在编程里面我们经常会遇到编历一个列表或数组做同一件事情或操作,当这个数组或列表很大时又或是需要进行很复杂的操作时,就会花费很长的时间。以前我就在想能不能在这种情况下使用多线程的方式提高效率,可惜一直都没机会和动力(实际需要)去研究。今天在网上查找资料,很偶然的发现.NET Framework 4.0中平行算法相关内容(Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach),原来.NET已经实现这项功能而且语法简化的异常简单。具体内容请大家查阅参考资料,下面将贴出我的测试结果与大家共享。
PS:首先确认开发环境(VS2010+.NET Framework 4)
第一轮测试:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//产生测试资料
List<int> testData = new List<int>();
Random Rand = new Random();
//产生乱数列表
for (int i = 0; i < 2147400; i++)
{
testData.Add(Rand.Next(1000));
}
//打印正确结果
Console.WriteLine(testData.Sum());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine();
TestFor(testData);
TestParallelFor(testData);
TestParallelForeach(testData);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void TestFor(List<int> testData)
{
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
//记录结果用
long resultData = 0;
foreach (var item in testData)
{
resultData += item;
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("ForEach: \t\t{0} in {1}", resultData, (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
static void TestParallelFor(List<int> testData)
{
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
//记录结果用
long resultData = 0;
Parallel.For(0, testData.Count , (i, loopState) =>
{
resultData += testData[i];
});
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Parallel.For: \t{0} in {1}", resultData, (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
static void TestParallelForeach(List<int> testData)
{
//记录结果用
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
long resultData = 0;
Parallel.ForEach(testData, (item, loopState) =>
{
resultData += item;
});
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Parallel.ForEach:\t{0} in {1}", resultData, (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
测试结果
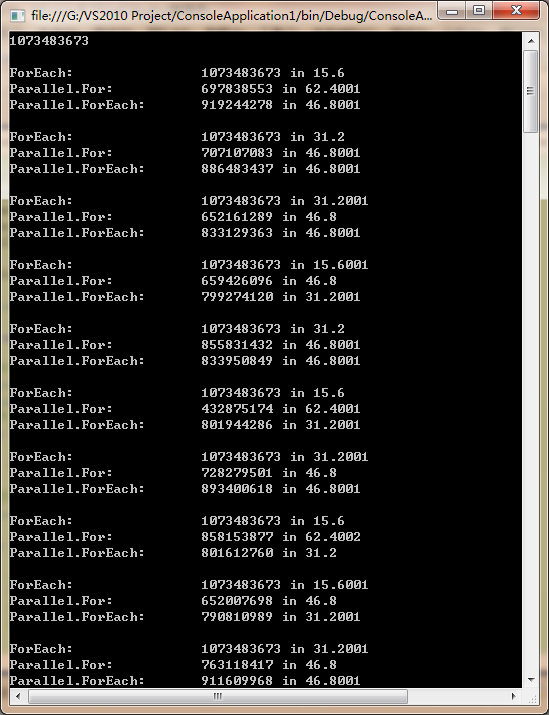
测试分析结果:Foreach胜出,且Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach计算均以错误告终,顿时让我失望不已。不过仔细一想,发现应该是平行运算时,因为是多线程同时使用resultData这个共享资源时的访问起了冲突,所以导致最后的求和失败。要想防止资源不起冲突,只能对共享资源进行加锁,但这又与平行算法的思想违背。于是乎改进方法重新测试。
第二轮测试:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//产生测试资料
List<int> testData = new List<int>();
Random Rand = new Random();
//产生乱数列表
for (int i = 0; i < 2147401; i++)
{
testData.Add(Rand.Next(1000));
}
//打印正确结果
Console.WriteLine(testData.Sum());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine();
TestFor(testData);
TestParallelFor(testData);
TestParallelForeach(testData);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void TestFor(List<int> testData)
{
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
//记录结果用
List<int> resultData = new List<int>();
foreach (var item in testData)
{
resultData.Add(item);
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("ForEach: \t\t{0} in {1}", resultData.Sum(), (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
static void TestParallelFor(List<int> testData)
{
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
//记录结果用
ConcurrentStack<int> resultData = new ConcurrentStack<int>();
Parallel.For(0, testData.Count, (i, loopState) =>
{
resultData.Push(testData[i]);
});
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Parallel.For: \t{0} in {1}", resultData.Sum(), (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
static void TestParallelForeach(List<int> testData)
{
//记录结果用
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
ConcurrentStack<int> resultData = new ConcurrentStack<int>();
Parallel.ForEach(testData, (item, loopState) =>
{
resultData.Push(item);
});
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Parallel.ForEach:\t{0} in {1}", resultData.Sum(), (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
测试结果

测试分析结果:Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach计算终于正确,这表明确实是资源访问的问题,但这个效率问题,还不如直接使用Foreach,这是怎么会事儿啊,没道理啊,怎么着我的电脑也还是个双核嘛。
再仔细分析一下,第一轮测试与第二轮的测试结果,虽然第一轮测试Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach计算错误,但好歹执行效率上与Foreach相差不大,那么效率应该是出在了ConcurrentStack.Push上了。(这是因为在 .Net 3.5 之前所提供的所有 Collections 都不是线程安全的,必須使用.Net 4.0 , System.Collections.Concurrent Namespace 下的泛型)于是有了以下的第三轮测试~~~~
第三轮测试:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//产生测试资料
List<int> testData = new List<int>();
Random Rand = new Random();
//产生乱数列表
for (int i = 0; i < 2147401; i++)
{
testData.Add(Rand.Next(1000));
}
//打印正确结果
Console.WriteLine(testData.Sum());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine();
TestFor(testData);
TestParallelFor(testData);
TestParallelForeach(testData);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void TestFor(List<int> testData)
{
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
foreach (var item in testData)
{
item.ToString();
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("ForEach: \t\t{0} in {1}", testData.Sum(), (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
static void TestParallelFor(List<int> testData)
{
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
Parallel.For(0, testData.Count, (i, loopState) =>
{
testData[i].ToString();
});
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Parallel.For: \t{0} in {1}", testData.Sum(), (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
static void TestParallelForeach(List<int> testData)
{
//记录结果用
DateTime time1 = DateTime.Now;
ConcurrentStack<int> resultData = new ConcurrentStack<int>();
Parallel.ForEach(testData, (item, loopState) =>
{
item.ToString();
});
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Parallel.ForEach:\t{0} in {1}", testData.Sum(), (DateTime.Now - time1).TotalMilliseconds));
}
测试结果
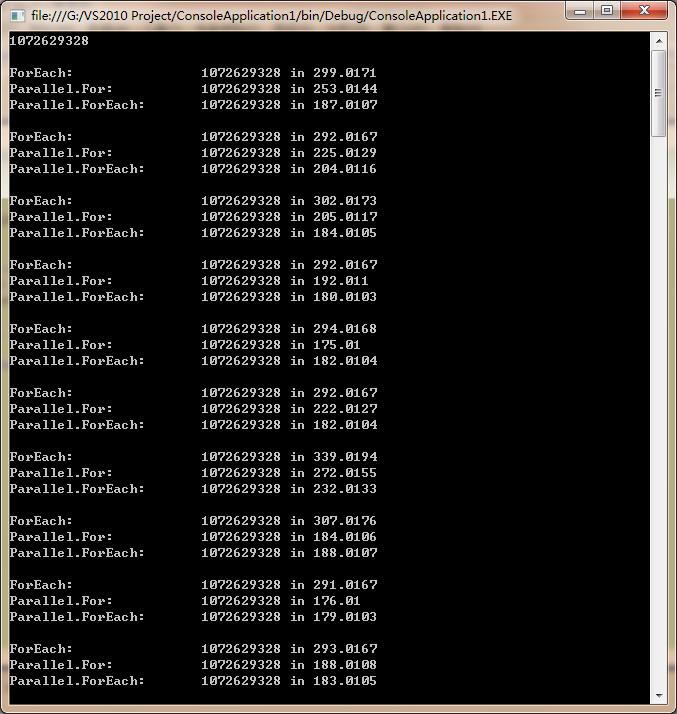
测试分析结果:这下子Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach终于发挥出了平行运算的优势,将效率提高了接近一半左右。
测试总结:对于Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach的使用应该要特别小心,它们的优势是处理列表很长,且对列表内的元素进行很复杂的业务逻辑,且不会使用共享资源,只针对自身的业务逻辑处理,方才能提升效率。因为如果逻辑过于简单的话,创建线程的花费将大于业务执行的花费,得不偿失。
参考资料
平行运算 (一):Parallel.For、Parallel.Foreach 用法及技巧
How to: Write a Simple Parallel.For Loop
How to: Write a Simple Parallel.ForEach Loop
Introducing ConcurrentStack < T >
System.Collections.Concurrent Namespace
The Parallel Programming Of .NET Framework 4.0(1) – Beginning
The Parallel Programming Of .NET Framework 4.0(2) - Task Library
The Parallel Programming Of .NET Framework 4.0(3) - Deep Into Task Library
The Parallel Programming Of .NET Framework 4.0(4) - Inside Out Of Task Library
The Parallel Programming Of .NET Framework 4.0(5) - Dive to Parallel Programming

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








