public byte[] getBytes(Charset charset)
Encodes this String into a sequence of bytes using the given charset, storing the result into a new byte array.
This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character sequences with this charset's default replacement byte array. The CharsetEncoder class should be used when more control over the encoding process is required.
当此字符串不能使用给定的字符集编码时,此方法的行为没有指定。如果需要对编码过程进行更多控制,则应该使用 CharsetEncoder 类。
在Java中,String.getBytes(Charset charset)方法会根据指定的 charset 编码返回某字符串在该编码下的byte数组表示,如
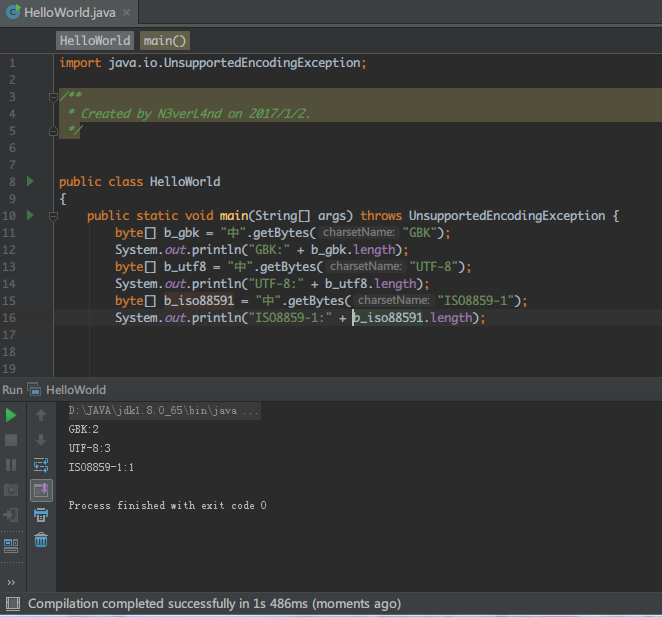
byte[] b_gbk = "中".getBytes("GBK"); byte[] b_utf8 = "中".getBytes("UTF-8"); byte[] b_iso88591 = "中".getBytes("ISO8859-1");
将分别返回“中”这个汉字在GBK、UTF-8和ISO8859-1编码下的byte数组表示。
此时b_gbk的长度为2,b_utf8的长度为3,b_iso88591的长度为1。
public String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName)
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified charset. The length of the new String is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length of the byte array.
This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The CharsetDecoder class should be used when more control over the decoding process is required.
通过使用指定的 charsetName 解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String(UTF-16)。新 String 的长度是字符集的函数,因此可能不等于 byte 数组的长度。
此方法总是使用此字符集的默认替代字符串替代错误输入和不可映射字符序列。如果需要对解码过程进行更多控制,则应该使用 CharsetDecoder 类。
这个new String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName)实际是使用 charsetName 指定的编码来将byte[]解码并生成UNICODE字符串。(按照什么存就得按照什么解)
String s_gbk = new String(b_gbk,"GBK"); String s_utf8 = new String(b_utf8,"UTF-8"); String s_iso88591 = new String(b_iso88591,"ISO8859-1");

通过打印s_gbk、s_utf8和s_iso88591,会发现,s_gbk和s_utf8都是“中”,而只有s_iso88591是?,为什么使用ISO8859-1编码再解码之后,无法还原“中”字呢?
其实原因很简单,因为ISO8859-1编码的编码表中,根本就没有包含汉字字符,当然也就无法通过"中".getBytes("ISO8859-1");来得到正确的“中”字在ISO8859-1中的编码值了,所以再通过new String()来还原就无从谈起了。
因此,通过String.getBytes(Charset charset)方法来得到byte[]时,一定要确定 charset 的编码表中确实存在String表示的码值,这样得到的byte[]数组才能正确被还原。
----------------------
有时候,为了让中文字符适应某些特殊要求(如http header头要求其内容必须为iso8859-1编码),可能会通过将中文字符按照字节方式来编码的情况,如
String s_iso88591 = new String("中".getBytes("UTF-8"),"ISO8859-1"),
这样得到的s_iso8859-1字符串实际是三个在 ISO8859-1中的字符,在将这些字符传递到目的地后,
目的地程序再通过相反的方式String s_utf8 = new String(s_iso88591.getBytes("ISO8859-1"),"UTF-8")来得到正确的中文汉字“中”。这样就既保证了遵守协 议规定、也支持中文。
String str = "中国"; String iso88591 = new String(str.getBytes("UTF-8"), "ISO-8859-1"); str = new String(iso88591.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "UTF-8"); System.out.println(str);
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
/**
* Created by N3verL4nd on 2017/1/2.
*/
public class HelloWorld
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String str=new String("我爱天安门");
byte by_gbk[]=str.getBytes("GBK");
String str_gbk=new String(by_gbk,"GBK");
System.out.println("str_gbk:"+str_gbk);
String str_utf8=new String(by_gbk,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("str_utf8:"+str_utf8);
System.out.println("----------------------");
byte by_utf8[]=str.getBytes("UTF-8");
String str2_gbk=new String(by_utf8,"GBK");
System.out.println("str2_gbk:"+str2_gbk);
String str2_utf8=new String(by_utf8,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("str2_utf8:"+str2_utf8);
}
}
tips:
字符串到byte[]的转换为编码;
byte[]到字符串的转换为解码。
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/u010234516/article/details/52853214







 本文详细介绍了Java中使用String.getBytes(Charset charset)方法进行字符编码的过程,包括不同字符集如GBK、UTF-8和ISO8859-1之间的转换,并通过实例展示了如何正确还原字符串。
本文详细介绍了Java中使用String.getBytes(Charset charset)方法进行字符编码的过程,包括不同字符集如GBK、UTF-8和ISO8859-1之间的转换,并通过实例展示了如何正确还原字符串。


















 5067
5067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










