程序性能( program performance),是指运行一个程序所需要的内存大小和时间。可以采用两种方法来确定一个程序的性能,一个是分析的方法,一个是实验的方法。
程序的空间复杂性(space complexity),是指运行完一个程序所需要的内存大小。
程序的时间复杂性( time complexity)是指运行完该程序所需要的时间。
一、数据空间
对于简单变量和常量来说,所需要的空间取决于所使用的计算机和编译器以及变量与常量的数目。
每字节所占用的位数依赖于具体的机器环境,因此每个变量所需要的空间也会有所不同。
Borland C++中每种简单变量所占用的空间如下所示:
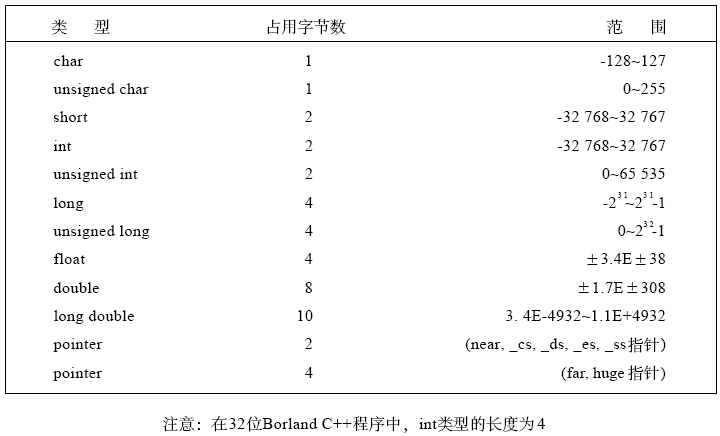
对于一个结构变量,可以把它的每个成员所占用的空间累加起来即可得到该变量所需要的内存。一个数组变量所需要的空间,方法是用数组的大小乘以单个数组元素所需要的空间。
如下的数组定义:
double a[100];
int maze[rows][cols];
数组a 需要的空间为1 0 0个d o u b l e类型元素所占用的空间,若每个元素占用8个字节,则分配给该数组的空间总量为8 0 0字节。数组m a z e有rows* cols个int类型的元素,它所占用的总空间为2 *rows* cols字节。
由于数据类型所占的字节数与机器有关,可用如下程序查看数据类型所占的字节数。
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- int main() {
- cout
- << "/n bool= " << sizeof(bool)
- << "/n char= " << sizeof(char)
- << "/n signed char= " << sizeof(signed char)
- << "/n unsigned char= " << sizeof(unsigned char)
- << "/n wchar_t = " << sizeof(wchar_t)
- << "/n short & short int & signed short & signed short int= " << sizeof(short)
- << "/n unsigned short & unsigned short int= " << sizeof(unsigned short)
- << "/n int & signed & signed int= " << sizeof(int)
- << "/n unsigned & unsigned int= " << sizeof(unsigned)
- << "/n long & long int & signed long & signed long int= " << sizeof(long)
- << "/n unsigned long & unsigned long int= " << sizeof(unsigned long)
- << "/n float= " << sizeof(float)
- << "/n double= " << sizeof(double)
- << "/n long double= " << sizeof(long double)
- << "/n long long & long long int & signed long long & signed long long int= "<<sizeof(long long)
- << "/n unsigned long long & unsigned long long int= "<<sizeof(unsigned long long)
- << endl;
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
对插入排序进行性能测试:
导致插入排序出现最坏复杂性的程序:CLK_TCK = 18.2
#include <iostream.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "insort.h"
void main(void)
{
int a[1000], step = 10;
clock_t start, finish;
for (int n = 0; n <= 1000; n += step) {
// 获得对应于n 值的时间
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = n - i; // 初始化
start = clock( );
InsertionSort(a, n);
finish = clock( );
cout << n << ' ' << (finish - start) / CLK_TCK << endl;
if (n == 100) step = 100;
}
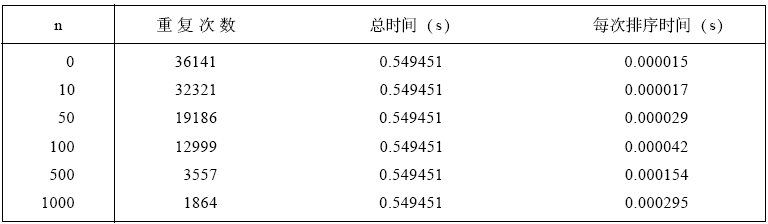
}误差在1 0 %以内的测试程序:
#include <iostream.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "insort.h"
void main(void)
{
int a[1000], n, i, step = 10;
long counter;
float seconds;
clock_t start, finish;
for (n = 0; n <= 1000; n += step) {
// 获得对应于n 值的时间
start = clock( ); counter = 0;
while (clock( ) - start < 10) {
c o u n t e r + + ;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = n - i; // 初始化
InsertionSort(a, n);
}
finish = clock( );
seconds = (finish - start) / CLK_TCK;
cout << n << ' ' << counter << ' ' << seconds << ' ' << seconds / counter << endl;
if (n == 100) step = 100;}
}






















 1848
1848

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








