8.1SPringMVC设置概览
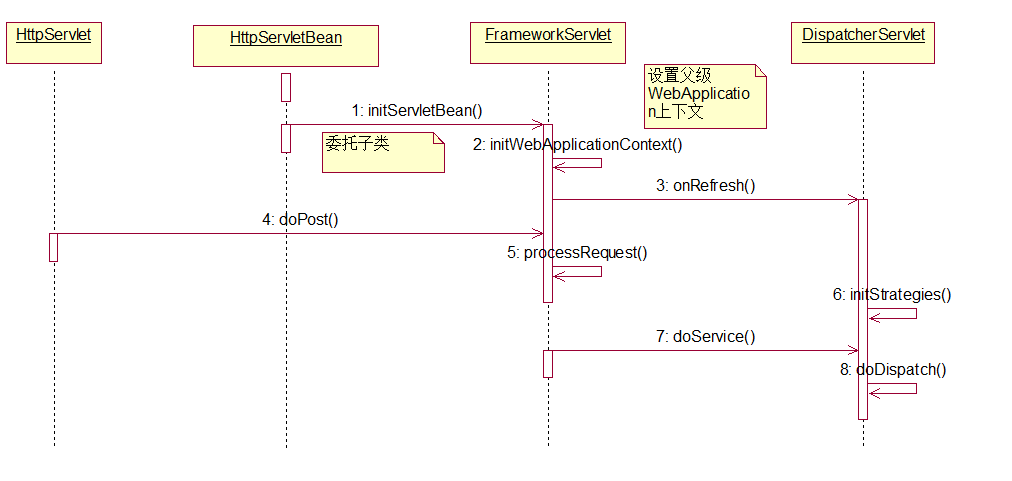
在web.xml文件里边配置的DispatcherServlet是web请求的入口,它的处理过程如下:
DispatcherServlet的任务有2个:
一个是 初始化部分,由initservletBean()启动,通过initWebApplicationContext方法最终调用DispatcherSevlet的initStrategies方法,在这个过程中DispatcherServlet对MVC模块的其他部分进行初始化,比如HandlerMapping、Viewresolver等,另一个是对HTTP请求进行响应,作为一个servlet,WEB容器会调用servlet的都跟他()和dopost()方法,在这个方法的调用封装了doDispatcher。
在FrameworkServlet的initWebApplicationContext()方法中主要是设置当前上下文的父级上下文
HttpServletBean完成初始化:
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
//获得servlet的初始化参数,即WEB.XML的配置
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.environment));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
//调用子类(FrameworkServlet)完成具体的初始化
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}具体的初始化在FrameworkServlet完成;
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化上下文
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}设置上下文:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
//使用WebApplicationContextUtils得到根山下文。这个根上下文是保存在servletContext中
//得到之后将其作为当前上下文的根上下文
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//设置bean配置的信息,调用refresh()完成IOC容器的最终初始化
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
//将当前建立的上下文保存咋servletcontext中(attrName="FrameworkServlet..CONTEXT."+servletname)
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}根上下文是WebApplication以ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE的名字设置在servletContext中的。然后被DispatcherServlet得到使用,可以通过getBean的方式
这个上下文,在FrameworkServlet的createWebApplicationContext得到,根据默认配置使用的也是XmlWebApplicationContext,实例化之后设置bean配置文件的路径,左后调研refresh完成最终初始化。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//使用XmlWebApplicationContext作为IOC容器
**ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);**
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
//调用refresh完成IOC的初始化
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}在SpringMvcDispatcher的初始化过程中,以对 HandlerMapping的初始化调用作为触发点,了解SPringMVC木块初始化的方法调用关系,在这个调用关系最初是由HttpservletBean的init方法触发的,这个HttpservletBean是 Httpservlet的子类。接着会在HttpservletBean的子类 FrameWorkServlet中对IOC容器完成初始化,这个初始化方法中,会调用DispatcherServlet的initStrategies方法,这个initStrategies方法中,启动整个SpringMVC框架的初始化。
代码如下:
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
**initHandlerMappings(context);**
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}initHandlerMappings中mapping关系的作用是为http请求找到相应的controller控制器,从而利用这些控制器controller去完成设计好的数据处理工作。handlermapping完成对mvc中国controller的定义和配置,只不过在web这个特定的应用环境中这些控制器是与具体的http请求对应的。
代码:
/**
* Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class.
* <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace,
* we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
*/
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
//取到所有的handlermapping,可以从当前容器里边取,也可以从父级容器里边取值,
//detectAllHandlerMappings默认为true,即从所有的容器里边取
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
//通过getbean的方式从容器取值
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
//如果没有取到,就用默认的handlerMappings 默认配置在DispatcherServlet.properties中。
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}8.2、MVC处理http分发请求
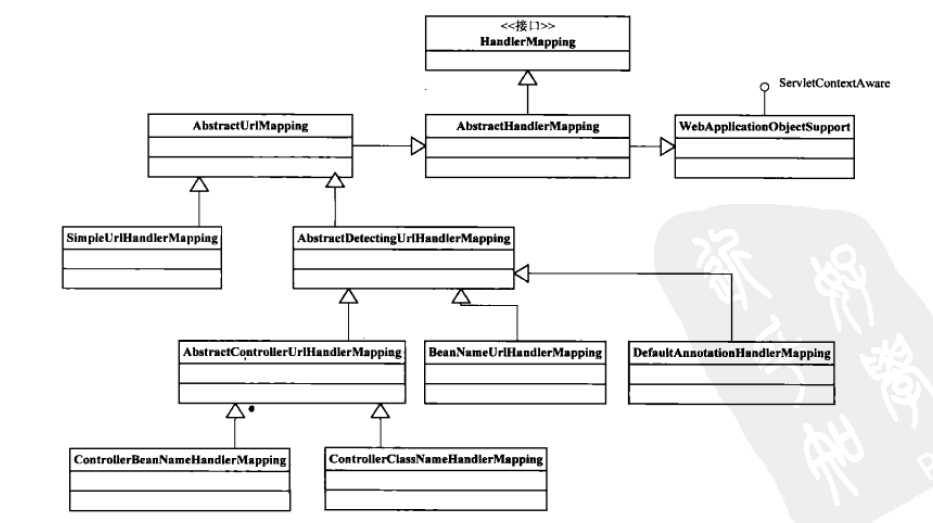
1、handlerMapping 的配置和设计原理:
以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的分析handlerMapping的设计与实现
接口HandlerMapping的代码:
public interface HandlerMapping {
String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping";
String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern";
String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping";
String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables";
String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes";
//调用getHandler实际上返回的是一个handlerExceptionChain,这是典型的command的模式的使用,这个
//HandlerExecutionChain不但持有handler本身,还包括了处理这个http请求的拦截器
//handler就是http请求对应的controller
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
HandlerExecutionChain 的代码如下:
public class HandlerExecutionChain {
private final Object handler;
private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors;
private List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList;
public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler) {
this(handler, null);
}
public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors) {
if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {
HandlerExecutionChain originalChain = (HandlerExecutionChain) handler;
this.handler = originalChain.getHandler();
this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<HandlerInterceptor>();
CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(originalChain.getInterceptors(),
this.interceptorList);
CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(interceptors, this.interceptorList);
}
else {
this.handler = handler;
this.interceptors = interceptors;
}
}
public Object getHandler() {
return this.handler;
}
public void addInterceptor(HandlerInterceptor interceptor) {
initInterceptorList();
this.interceptorList.add(interceptor);
}
public void addInterceptors(HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors) {
if (interceptors != null) {
initInterceptorList();
this.interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
private void initInterceptorList() {
if (this.interceptorList == null) {
this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<HandlerInterceptor>();
}
if (this.interceptors != null) {
this.interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(this.interceptors));
this.interceptors = null;
}
}
public HandlerInterceptor[] getInterceptors() {
if (this.interceptors == null && this.interceptorList != null) {
this.interceptors = this.interceptorList.toArray(new HandlerInterceptor[this.interceptorList.size()]);
}
return this.interceptors;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (this.handler == null) {
return "HandlerExecutionChain with no handler";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("HandlerExecutionChain with handler [").append(this.handler).append("]");
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptorList)) {
sb.append(" and ").append(this.interceptorList.size()).append(" interceptor");
if (this.interceptorList.size() > 1) {
sb.append("s");
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
HandlerExecutionChain 中的handler和interceptors需要在定义HandlerMapping的时候配置好,这牵涉到一个bean的注册过程,接下来分析SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的注册过程:
public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
super.initApplicationContext();
registerHandlers(this.urlMap);
}
protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("Neither 'urlMap' nor 'mappings' set on SimpleUrlHandlerMapping");
}
else {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : urlMap.entrySet()) {
String url = entry.getKey();
Object handler = entry.getValue();
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
}
}
}SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的基类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping完成registerHandler方法的实现:
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
// Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.
//直接用bean的名字映射,那就直接从容器中获取handler
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
if (getApplicationContext().isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
//处理URL是“/”的映射,把这个“ /”映射的controller设置到rootHandler中
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
//处理“/*”的url,将“/*”映射的controller设置到DefaultHandler中去。
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {
//处理正常的、URL映射,将URL和controller分别设置为key和value
//这个handlerMap是一个LinkedHashMap
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped URL path [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
}2、 使用handlerMapping完成请求的映射处理
SimpleHandlerMapping的接口方法getHandler,会根据初始化时得到的映射关系生产DispatcherServlet需要的HandlerExecutionChain。AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler:
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
//通过默认的Handler ,“/”
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
//通过bean的名字得到handler
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//把handler封装成getHandlerExecutionChain并且加上拦截器
return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
}getHandlerExecutionChain的代码如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain =
(handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler);
chain.addInterceptors(getAdaptedInterceptors());
String lookupPath = urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor : mappedInterceptors) {
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
return chain;
}取得handler的具体过程在getHandlerInternal方法中,根据http请求作为参数,得到URL并根据URL到uurlMapping中获得handler,具体实现再起子类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中:
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//根据http得到URL,通过URL与handler进行匹配,得到handler,如果你找不到就返回null,期间调用默认的handler会被使用
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//lookHandler根据URL路径启动在handlerMapping中对handler的检索,并最终返回handler对象
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
//对默认的handler的处理
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
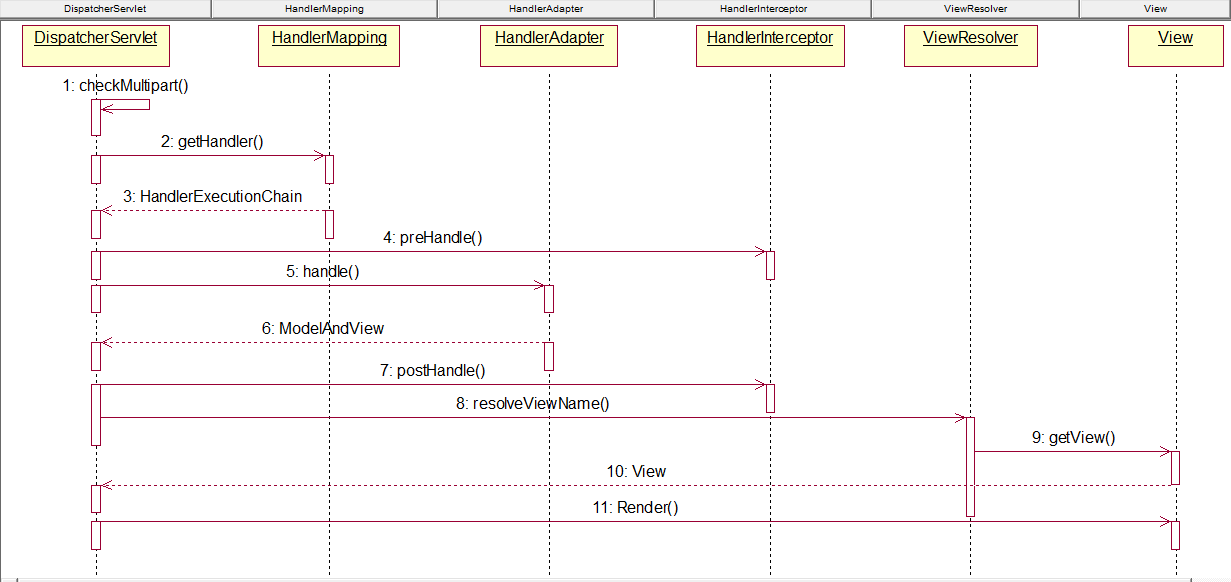
}3、springmvc对http请求的分发处理
回到dispatcherServlet这个servlet担负了自有容器的建立与请求分发处理,所有的请求都会走都service方法:
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "' processing " + request.getMethod() +
" request for [" + requestUri + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
logger.debug("Taking snapshot of request attributes before include");
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
//http请求参数快照处理
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
//请求分发的主要处理方法
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}doDispatch的实现(典型的command模式的应用):
Dodispatcher协同模型和控制器的过程:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
int interceptorIndex = -1;
try {
//ModelAndView 持有handler处理请求的结果
ModelAndView mv;
boolean errorView = false;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//根据请求得到对应的handler,handler的注册以及gethandler的实现
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//执行handler之前检查handler的合法性,是不是按spring的要求编写的handler
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + requestUri + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// Apply preHandle methods of registered interceptors.
//调用handler的拦截器,从HandlerExecutionchain中取得Interceptor进行处理。
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = mappedHandler.getInterceptors();
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())) {
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
return;
}
interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
//通过调用handleAdapter的handler方法,实际触发对controller的handleRequest方法的调用。
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Do we need view name translation?
//判断是否需要视图名的翻译与转换
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
// Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler(), mv);
}
}
}
catch (ModelAndViewDefiningException ex) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", ex);
mv = ex.getModelAndView();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(processedRequest, response, handler, ex);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
//使用视图对modelAndView数据的展现
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, processedRequest, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
// Trigger after-completion for successful outcome.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Trigger after-completion for thrown exception.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
ServletException ex = new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err);
// Trigger after-completion for thrown exception.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (processedRequest != request) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
下面看看dispatcherservler是怎么得到handler的:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//从handlerMappings得到handler与前面的初始化对接上
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
//与前面的分析对接,前面分析的simpleUrlhandlerMapping的基类getHandler得
//HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}经过handler对业务逻辑处理后将返回的数据封装为ModelAndView交给视图类处理,处理的入口方法是doDispatch的render方法。至此到handler的调用,业务数据的处理完毕。






















 120
120

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








