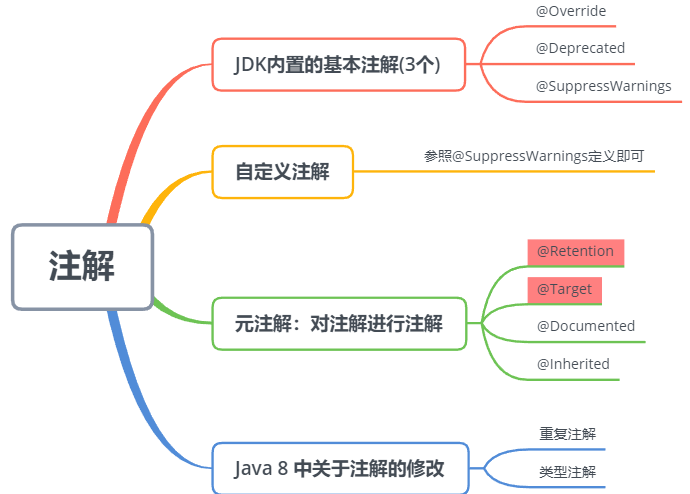
一、概述
注解(Annotation)其实是代码里的特殊标记 ,这些标记可以在编译、类加载河运行时被读取,并执行响应的处理,在JavaSE中,注解的使用目的比较简单,例如标记过时的功能,忽略警告等,在JavaEE中注解占据了更重要的角色,例如用例配置应用程序的任何切面,代替XML的配置。
二、JDK内置的基本注解(3个)
- @Override:限定重写父类方法,改注解只能用于方法
- @Deprecated:用于表示某个程序元素(类、方法等)已过时
- @SuppressWarnings:抑制编译器警告
例:
class Person{
public void show(){
System.out.println("人");
}
}
class Student extends Person{
@Override
public void show(){//如果使用该注解,但在父类中没有改方法,则编译不通过。
System.out.println("学生");
}
}
public class AnnotationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
@SuppressWarnings(value = "noused")//忽略警告
String name = "laowang";
}
}
三、元注解:对注解进行注解(4个)
1.@Retention
该元注解用于指定Anntation可以保留多长时间,@Retention包含一个RetentionPolicy类型的成员变量,该变量用来指定Anntation保留的时间。
- RetentionPolicy.SOURCE: 编译器直接丢弃这种策略的注释
- RetentionPolicy.CLASS: 编译器将把注释记录在 class 文件中. 当运行 Java 程序时, JVM 不会保留注解。 这是默认值
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:编译器将把注释记录在 class 文件中. 当运行 Java 程序时, JVM 会保留注释. 程序可以通过反射获取该注释
例:
@SuppressWarnings注解定义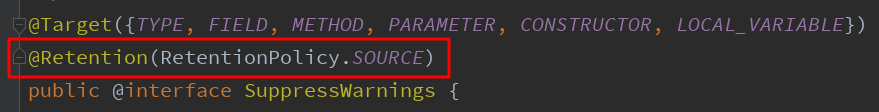
2.@Target
用于指定被修饰的Annotation能用于修饰那些程序元素,也包含一个名为value的成员变量,其类型为ElementType枚举类数组。
ElementType定义如下:
public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
TYPE,
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation type declaration */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,
/**
* Type parameter declaration
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* Use of a type
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE
}
3.@Documented
用于指定所修饰的Annotation被javadoc工具提取成文档时,是否存在文档中。
4.@Inherited
@Inherited修饰的Annotation将具有继承性。
自定义注解
- 使用@interface关键字修饰
- Annotation的成员变量使用无参方法形式来声明,其方法名和返回值定义了该成员的名字和类型。
- 可以使用default关键,设置成员变量的默认值
- 没有定义成员的Annotation成为标记,包含成员变量的Annotation成为元数据Annotation
例:
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD})//适用场景
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)//存活时间
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();//注解接收的数据,如@SuppressWarnings(value = "noused")
}
四、Java 8 中对注解的新规范
1.重复注解
(1)java 8以前实现重复注解
//自定义注解
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE,TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "hello";
}
//对上面的注解进行封装
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface MyAnnotations {
MyAnnotation[] value();//同数组形式实现多注解
}
//使用包装的注解,通过数据形式实现重复注解
@MyAnnotations({@MyAnnotation("initial"),@MyAnnotation("initial")})
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
(2)java 8 以后实现重复注解
//自定义的注解
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE,TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
//java 8新增元注解,要绑定一个封装的注解,即是用数组对本注解进行封装的注解
@Repeatable(MyAnnotations.class)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "hello";
}
//对上面的注解进行封装
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface MyAnnotations {
MyAnnotation[] value();
}
//可以直接重复使用注解
@MyAnnotation("initial")
@MyAnnotation("initial1")
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
2.类型注解
在Java8中能够得到方法参数的名称。这会简化标注在方法参数上的注解。
class Student extends @MyAnnotation Person{
public Student(@MyAnnotation String name){ //Checker第三方的.jar包。 @NonNull
super(name);
}
}





















 187
187











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








