这篇文章主要和大家分享一下,在我们基础软件升级过程中遇到的经典Netty问题。当然, 官方资料 也许是一个更好的补充。另外,大家如果对Netty及其Grizzly架构以及源码有疑问的,欢迎交流。后续会为大家奉献我们基于Grizzly和Netty构建的RPC框架的压测分析,希望大家能够喜欢!
好了,言归正传~
依赖
Netty团队大概从3.3.0开始,将依赖坐标从
<dependency> <groupId>org.jboss.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty</artifactId> <version>3.2.10.Final</version> </dependency>
改成了(Netty作者离开了Jboss公司)
<dependency> <groupId>io.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty</artifactId> <version>3.3.0.Final</version> </dependency>
这样,将其替换为Netty4,只需要替换一下版本就ok了,如替换成最新稳定版本:
<dependency> <groupId>io.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty-all</artifactId> <version>4.0.23.Final</version> </dependency>
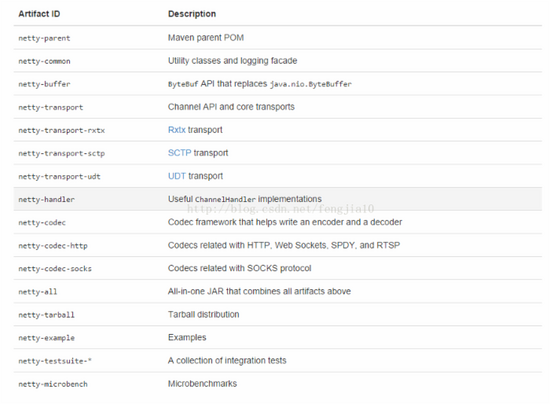
但请注意,从4开始,Netty团队做了模块依赖的优化,像Grizzly一样,分离出很多功能独立的Package。比方说,你希望使用Netty的buffer组件,只需简单依赖这个包就好了。不过本着严谨的态度,我们还是来看下netty-all这个一揽子包里究竟都有哪些依赖,如:
<dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-buffer</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-codec</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-codec-http</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-codec-socks</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-common</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-handler</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-transport</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-transport-rxtx</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-transport-sctp</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-transport-udt</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
每个包都代表什么呢?描述如下:
通过依赖分析,最终我选择了精简依赖,如下:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty-handler</artifactId> <version>4.0.23.Final</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
为什么?因为 netty-handler依赖了 netty-codec, netty-transport, netty-buffer等,所以我的依赖最终可以瘦身到只依赖这个包。顺便说一下,在版本4中,针对Linux平台做了AIO的优化实现,如:
<dependency> <groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId> <artifactId>netty-transport-native-epoll</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> <classifier>${os.detected.classifier}</classifier> <scope>compile</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
更多的细节,可以参看 这里 。
顺便说一句,Netty3和Netty4是可以共存的,其根本原因在于Netty团队为3和4分别设计了不同的基础package名(org.jboss.netty与io.netty)。就像我的工程,服务发现依赖了Curator,而它依赖了ZK,依赖了Netty3,而我的RPC部分仅仅依赖Netty4。
线程模型
Netty3只保证 upstream事件在IO线程里执行,但是所有的downstream事件会被调用线程处理,它可能是IO线程,也可能是用户自定义线程,这就带来了一个问题,用户需要小心地处理同步操作。除此之外,还会面临线程上下文切换的风险,设想一下,你在write的时候遇到了异常,转而触发exceptionCaught,但这是一个upstream事件,怎么办?
Netty4的线程模型则不存在此类问题,因为所有的操作都被保证在同一个EventLoop里的同一个Thread完成。也就是说Netty4不存在并发访问 ChannelHandler,当然这个前提是你没有给该handler打上Sharable注解。同时它也能保证 happens-before关系,所以你也没必要在 ChannelHandler声明volatile field。
用户可以指定自己的 EventExecutor来执行特定的 handler。通常情况下,这种EventExecutor是单线程的,当然,如果你指定了多线程的 EventExecutor或者 EventLoop,线程sticky特性会保证,除非出现 deregistration,否则其中的一个线程将一直占用。如果两个handler分别注册了不同的EventExecutor,这时就要注意线程安全问题了。
Netty4的线程模型还是有很多可以优化的地方,比方说目前Eventloop对channel的处理不均等问题,而这些问题都会在Netty 5里面优化掉,感兴趣的朋友可以参看 官方Issues
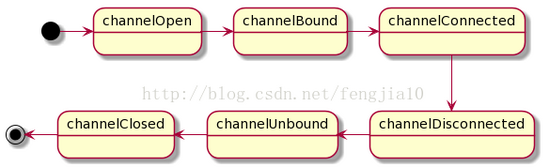
Channel状态模型
先来看两幅图,第一幅图是Netty3的Channel状态模型,第二附图是Netty4优化过的模型。可以看到,channelOpen,channelBound,和channelConnected 已经被channelActive替代。channelDisconnected,channelUnbound和channelClosed 也被 channelInactive替代。
Netty 3
Netty 4
这里就产生了两个问题:
其一,channelRegistered and channelUnregistered 不等价于 channelOpen and channelClosed,它是Netty4新引入的状态为了实现Channel的dynamic registration, deregistration, and re-registration。
第二, 既然是合并,那原先针对channelOpen的方法如何迁移?简单来做,可以直接迁移到替代方法里面。
Handler
1. ChannelPipelineFactory ----> ChannelInitializer
这里需要注意的是,ChannelPipeline的创建方式发生了变化,原先是这么玩的,
ChannelPipeline cp = Channels.pipeline();现在得这么玩
ChannelPipeline cp = ch.pipeline();
用Netty团队的话来说就是:
“Please note that you don't create a new ChannelPipeline by yourself. After observing many use cases reported so far, the Netty project team concluded that it has no benefit for a user to create his or her own pipeline implementation or to extend the default implementation. Therefore, ChannelPipeline is not created by a user anymore. ChannelPipeline is automatically created by a Channel.”
2. SimpleChannelHandler ----> ChannelDuplexHandler
之前是这么玩的
public void handleUpstream(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelEvent e)
throws Exception
{
if (e instanceof ChannelStateEvent) {
ChannelStateEvent cse = (ChannelStateEvent) e;
switch (cse.getState()) {
case OPEN:
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(cse.getValue())) {
// connect
channelCount.incrementAndGet();
allChannels.add(e.getChannel());
}
else {
// disconnect
channelCount.decrementAndGet();
allChannels.remove(e.getChannel());
}
break;
case BOUND:
break;
}
}
if (e instanceof UpstreamMessageEvent) {
UpstreamMessageEvent ume = (UpstreamMessageEvent) e;
if (ume.getMessage() instanceof ChannelBuffer) {
ChannelBuffer cb = (ChannelBuffer) ume.getMessage();
int readableBytes = cb.readableBytes();
// compute stats here, bytes read from remote
bytesRead.getAndAdd(readableBytes);
}
}
ctx.sendUpstream(e);
}
public void handleDownstream(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelEvent e)
throws Exception
{
if (e instanceof DownstreamMessageEvent) {
DownstreamMessageEvent dme = (DownstreamMessageEvent) e;
if (dme.getMessage() instanceof ChannelBuffer) {
ChannelBuffer cb = (ChannelBuffer) dme.getMessage();
int readableBytes = cb.readableBytes();
// compute stats here, bytes written to remote
bytesWritten.getAndAdd(readableBytes);
}
}
ctx.sendDownstream(e);
}改成ChannelDuplexHandler之后,我只需要重写read和write方法,来完成同样的功能。
其它
1. 通过下面的代码来完成Channel的限流
ctx.channel().setReadable(false);//Before ctx.channel().config().setAutoRead(false);//After2. TCP参数优化
// Before: cfg.setOption("tcpNoDelay", true); cfg.setOption("tcpNoDelay", 0); // Runtime ClassCastException cfg.setOption("tcpNoDelays", true); // Typo in the option name - ignored silently // After: cfg.setOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true); cfg.setOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, 0); // Compile error3. 单元测试经常用到的CodecEmbedder类已经变名为EmbeddedChannel
@Test
public void testMultipleLinesStrippedDelimiters() {
EmbeddedChannel ch = new EmbeddedChannel(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, true,
Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
ch.writeInbound(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("TestLine\r\ng\r\n", Charset.defaultCharset()));
assertEquals("TestLine", releaseLater((ByteBuf) ch.readInbound()).toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
assertEquals("g", releaseLater((ByteBuf) ch.readInbound()).toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
assertNull(ch.readInbound());
ch.finish();
}if (serverChannel != null) {
log.info("stopping transport {}:{}",getName(), port);
// first stop accepting
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
serverChannel.close().addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
// stop and process remaining in-flight invocations
if (def.getExecutor() instanceof ExecutorService) {
ExecutorService exe = (ExecutorService) getExecutor();
ShutdownUtil.shutdownExecutor(exe, "dispatcher");
}
latch.countDown();
}
});
latch.await();
serverChannel = null;
}
// If the channelFactory was created by us, we should also clean it up. If the
// channelFactory was passed in by Bootstrap, then it may be shared so don't clean it up.
if (channelFactory != null) {
ShutdownUtil.shutdownChannelFactory(channelFactory, bossExecutor, ioWorkerExecutor,allChannels);
}
}public void stop() throws InterruptedException {
// Wait until the server socket is closed.
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully().syncUninterruptibly();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully().syncUninterruptibly();
}FrameDecoder ----> ByteToMessageDecoder
OneToOneEncoder ----> MessageToMessageEncoder
OneToOneDecoder ----> MessageToMessageDecoder
6. 心跳逻辑优化,之前我是这么玩的
cp.addLast("idleTimeoutHandler", new IdleStateHandler(getTimer(), getClientIdleTimeout().toMillis(), NO_WRITER_IDLE_TIMEOUT, NO_ALL_IDLE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); cp.addLast("heartbeatHandler", new HeartbeatHandler());
其中HeartbeatHandler 继承了IdleStateAwareChannelHandler。在Netty4里,IdleStateAwareChannelHandler已经去除,但 IdleStateHandler类还存在,所以我会这么玩
cp.addLast("idleTimeoutHandler", new IdleStateHandler( NO_WRITER_IDLE_TIMEOUT, NO_WRITER_IDLE_TIMEOUT, NO_ALL_IDLE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); cp.addLast("heartbeatHandler", new HeartbeatHandler());
其中,HeartbeatHandler 继承了ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter。具体的实现逻辑这里就不贴出来了。再啰嗦几句,很多同学喜欢自己启线程去做心跳逻辑,我是不推荐这种方式的。利用Netty的链路空闲检测机制可以很好的完成这个功能,能更好地配合Netty线程模型和异常捕获机制。自己定制,处理不好,会带来很大的线上隐患。
小结
这篇文章简单记录了升级过程中遇到的一些比较higher的话题,配上代码,希望能更好的重现整个升级思路和过程,也希望能给大家带来帮助。如果你在升级过程中遇到了问题,欢迎留言交流。最后,祝玩的开心~
参考文档
1. http://www.infoq.com/news/2013/11/netty4-twitter
2. http://netty.io/wiki/all-documents.html
3. http://netty.io/wiki/index.html





 本文分享了从Netty 3升级到Netty 4的过程中遇到的问题及解决方案,包括依赖管理、线程模型改进、Channel状态模型变化、Handler类调整等方面的内容。
本文分享了从Netty 3升级到Netty 4的过程中遇到的问题及解决方案,包括依赖管理、线程模型改进、Channel状态模型变化、Handler类调整等方面的内容。

















 677
677

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








