InputDispatcher的过程讲到 调用InputChanel通过socket与远程进程通信,本文便展开讲解这个socket是如何建立的。
对于InputReader和InputDispatcher都是运行在system_server进程; 用户点击的界面往往可能是某一个app,而每个app一般地都运行在自己的进程,这里就涉及到跨进程通信,app进程是如何与system进程建立通信。
要解答这些问题,从Activity最基本的创建过程开始说起。我们都知道一般地Activity对应一个应用窗口, 每一个窗口对应一个ViewRootImpl。窗口是如何添加到Activity的,从Activity.onCreate()为起点讲解。
二. UI线程
总所周知,Activity的生命周期的回调方法都是运行在主线程,也称之为UI线程,所有UI相关的操作都需要运行在该线程。本文虽然是UI线程,但并非只介绍所有运行在UI线程的流程,文中还涉及binder thread。
2.1 onCreate
[-> Activity.java]
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_account_bind);
...
}
Activity启动是由system进程控制:
- handleLaunchActivity():会调用Activity.onCreate(), 该方法内再调用setContentView(),经过AMS与WMS的各种交互,层层调用后,进入step2
- handleResumeActivity():会调用Activity.makeVisible(),该方法继续调用便会执行到WindowManagerImpl.addView(), 该方法内部再调用WindowManagerGlobal.addView(),
2.2 addView
[-> WindowManagerGlobal.java]
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
//[见小节2.3]
ViewRootImpl root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
//[见小节2.3.3]
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
...
}
2.3 ViewRootImpl
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
//获取IWindowSession的代理类【见小节2.3.1】
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
mDisplay = display;
mThread = Thread.currentThread(); //主线程
mWindow = new W(this);
mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();
...
}
2.3.1 getWindowSession
[-> WindowManagerGlobal.java]
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
//获取IMS的代理类
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
//获取WMS的代理类
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
//经过Binder调用,最终调用WMS[见小节2.3.2]
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {...},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
}
return sWindowSession
}
}
2.3.2 WMS.openSession
public IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback, IInputMethodClient client,
IInputContext inputContext) {
//创建Session对象
Session session = new Session(this, callback, client, inputContext);
return session;
}
再次经过Binder将数据写回app进程,则获取的便是Session的代理对象。
2.3.3 setView
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
...
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel(); //创建InputChannel对象
}
//通过Binder调用,进入system进程的Session[见小节2.4]
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
...
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
//创建WindowInputEventReceiver对象[见3.1]
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建Java层的InputChannel对象mInputChannel
- 向WMS注册InputChannel信息,通过InputChannel.openInputChannelPair创建的socket pair,将其中的客户端赋值给mInputChannel.
- 创建WindowInputEventReceiver对象
跨进程调用,进入binder thread执行如下方法:
2.4 Session.addToDisplay
[-> Session.java]
final class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
Rect outOutsets, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
//[见小节2.5]
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outInputChannel);
}
}
2.5 WMS.addToDisplay
[-> WindowManagerService.java]
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
InputChannel outInputChannel) {
...
//创建WindowState【见小节2.5.1】
WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token,
attachedWindow, appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayContent);
if (outInputChannel != null && (attrs.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
//根据WindowState的HashCode以及title来生成InputChannel名称
String name = win.makeInputChannelName();
//创建一对InputChannel[见小节2.6]
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);
//将socket服务端保存到WindowState的mInputChannel
win.setInputChannel(inputChannels[0]);
//socket客户端传递给outInputChannel [见小节2.7]
inputChannels[1].transferTo(outInputChannel);
//利用socket服务端作为参数[见小节2.8]
mInputManager.registerInputChannel(win.mInputChannel, win.mInputWindowHandle);
}
...
boolean focusChanged = false;
if (win.canReceiveKeys()) {
//新添加window能接收按下操作,则更新聚焦窗口。
focusChanged = updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS,
false /*updateInputWindows*/);
}
...
if (focusChanged) {
mInputMonitor.setInputFocusLw(mCurrentFocus, false /*updateInputWindows*/);
}
//设置当前聚焦窗口【见小节2.5.2】
mInputMonitor.updateInputWindowsLw(false /*force*/);
}
inputChannels数组:
- inputChannels[0]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(server); - inputChannels[1]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(client);
其中:
- 服务端inputChannels[0]保存到WindowState的mInputChannel;
- 客户端inputChannels[1]传递给outInputChannel,最终传递给ViewRootImpl的mInputChannel;
2.5.1 WindowState初始化
[-> WindowState.java]
WindowState(WindowManagerService service, Session s, IWindow c, WindowToken token,
WindowState attachedWindow, int appOp, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams a,
int viewVisibility, final DisplayContent displayContent) {
...
WindowState appWin = this;
while (appWin.mAttachedWindow != null) {
appWin = appWin.mAttachedWindow;
}
WindowToken appToken = appWin.mToken;
while (appToken.appWindowToken == null) {
WindowToken parent = mService.mTokenMap.get(appToken.token);
if (parent == null || appToken == parent) {
break;
}
appToken = parent;
}
mAppToken = appToken.appWindowToken;
//创建InputWindowHandle对象
mInputWindowHandle = new InputWindowHandle(
mAppToken != null ? mAppToken.mInputApplicationHandle : null, this,
displayContent.getDisplayId());
}
2.5.2 updateInputWindowsLw
[-> InputMonitor.java]
public void updateInputWindowsLw(boolean force) {
...
final InputWindowHandle dragWindowHandle = mService.mDragState.mDragWindowHandle;
if (dragWindowHandle != null) {
//将dragWindowHandle赋值给mInputWindowHandles
addInputWindowHandleLw(dragWindowHandle);
}
...
//将当前mInputWindowHandles传递到native【】
mService.mInputManager.setInputWindows(mInputWindowHandles);
...
}
setInputWindows的调用链:(最终设置mFocusedWindowHandle值)
-> IMS.setInputWindows
-> NativeInputManager::setInputWindows
-> InputDispatcher::setInputWindows
dragWindowHandle的初始化过程:
View.startDrag
Session.prepareDrag
WMS.prepareDragSurface
mDragState = new DragState(...);
Session.performDrag
DragState.register
mDragWindowHandle = new InputWindowHandle(...);
2.6 openInputChannelPair
[-> InputChannel.java]
public static InputChannel[] openInputChannelPair(String name) {
return nativeOpenInputChannelPair(name);
}
这个过程的主要功能
- 创建两个socket通道(非阻塞, buffer上限32KB)
- 创建两个InputChannel对象;
- 创建两个NativeInputChannel对象;
- 将nativeInputChannel保存到Java层的InputChannel的成员变量mPtr
2.6.1 nativeOpenInputChannelPair
[-> android_view_InputChannel.cpp]
static jobjectArray android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair(JNIEnv* env,
jclass clazz, jstring nameObj) {
const char* nameChars = env->GetStringUTFChars(nameObj, NULL);
String8 name(nameChars);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(nameObj, nameChars);
sp<InputChannel> serverChannel;
sp<InputChannel> clientChannel;
//创建一对socket[见小节2.6.2]
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);
//创建Java数组
jobjectArray channelPair = env->NewObjectArray(2, gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz, NULL);
...
//创建NativeInputChannel对象[见小节2.6.3]
jobject serverChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env,
new NativeInputChannel(serverChannel));
...
//创建NativeInputChannel对象[见小节2.6.3]
jobject clientChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env,
new NativeInputChannel(clientChannel));
...
//将client和server 两个插入到channelPair
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 0, serverChannelObj);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 1, clientChannelObj);
return channelPair;
}
2.6.2 openInputChannelPair
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(const String8& name,
sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) {
int sockets[2];
//真正创建socket对的地方【核心】
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) {
...
return result;
}
int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE; //32k
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
String8 serverChannelName = name;
serverChannelName.append(" (server)");
//创建InputChannel对象
outServerChannel = new InputChannel(serverChannelName, sockets[0]);
String8 clientChannelName = name;
clientChannelName.append(" (client)");
//创建InputChannel对象
outClientChannel = new InputChannel(clientChannelName, sockets[1]);
return OK;
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建socket pair; (
非阻塞式的socket) - 设置两个socket的接收和发送的buffer
上限为32KB; - 创建client和server的Native层InputChannel对象;
- sockets[0]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(server); - sockets[1]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(client)
- sockets[0]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
创建InputChannel对象位于文件InputTransport.cpp,如下:
InputChannel::InputChannel(const String8& name, int fd) :
mName(name), mFd(fd) {
//将socket设置成非阻塞方式
int result = fcntl(mFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
}
另外,创建NativeInputChannel对象位于文件android_view_InputChannel.cpp,如下:
NativeInputChannel::NativeInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) :
mInputChannel(inputChannel), mDisposeCallback(NULL) {
}
2.6.3 android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel
[-> android_view_InputChannel.cpp]
static jobject android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(JNIEnv* env,
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel) {
//创建Java的InputChannel
jobject inputChannelObj = env->NewObject(gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz,
gInputChannelClassInfo.ctor);
if (inputChannelObj) {
//将nativeInputChannel保存到Java层的InputChannel的成员变量mPtr
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj, nativeInputChannel);
}
return inputChannelObj;
}
static void android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj,
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel) {
env->SetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr,
reinterpret_cast<jlong>(nativeInputChannel));
}
此处:
- gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz是指Java层的InputChannel类
- gInputChannelClassInfo.ctor是指Java层的InputChannel构造方法;
- gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr是指Java层的InputChannel的成员变量mPtr;
2.7 transferTo
[-> InputChannel.java]
public void transferTo(InputChannel outParameter) {
nativeTransferTo(outParameter);
}
2.7.1 nativeTransferTo
[-> android_view_InputChannel.cpp]
static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
jobject otherObj) {
if (android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj) != NULL) {
return; //当Java层的InputChannel.mPtr不为空,则返回
}
//将当前inputChannels[1]的mPtr赋值给nativeInputChannel
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);
// 将该nativeInputChannel保存到outInputChannel的参数
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj, nativeInputChannel);
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);
}
inputChannels[1].transferTo(outInputChannel)主要功能:
- 当outInputChannel.mPtr不为空,则直接返回;否则进入step2;
- 将inputChannels[1].mPtr的值赋给outInputChannel.mPtr;
- 清空inputChannels[1].mPtr值;
也就是将socket客户端inputChannels[1]传递给outInputChannel;
2.8 IMS.registerInputChannel
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel,
InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle) {
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, false);
}
- inputChannel是指inputChannels[0],即socket服务端;
- inputWindowHandle是指WindowState.mInputWindowHandle;
2.8.1 nativeRegisterInputChannel
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj, jobject inputWindowHandleObj, jboolean monitor) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle =
android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle(env, inputWindowHandleObj);
//[见小节2.8.2]
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(
env, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
...
if (! monitor) {
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
}
}
2.8.2 registerInputChannel
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
status_t NativeInputManager::registerInputChannel(JNIEnv* /* env */,
const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) {
//[见小节2.8.3]
return mInputManager->getDispatcher()->registerInputChannel(
inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
}
mInputManager是指NativeInputManager初始化过程创建的InputManager对象(C++).
2.8.3 registerInputChannel
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
status_t InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
...
//创建Connection[见小节2.8.4]
sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd.add(fd, connection);
...
//将该fd添加到Looper监听[见小节2.8.5]
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
}
mLooper->wake(); //connection改变, 则唤醒looper
return OK;
}
将新创建的connection保存到mConnectionsByFd成员变量,“InputDispatcher”线程的Looper添加对socket服务端的监听功能; 当该socket有消息时便会唤醒该线程工作。
2.8.4 初始化Connection
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
InputDispatcher::Connection::Connection(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) :
status(STATUS_NORMAL), inputChannel(inputChannel), inputWindowHandle(inputWindowHandle),
monitor(monitor),
inputPublisher(inputChannel), inputPublisherBlocked(false) {
}
其中InputPublisher初始化位于文件InputTransport.cpp
InputPublisher:: InputPublisher(const sp<InputChannel>& channel) :
mChannel(channel) {
}
此处inputChannel是指前面openInputChannelPair创建的socket服务端,将其同时保存到Connection.inputChannel和InputPublisher.mChannel。
2.8.5 Looper.addFd
[-> system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp]
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, Looper_callbackFunc callback, void* data) {
// 此处的callback为handleReceiveCallback
return addFd(fd, ident, events, callback ? new SimpleLooperCallback(callback) : NULL, data);
}
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, const sp<LooperCallback>& callback, void* data) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Request request;
request.fd = fd;
request.ident = ident;
request.events = events;
request.seq = mNextRequestSeq++;
request.callback = callback; //是指SimpleLooperCallback
request.data = data;
if (mNextRequestSeq == -1) mNextRequestSeq = 0;
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex < 0) {
//通过epoll监听fd
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.add(fd, request); //该fd的request加入到mRequests队列
} else {
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.replaceValueAt(requestIndex, request);
}
}
return 1;
}
此处Loop便是“InputDispatcher”线程的Looper,将socket服务端的fd采用epoll机制注册监听.
小节
虽然本文介绍的UI线程的工作,
- [小节2.1 ~ 2.3]: 运行在UI线程;
- [小节2.4 ~ 2.8]:通过IWindowSession的Binder IPC调用,运行在system_server的binder thread;
ViewRootImpl的setView()过程:
- 创建socket pair,作为InputChannel:
- socket服务端保存到system_server中的WindowState的mInputChannel;
- socket客户端通过binder传回到远程进程的UI主线程ViewRootImpl的mInputChannel;
- IMS.registerInputChannel()注册InputChannel,监听socket服务端:
- Loop便是“InputDispatcher”线程的Looper;
- 回调方法handleReceiveCallback。
三. WindowInputEventReceiver
接下来,看看【小节2.3.3】创建WindowInputEventReceiver对象
3.1 WindowInputEventReceiver初始化
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
//inputChannel是指socket客户端,Looper是指UI线程的Looper
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper); //【见小节3.2】
}
...
}
3.2 InputEventReceiver
[-> InputEventReceiver.java]
public InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
...
mInputChannel = inputChannel;
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue(); //UI线程消息队列
//【加小节3.3】
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),
inputChannel, mMessageQueue);
}
3.3 nativeInit
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,
jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
//获取UI主线程的消息队列
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
//创建NativeInputEventReceiver对象【见小节3.4】
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,
receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue);
//【见小节3.5】
status_t status = receiver->initialize();
...
receiver->incStrong(gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(receiver.get());
}
3.4 NativeInputEventReceiver
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
class NativeInputEventReceiver : public LooperCallback {
InputConsumer mInputConsumer;
sp<MessageQueue> mMessageQueue;
int mFdEvents;
bool mBatchedInputEventPending;
...
NativeInputEventReceiver::NativeInputEventReceiver(JNIEnv* env,
jobject receiverWeak, const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<MessageQueue>& messageQueue) :
mReceiverWeakGlobal(env->NewGlobalRef(receiverWeak)),
//【见3.4.1】
mInputConsumer(inputChannel), mMessageQueue(messageQueue),
mBatchedInputEventPending(false), mFdEvents(0) {
}
}
3.4.1 InputConsumer
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
InputConsumer::InputConsumer(const sp<InputChannel>& channel) :
mResampleTouch(isTouchResamplingEnabled()),
mChannel(channel), mMsgDeferred(false) {
}
此处inputChannel是指socket客户端。
3.5 initialize
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() {
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT); //【见小节3.6】
return OK;
}
3.6 setFdEvents
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
if (mFdEvents != events) {
mFdEvents = events;
int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();
if (events) {
//将socket客户端的fd添加到主线程的消息池【见小节3.6.1】
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, NULL);
} else {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);
}
}
}
3.6.1 Looper.addFd
[-> system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp]
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, const sp<LooperCallback>& callback, void* data) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Request request;
request.fd = fd;
request.ident = ident;
request.events = events;
request.seq = mNextRequestSeq++;
request.callback = callback; //是指ativeInputEventReceiver
request.data = data;
if (mNextRequestSeq == -1) mNextRequestSeq = 0;
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex < 0) {
//通过epoll监听fd
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.add(fd, request); //该fd的request加入到mRequests队列
} else {
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.replaceValueAt(requestIndex, request);
}
}
return 1;
}
此处的Looper便是UI主线程的Looper,将socket客户端的fd添加到UI线程的Looper来监听,回调方法为NativeInputEventReceiver。
四. 总结
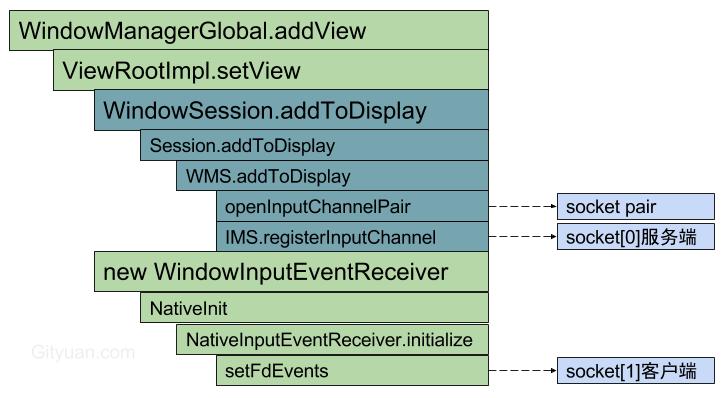
首先,通过openInputChannelPair来创建socket pair,作为InputChannel:
- socket服务端保存到system_server中的WindowState的mInputChannel;
- socket客户端通过binder传回到远程进程的UI主线程ViewRootImpl的mInputChannel;
紧接着,完成了两个线程的epoll监听工作:
- [小节2.8]IMS.registerInputChannel(): “InputDispatcher”线程监听socket服务端,收到消息后回调InputDispatcher.handleReceiveCallback();
- [小节3.6]setFdEvents(): UI主线程监听socket客户端,收到消息后回调NativeInputEventReceiver.handleEvent().
有了这些“InputDispatcher”和“UI”主线程便可以进行跨进程通信与交互。





















 512
512











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








