12月份的第一篇博文,很久没敲代码了,毕竟是弱菜一枚,我也就不多说什么了, 得过且过的大二,悔、、!
A - Arcane Numbers 1
Description
Input
For each case, there’s a single line contains A and B.
Output
Sample Input
3
5 5
2 3
1000 2000
Sample Output
Case #1: YES Case #2: NO Case #3: YES
这题就是要求给定的两个数,问A 里面的因子,是否在B 里都有,可以说是gcd 的模版题了吧、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef __int64 LL;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
LL t;
if(a < b)
{
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
LL r;
r = a % b;
while(r)
{
a = b;
b = r;
r = a % b;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
int t;
LL a, b, tmp;
while(~scanf("%d",&t))
{
int icase = 1;
while(t --)
{
scanf("%I64d%I64d", &a, &b);
while(a != 1)
{
tmp = gcd(a, b);
if(tmp == 1)
{
break;
}
a = a / tmp;
}
printf("Case #%d: ", icase ++);
if(a == 1)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
}B - Candy
Description
Input
For each case starts with a line containing three integers N, M, K (1<=N<=13, 1<=M<=13, 2<=K<=10)
The next line contains M numbers which is B[i](0<=B[i]<=1000). Separated by a single space.
Then there are M*N like[i][j] , if the i-th kids like the j-th sugar like[i][j]=1 ,or like[i][j]=0.
Output
Sample Input
2
3 2 2
2 2
0 0 0
0 0 1
3 2 2
2 2
0 0 0
0 0 0
Sample Output
Case #1: YES
Case #2: NO
Hint
Give the first and second candy to the first kid. Give the third candy to the second kid. This allocate make all kids happy.
这题题意简单,但是我用的是模拟+暴力,不知道为何过不了,因为写的比较复杂,也不想再去debug了,先mark 一下,以后再来看看,据说是网络流、、
(错误的代码!)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int like[15][15];
int b[15];
int tt[15];
int t;
int n, m, k;
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&t))
{
int icase = 1;
while(t --)
{
memset(like, 0, sizeof(like));
memset(tt, 0, sizeof(tt));
scanf("%d%d%d",&n, &m, &k);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j ++)
{
scanf("%d",&like[i][j]);
if(like[i][j] == 1)
tt[i] ++;
}
}
int cnt = 0;
int tmp = n;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
int ok = 0;
if(tmp < 0)
break;
if(tt[i] * k >= b[i])
{
for(int j = 0; j <= tt[i]; j ++)
{
if(j * k >= b[i])
{
if(tmp - j >= 0)
{
cnt ++;
tmp = tmp - j;
ok = 1;
break;
}
}
if(ok)
break;
}
}
else
{
int cc = tt[i] * k;
if(tmp - b[i] - cc >= 0)
{
tmp = tmp - b[i] - cc;
cnt ++;
}
}
}
//printf("%d\n", cnt);
if(cnt == m)
printf("Case #%d: YES\n", icase ++);
else
printf("Case #%d: NO\n", icase ++);
}
}
}D - Triangle LOVE
Description
Now, scientists want to know whether or not there is a “Triangle Love” among N people. “Triangle Love” means that among any three people (A,B and C) , A loves B, B loves C and C loves A.
Your problem is writing a program to read the relationship among N people firstly, and return whether or not there is a “Triangle Love”.
Input
For each case, the first line contains one integer N (0 < N <= 2000).
In the next N lines contain the adjacency matrix A of the relationship (without spaces). A i,j = 1 means i-th people loves j-th people, otherwise A i,j = 0.
It is guaranteed that the given relationship is a tournament, that is, A i,i= 0, A i,j ≠ A j,i(1<=i, j<=n,i≠j).
Output
Take the sample output for more details.
Sample Input
2
5
00100
10000
01001
11101
11000
5
01111
00000
01000
01100
01110
Sample Output
Case #1: Yes
Case #2: No
可以用搜索A 掉它, 但是看题解是 用拓扑的思路、、、
我写的是错的,都不好意思贴出来了 - -#
E - Flowers
Description
Input
For each case, the first line contains two integer N and M, where N (1 <= N <= 10^5) is the number of flowers, and M (1 <= M <= 10^5) is the query times.
In the next N lines, each line contains two integer S i and T i (1 <= S i <= T i <= 10^9), means i-th flower will be blooming at time [S i, T i].
In the next M lines, each line contains an integer T i, means the time of i-th query.
Output
Sample outputs are available for more details.
Sample Input
2
1 1
5 10
4
2 3
1 4
4 8
1
4
6
Sample Output
Case #1: 0 Case #2: 1 2 1
线段树 || 树状数组 + 离散化。
这边稍微提一下,函数lower_bound()在first和last中的前闭后开区间进行二分查找,返回大于或等于val的第一个元素位置。如果所有元素都小于val,则返回last的位置。unique的函数是去除相邻的重复元素(只保留一个)。其返回值为地址,unique(num, num + n) - num 表示不重复的个数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 100010
int sum[N];
typedef struct node
{
int s, e;
}Node;
Node tt[N];
int a[N * 4];
int flo[N];
int n, m;
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x & (-x);
}
void add(int i, int x, int f)
{
while(i <= f)
{
sum[i] += x;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int x)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(x > 0)
{
cnt += sum[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
int t;
while(~scanf("%d",&t))
{
int icase = 1;
while(t --)
{
int cot = 0;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &tt[i].s , &tt[i].e);
a[cot ++] = tt[i].s;
a[cot ++] = tt[i].e;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
scanf("%d", &flo[i]);
a[cot ++] = flo[i];
}
sort (a, a + cot);
cot = unique(a, a + cot) - a;
for(int i = 0;i < n; i ++)
{
int tmp1 = lower_bound(a, a + cot, tt[i].s) - a + 1;
int tmp2 = lower_bound(a, a + cot, tt[i].e) - a + 1;
add(tmp1, 1, cot);
add(tmp2 + 1, -1, cot);
}
printf("Case #%d:\n", icase ++);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
int ans = lower_bound(a, a + cot, flo[i]) - a + 1;
printf("%d\n", getsum(ans));
}
}
}
}
F - Binary Tree Traversals
Description
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
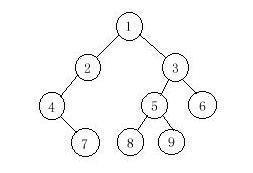
Input
Output
Sample Input
9
1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6
4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
该题就是给你中序遍历和后序遍历二叉树的结果,让你求出先序遍历的结果。主要是用到递归,搞的我好久,最后还是在别人的帮忙下,搞定的。当然,你也可以自己想想知道三个中的任意两个,求另外一个的思路、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct tree
{
tree *l, *r;
int data;
}tree;
int n;
int a[1010];
int b[1010];
tree * c;
tree *creat(int *a, int *b, int t)
{
tree *p;
for(int i = 0; i < t; i ++)
{
if(a[0] == b[i])
{
p = (tree* )malloc(sizeof(tree));
p ->data = a[0];
p -> l = creat(a + 1, b, i);
p -> r = creat(a + i + 1, b + i + 1, t - i - 1);
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
void out(tree *h)
{
if(h != NULL)
{
out(h ->l);
out(h ->r);
if(h == c)
printf("%d\n",h ->data);
else
printf("%d ",h ->data);
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d", &n))
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
}
c = creat(a, b, n);
out(c);
}
return 0;
}G - 美素数
小明对数的研究比较热爱,一谈到数,脑子里就涌现出好多数的问题,今天,小明想考考你对素数的认识。
问题是这样的:一个十进制数,如果是素数,而且它的各位数字和也是素数,则称之为“美素数”,如29,本身是素数,而且2+9 = 11也是素数,所以它是美素数。
给定一个区间,你能计算出这个区间内有多少个美素数吗?
Input
接下来共T行,每行输入两个整数L,R(1<= L <= R <= 1000000),表示区间的左值和右值。
Output
每组数据占一行,具体输出格式参见样例。
Sample Input
3
1 100
2 2
3 19
Sample Output
Case #1: 14 Case #2: 1 Case #3: 4
第一眼看到这个范围,我就已经不敢写了,就怕超时,后来鼓起勇气,用遍历 + 素数筛选 过了,343 ms。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define N 1000010
int prime[N];
bool is_prime[N + 10];
int beaprime[80000]; // 一开始计算过范围的。
void sieve(int n) // 素数筛选
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i ++)
is_prime[i] = true;
is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = false;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
{
if(is_prime[i])
prime[p ++] = i;
for(int j = 2* i; j <= n; j += i)
{
is_prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
int n, m;
sieve(1000010);
int coutt = 1;
/*for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
{
printf("prime %d\n", prime[i]);
}*/
for(int i = 0; i <= 80000; i ++)
{
int ttp = prime[i];
int hh = 0;
while(ttp)
{
hh += ttp % 10;
ttp = ttp / 10;
}
if(is_prime[hh])
beaprime[coutt ++] = prime[i]; // 美素数、
}
while(~scanf("%d",&t))
{
int icase = 1;
while(t --)
{
/*for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
{
printf("beaprime %d\n", beaprime[i]);
}*/
int cnt = 0;
scanf("%d%d",&n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= 80000; i ++)
{
if(beaprime[i] > m)
break;
if(beaprime[i] >= n && beaprime[i] <= m)
{
cnt ++;
}
}
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",icase ++, cnt);
}
}
}






















 1934
1934

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








