spring核心IOC和AOP,终于到aop,看起来真心费力。
demo
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:ss="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<bean id="test" class="qbb.aop.TestBean" />
<bean class="qbb.aop.AspectJTest" />
</beans>public class TestBean {
private String testStr = "testStr";
public String getTestStr() {
return testStr;
}
public void setTestStr(String testStr) {
this.testStr = testStr;
}
public void cout(){
System.out.println("test");
}
}@Aspect
public class AspectJTest {
@Pointcut("execution(* *.cout(..))")
public void test(){
}
@Before("test()")
public void beforeTest(){
System.out.println("beforeTest");
}
@After("test()")
public void afterTest(){
System.out.println("afterTest");
}
@Around("test()")
public Object arroundTest(ProceedingJoinPoint p){
System.out.println("before1");
Object o = null;
try {
o = p.proceed();
}catch (Throwable e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after1");
return o;
}
}
test
public class AopTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-aop.xml");
TestBean testBean = (TestBean) ctx.getBean("test");
testBean.cout();
}
}aop自定义标签分析
aop采用自定义标签解析。
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop=org.springframework.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandlerhttp\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd=org/springframework/aop/config/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd=org/springframework/aop/config/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd=org/springframework/aop/config/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.1.xsd=org/springframework/aop/config/spring-aop-3.1.xsd
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd=org/springframework/aop/config/spring-aop-3.1.xsd标签的处理AopNamespaceHandler:
//AopNamespaceHandler
public class AopNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
public void init() {
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.1 XSD.
//处理xml中的配置advisor
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
//注解的Aspect解析
registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());
//下面2个没用过
registerBeanDefinitionDecorator("scoped-proxy", new ScopedProxyBeanDefinitionDecorator());
// Only in 2.0 XSD: moved to context namespace as of 2.1
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}之前自定义标签看过,遇到自定义自定义标签,首先uri找到namespacehandler,调用init方法注册标签的解析beanDefinitionparser,然后调用beanDefinitionParser的parser解析返回beanDefinition注册到beanfactory里面去。
aop这里注册了不同的标签解析handler,主要看下aspectj-autoproxy的handlerAspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser。
//AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//解析aspectj-autoproxy标签
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
//解析子标签
extendBeanDefinition(element, parserContext);
return null;
}
//AopNamespaceUtils
public static void registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
//设置proxy-target-class和expose-proxy2个属性
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
//注册组件,然后fire
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}
//AopConfigUtils
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
//注册或升级解析bean:AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//如果已经有,就比较优先级,改变beanClassName
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
//注册beanDefinition,最终aop通过这个bean来实现
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}这里只是注册了一个解析bean,没有真正实现aop的功能,功能实现通过注册的bean:AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在getbean的时候通过BeanPostProcessor实现。
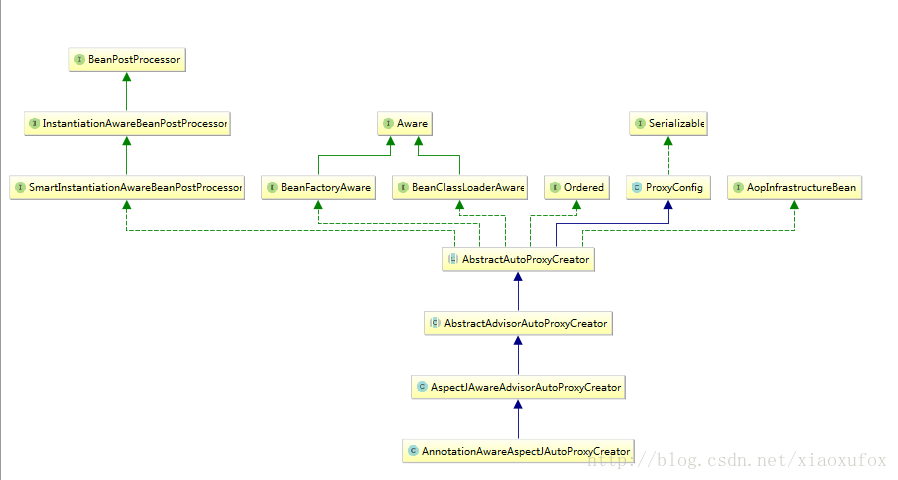
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是实现了BeanPostProcessor(初始化前,初始化后处理器)和InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(实例化前,实例化后处理器)2个接口来实现aop功能。
大致看下方法实现:
//AbstractAutoProxyCreator
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); //缓存取现
if (!this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(cacheKey)) {
//是否处理过或者不需要
if (this.advisedBeans.contains(cacheKey) || this.nonAdvisedBeans.contains(cacheKey)) {
return null;
}
//是否基础类或者跳过
//isInfrastructureClass判断是否Advisor、Advice、AopInfrastructureBean
//shouldSkip子类实现,如果aspect切面类和要代理的类名相同,那就skip
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.nonAdvisedBeans.add(cacheKey);
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.
// 自定义的TargetSource,如果你需要在运行时,动态切换代理实例或者新生成一个,就可以试试这个玩意
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
//获取bean适配的Advice
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
//创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
return null;
}
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) {
return true;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
//是否需要aop解析
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (this.nonAdvisedBeans.contains(cacheKey)) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.nonAdvisedBeans.add(cacheKey);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.add(cacheKey);
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.nonAdvisedBeans.add(cacheKey);
return bean;
}最重要的2个方法
//获取适合的advise
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
//创建代理类
createProxygetAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean获取适合的advise
//AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
List advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
//获取匹配的Advisor
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
//获取所有Advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//获取匹配的
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}逻辑清晰,首先获取所有的advisor,然后找到匹配当前bean的advisor。
findCandidateAdvisors获取所有的advisor
// AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
// 获取所有的advisor
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
// 获取xml里面配置advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
// 获取aspect注解的advisor
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
}findCandidateAdvisors获取xml里面配置的advisor分2步:
1. 从beanfactory中获取beanNameType为Advisor的所有beanNames;
2. 从beanfactory中getBean,创建这些advisor的bean。
buildAspectJAdvisors获取注解Aspect的advisor
// BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder
// 获取注解Aspect的advisor
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = null;
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
aspectNames = new LinkedList<String>();
String[] beanNames =
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this
// case they would be cached by the Spring container but would not
// have been weaved
Class beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 过滤类型必须为Aspect类型
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
// AspectMetadata是aspect的元数据
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
// 默认就是SINGLETON
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
// factory的实现可以保证AspectMetadata实例化一次
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 获取注解Aspect的advisor
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
}
//如果已经处理过了,直接从缓存取
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}首先看是否解析过Aspect元数据,没解析过就重头开始,解析过就从缓存里面取wrap的factory,获取advisor。
getAdvisors
//ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory maaif) {
// 都是通过Aspect元数据的来解析,解析标记Aspect的类的class
final Class<?> aspectClass = maaif.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
// 获取name
final String aspectName = maaif.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
// 校验aspect类的是否有注解Aspect,为Singleton
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
// 保证元数据Aspect生成的实例唯一
final MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(maaif);
final List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
// doWithMethods的时候不但解析本Aspect,如果有Superclass,也会,如果不是superlclass,是接口的话,解析所有接口的
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// Exclude pointcuts
// 不解析pointCut注解,这个注解是在匹配canApplay的getClassFilter过滤时处理
if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {
// 解析方法上的advisor
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
}
});
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
// advisor不为空,且配置的是延迟初始化,加入同步实例化advisor
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
// declareParents注解
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}看到处理方式是对Aspect类的非pointcut方法进行解析:
//ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aif,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aif.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
// 方法注解上的注解表达式
// 注解:Before, Around, After, AfterReturning, AfterThrowing, Pointcut
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
getPointcut(candidateAdviceMethod, aif.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (ajexp == null) {
return null;
}
// 封装advisor,构造会区分不同注解的Advice
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(
this, ajexp, aif, candidateAdviceMethod, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
//获取注解表达式
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class<?> candidateAspectClass) {
// 注解:Before, Around, After, AfterReturning, AfterThrowing, Pointcut
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// 解析注解表达式,只是单纯注解上表达式,不会关联pointcut
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class[0]);
ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());
return ajexp;
}注意在解析method上注解表达式后会根据统一封装成InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl,该类的构造会区分不同的Advice:
// ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aif, int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aif.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
...
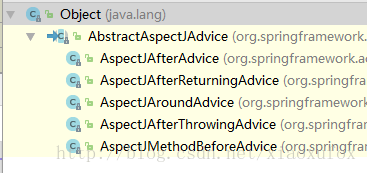
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, ajexp, aif);
break;
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrderInAspect);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}不同的注解对应不同的封装。虽然都是Advice的封装,但是AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice、AspectJAfterReturningAdvice不是通过MethodInterceptor实现,其他几个是通过MethodInterceptor的invoke实现,
不过最后的最后所有Advice都会统一封装成MethodInterceptor的实现类。
记得一点:所有的Advice最后都会封装成MethodInterceptor实现类。
findAdvisorsThatCanApply匹配当前bean的advisor
// AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
// 在找到所有advisor后,再查找匹配当前要代理bean的advisor
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
// AopUtils
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 引介增强
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 过滤处理过的
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 匹配
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
// 查找是否匹配
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
// 引介增强
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// 一般的advisor
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
里面有个特殊的引介IntroductionAdvisor,当已经有一个类,你想在运行时动态的为这个类增加一些运行方法(相当于又实现了其他接口方法),就可以尝试引介advisor。
canApply
// AopUtils
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
// 在getClassFilter调用中buildPointcutExpression方法完成PointCut注解的解析,这里是匹配类级别
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
// 获取目标代理类的所有实现接口
Set<Class> classes = new HashSet<Class>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
// 匹配方法级
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}这里首先完成pointcut注解的解析,然后匹配类级别,然后对目标类的每个实现方法,完成方法级别的匹配,里面太复杂,看了几遍,还是有些细节没把握好。
createProxy创建代理类
在找到目标类的所有匹配的advisor后,开始创建代理对象。
// AbstractAutoProxyCreator
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// Copy our properties (proxyTargetClass etc) inherited from ProxyConfig.
// 复制一些属性 other.optimize; proxyTargetClass\optimize\exposeProxy\frozen\opaque
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 给定的bean是否使用targetClass作为target还是接口代理
// 基本是proxyTargetClass和bean配置的preserveTargetClass2个属性值
if (!shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to
// the target's interfaces only.
// 加入所有实现接口
Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, this.proxyClassLoader);
for (Class<?> targetInterface : targetInterfaces) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(targetInterface);
}
}
// 对之前匹配的advisor处理下
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); //子类实现,可以更改一些设置
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 获取代理
return proxyFactory.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}buildAdvisors
// AbstractAutoProxyCreator
protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors) {
// Handle prototypes correctly...
// 解析this.interceptorNames中的Advisor,通过beanName获取bean,加到advisor里面,说实话,暂时没看到有调用设置的地方,可以pass先
// 可以配置一些通用的
Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames();
List<Object> allInterceptors = new ArrayList<Object>();
if (specificInterceptors != null) {
// 当前匹配的
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(specificInterceptors));
if (commonInterceptors != null) {
if (this.applyCommonInterceptorsFirst) {
allInterceptors.addAll(0, Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
}
else {
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
int nrOfCommonInterceptors = (commonInterceptors != null ? commonInterceptors.length : 0);
int nrOfSpecificInterceptors = (specificInterceptors != null ? specificInterceptors.length : 0);
logger.debug("Creating implicit proxy for bean '" + beanName + "' with " + nrOfCommonInterceptors +
" common interceptors and " + nrOfSpecificInterceptors + " specific interceptors");
}
Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor[allInterceptors.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < allInterceptors.size(); i++) {
// wrap操作:统一封装成advisor
advisors[i] = this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(allInterceptors.get(i));
}
return advisors;
}
// DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry
// 将拦截器,advisor、advice什么的都统一封装成advisor先
public Advisor wrap(Object adviceObject) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
if (adviceObject instanceof Advisor) {
return (Advisor) adviceObject;
}
if (!(adviceObject instanceof Advice)) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(adviceObject);
}
Advice advice = (Advice) adviceObject;
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
// So well-known it doesn't even need an adapter.
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice);
}
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
// Check that it is supported.
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice);
}
}
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advice);
}可以认为buildAdvisors,这一步是将所有拦截器、advisor、Advice什么的都统一封装成Advisor,方便后面处理。
getProxy创建代理对象
// ProxyFactory
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 创建代理,生成代理对象
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}createAopProxy创建代理
// ProxyFactory
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
// DefaultAopProxyFactory
// 决定是jdk代理还是cglib代理
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface()) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
if (!cglibAvailable) {
throw new AopConfigException(
"Cannot proxy target class because CGLIB2 is not available. " +
"Add CGLIB to the class path or specify proxy interfaces.");
}
return CglibProxyFactory.createCglibProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}这里主要是决定是jdk代理还是cglib代理。 jdk只能代理接口,所以如果目标类有实现接口的情况,aop配置proxyTargetClass=true,那就cglib,否则jdk代理,没有实现接口,那只能cglib代理。
JdkDynamicAopProxy
jdk动态代理通过InvocationHandler的invoke方法。
// JdkDynamicAopProxy
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
// equals\hashCode方法,内部直接调用返回
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
// 内部调用是否拦截,通过配置exposeProxy控制
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
// Get the interception chain for this method.
// 所有拦截器-会将之前没有实现MethodInterceptor的advice全部转为实现该接口的类
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
// 拦截器链空,直接调用
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
// 拦截器链调用
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
if (retVal != null && retVal == target && method.getReturnType().isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
这一步主要是回去方法匹配的拦截器链。
// DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, Class targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... we have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, targetClass);
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
// 对所有advisor循环判断
for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
// 类是否匹配
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
// 这里做转换,没有实现methodInterceptor的做适配
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
// 方法是否匹配
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) {
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
// 又做一层封装InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher,累死
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// 引介增强处理
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
// 其他
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}看下registry.getInterceptors适配:
// DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
// 除下面那3个其他都是实现MethodInterceptor
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
// 做适配MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter\AfterReturningAdviceAdapter\ThrowsAdviceAdapter
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);
}看文档都是说最后统一转成methodInterceptor处理,一直疑惑在哪里做的转换,这段代码找了好久。
invocation-proceed
在封装好所有适配的拦截器链后,通过ReflectiveMethodInvocation封装所有执行数据,然后procced处理拦截器链和joinpoint。
// JdkDynamicAopProxy
// We need to create a method invocation...
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();// ReflectiveMethodInvocation
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
// 执行到最后执行joinpoint方法
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// 拦截器链的执行,获取下一个要执行的
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
// 执行方法匹配
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
// 不匹配就不执行拦截器
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
// 普通拦截器,直接执行
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}Cglib2AopProxy
通过Enhancer实现代理。顺序:
1. getProxy:
2. getCallbacks:
// 拦截器回调Callback实现MethodInterceptor
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
....
// 将拦截器的回调加入整个回调数组
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[]{
aopInterceptor, // for normal advice
targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
....这DynamicAdvisedInterceptor通过实现的intercept来实现拦截。而在DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的Intercept中也进行了
// DynamicAdvisedInterceptor-intercept
....
// 封装拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, args);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// CglibMethodInvocation继承ReflectiveMethodInvocation,处理方式上面说过
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
....总结:
- 所有Advice最后封装成MethodInterceptor处理;
- aop看起来真累,aop有些配置没用过,只能自己写Test,慢慢debug代码跟,有时候就会看到后面忘了前面,看了好几遍才算理清结构;
- spring框架封装真心厉害。
参考:
- Spring AOP之Introduction(@DeclareParents)简介:http://www.blogjava.net/jackfrued/archive/2010/02/27/314060.html






















 1175
1175











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








