@Api:修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用
@ApiOperation:描述一个类的一个方法,或者说一个接口
@ApiParam:单个参数描述
@ApiModel:用对象来接收参数
@ApiProperty:用对象接收参数时,描述对象的一个字段@ApiResponse:HTTP响应其中1个描述
@ApiResponses:HTTP响应整体描述
@ApiClass
@ApiError
@ApiErrors
@ApiParamImplicit
@ApiParamsImplicit
例子:@ApiOperation(value = "获得用户列表", notes = "列表信息", httpMethod = "POST", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "list", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Result<User> list(
@ApiParam(value = "分类ID", required = true) @RequestParam Long categoryId,
@ApiParam(value = "token", required = true) @RequestParam String token) {
Result<User> result = new Result<User>();
User user = new User();
result.setData(user);
return result;
}
Web前端/移动端HTTP请求方式:直接把参数附带到URL后面,或者用AJAX方法,表单提交。
例子2:
@ApiOperation(value = "update用户", notes = ")", httpMethod = "POST", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "update", method = RequestMethod.GET/*,produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED_VALUE*/)
public Result<String> update(User user) {
String u = findUser(user);
System.out.println(u);
return null;
}
这个时候,可以使用对象来接收。
@ApiModel(value = "用户对象",description="user2")
public class User extends CommonParam{
}
Web前端/移动端HTTP请求方式:直接把参数附带到URL后面,或者用AJAX方法,表单提交。
这里面存在一个小问题,当后端用对象User来接收参数的时候,Swagger自带的工具是这样的:
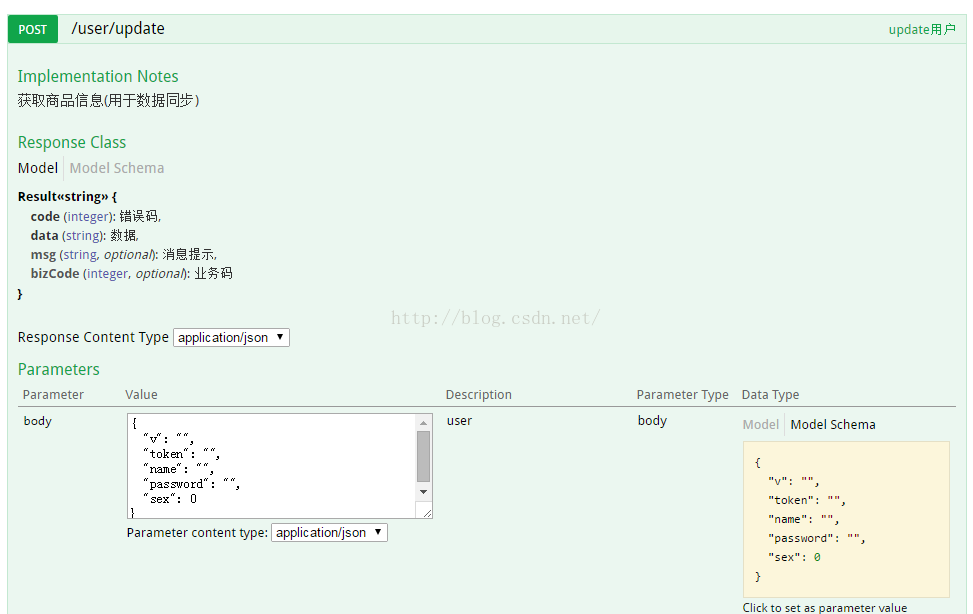
这种形式,并不是表单提交,或者把参数附加到URL的后面。
我们只能手动构造URL,附带参数去提交。
如果需要测试的话!
例子3:
public Result<String> add(@RequestBody User user) {
String u = findUser(user);
System.out.println(u);
return null;
}
Web前端/移动端HTTP请求方式:必须把参数,放到request请求的body中去。
后端不能直接用request.getParam("token")这种。
获得request body中的数据,手动转换成目标数据。
String charReader(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = request.getReader();
String str, wholeStr = "";
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
wholeStr += str;
}
return wholeStr;
}





















 1282
1282

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








