目录
1、bash介绍
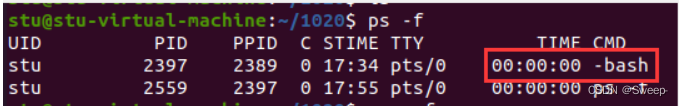
bash自身fork复制一份,子进程替换一份。
2、命令的分类
①内置命令:cd exit等;
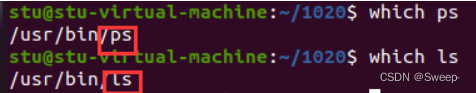
②普通命令: ls pwd cp ps等,通过which可以找到。
bash :复制自身,复制出来一个子进程, 替换ps/ls
3、项目框架

4、my_bash项目代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<pwd.h>
#define PATH_BIN "/home/stu/1020/mybin"//自己的文件路径
#define ARG_MAX 10
void print_info()
{
char *user_str="$";
int user_id=getuid();
if(user_id==0)
{
user_str="#";
}
struct passwd*ptr=getpwuid(user_id);
if(ptr==NULL)
{
printf("my_bash1.0>> ");
fflush(stdout);
return;
}
char hostname[128]={0};
if(gethostname(hostname,128)==-1)
{
printf("my_bash1.0>> ");
fflush(stdout);
return;
}
char dir[256]={0};
if(getcwd(dir,256)==NULL)
{
printf("my_bash1.0>> ");
fflush(stdout);
return;
}
printf("\033[1;32m%s@%s\033\[0m::\033[1;34m %s\033[0m%s ",ptr->pw_name,hostname,dir,user_str);
fflush(stdout);
}
char *get_cmd(char *buff,char*myargv[])
{
if(buff==NULL||myargv==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
int i=0;
char*s=strtok(buff," ");
while(s!=NULL)
{
myargv[i++]=s;
s=strtok(NULL," ");
}
return myargv[0];
}
void run_cmd(char*path,char*myargv[])
{
if(path==NULL||myargv==NULL )
{
return;
}
pid_t pid=fork();
if(pid==-1)
{
return;
}
if(pid==0)
{
//ti huan
// execvp(path,myargv);
char pathname[128]={0};
if(strncmp(path,"/",1)==0||strncmp(path,"/",2)==0)
{
strcpy(pathname,path);
}
execv(pathname,myargv);
else
{
strcpy(pathname,PATH_BIN);
strcat(pathnamme,path);
}
execv(pathname,myargv);
perror("execvp error\n");
exit(0);//子进程必须要退出
}
else
{
wait(NULL);
}
}
int main()
{
while(1)
{
// printf("stu@localhost ~$");//默认
print_info();
fflush(stdout);
char buff[128]={0};
fgets(buff,128,stdin);
buff[strlen(buff)-1]=0;
char*myargv[ARG_MAX]={0};
char*cmd=get_cmd(buff,myargv);
if(cmd==NULL)
{
continue;
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"cd")==0)
{
if(myargv[1]!=NULL)
{
if(chdir(myargv[1])==-1)
{
perror("cd err");
}
}
}
else if(strcmp(cmd,"exit")==0)
{
break;
}
else//普通命令
{
//fork+exec;
run_cmd(cmd,myargv);
}
}
exit(0);
}
5、项目运行结果
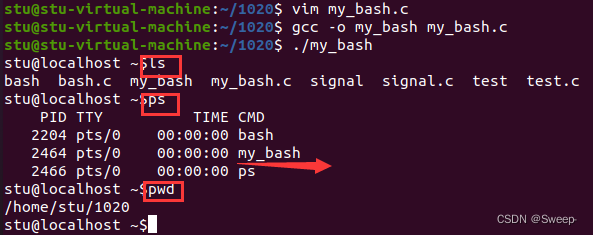
my_bash项目中有两个冒号::(与系统中bash区分开) ,这是个没有修改颜色之前的运行结果,可以看出my_bash与系统bash的区别。
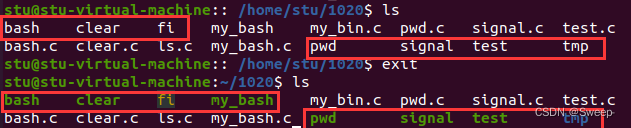
6、mybin代码
主要写了clear.c、pwd.c、ls.c三个主要代码。
//clear.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("\033[2J\033[0H");
}
//pwd.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
char path[256]={0};
if(getcwd(path,256)==NULL)
{
perror("getcwd error");
exit(1);
}
printf("%s\n",path);
exit(0);
}
//ls.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char path[256]={0};
if(getcwd(path,256)==NULL)
{
perror("getcwd error");
exit(1);
}
// printf("%s\n",path);
DIR *pdir=opendir(path);
if(pdir==NULL)
{
perror("opendir error");
exit(0);
}
struct dirent *s=NULL;
while((s=readdir(pdir))!=NULL)
{
if(strncmp(s->d_name,". ",1)==0)
{
continue;
}
// printf("%s ",s->d_name);
struct stat filestat;
stat(s->d_name,&filestat);
if(S_ISDIR(filestat.st_mode))
{
printf("\033[1;34m%s\033[0m ",s->d_name);
}
else
{
if(filestat.st_mode&(S_IXUSR|S_IXGRP|S_IXOTH))
{
printf("\033[1;32m%s\033[0m ",s->d_name);
}
else
{
printf("%s ",s->d_name);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
closedir(pdir);
exit(0);
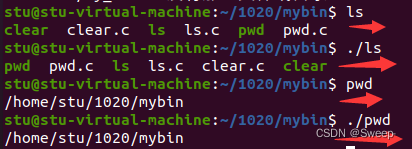
}以下是运行mybin中与系统给出的结果,可以看出mybin与系统一致。
7、关于修改颜色的printf命令
- 关键部分的基本格式是:
printf("\033[字背景颜色;字体颜色m字符串\033[0m" );
- 举例:
printf("\033[47;31mhello world\033[0m");
47是字背景颜色, 31是字体的颜色, hello world是字符串. 后面的\033[0m是控制码
printf("\033[1;32m%s\033[0m ",s->d_name);
32是字体颜色(绿色),%s是字符串,\033[0m是控制码(关闭所有属性)
字背景颜色范围: 40--49 字颜色: 30--39
40: 黑 30: 黑
41: 红 31: 红
42: 绿 32: 绿
43: 黄 33: 黄
44: 蓝 34: 蓝
45: 紫 35: 紫
46: 深绿 36: 深绿
47: 白色 37: 白色
- 其他的控制码:(标红的是经常使用的)
\033[0m 关闭所有属性
\033[1m 设置高亮度
\03[4m 下划线
\033[5m 闪烁
\033[7m 反显
\033[8m 消隐
\033[30m -- \033[37m 设置前景色
\033[40m -- \033[47m 设置背景色
\033[nA 光标上移n行
\03[nB 光标下移n行
\033[nC 光标右移n行
\033[nD 光标左移n行
\033[y;xH设置光标位置
\033[2J 清屏
\033[K 清除从光标到行尾的内容
\033[s 保存光标位置
\033[u 恢复光标位置
\033[?25l 隐藏光标
\33[?25h 显示光标
如有错误,敬请指正。
您的收藏与点赞都是对我最大的鼓励和支持!

























 576
576











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










