目录
Voctor、ArrayList、LinkedList 之间的区别
HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet 之间的区别
3.1 HashTable、HashMap、TreeMap、LinkedHashMap 之间的区别
3.2 为什么 HashMap 的键值可以为 null,HashTable 不能为 null?
3.7 HashMap扩容时,为什么时2的冥次方,而且要再做一次 Hash 计算?
3.8 JDK 1.7,多线程情况下 HashMap扩容会存在什么问题?如何解决?
一、集合
List、Set、Map之间的关系图
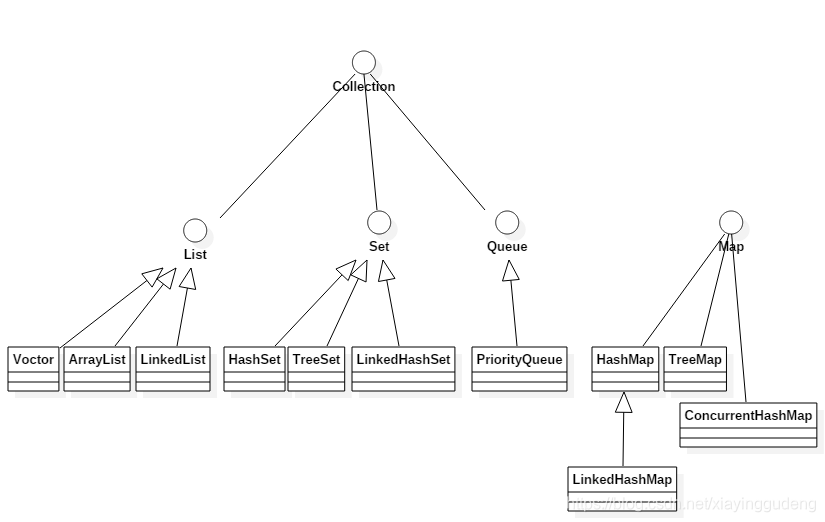
二、List
Voctor、ArrayList、LinkedList 之间的区别
| Vector | ArrayList | LinkedList | |
| 底层数据结构 | 数组 | 数组 | 链表 |
| 默认初始容量 | 10 | 10 | |
| 加载因子 | 1 | 1 | |
| 扩容后容量 | 20 | 16 | |
| 同步机制 | 线程安全 | 线程不安全 | |
| 优点 | 基于下标随机查询 | 插入、删除速度快 | |
| 缺点 | 插入、删除速度慢 | 查询速度慢 |
三、Set
HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet 之间的区别
| HashSet | TreeSet | LinkedHashSet | |
| 底层实现 | HashMap | TreeMap | LinkedHashMap |
| 默认初始容量 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 加载因子 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| 扩容后容量 | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| 同步机制 | 线程不安全 | 线程不安全 |
四、Map
3.1 HashTable、HashMap、TreeMap、LinkedHashMap 之间的区别
| HashTable | HashMap | TreeMap | LinkedHashMap | |
| 接口或类 | Dictionary 类 | Map 接口 | Map 接口 | Map 接口 |
| 底层数据结构 | 散列表(数组+链表) | 散列表(数组+链表) | 数组+红黑树 | 双向链表 |
| 默认初始容量 | 11 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 加载因子 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| 扩容后容量 | 23 | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| 同步机制 | 线程安全 | 线程不安全 | 线程不安全 | 线程不安全 |
| key/value为null | 不允许 | 允许 | 允许 | 允许 |
| 根据hash值计算数组下标的算法 | 不同的hash值计算得到相同下标值的几率较高 | 对 Key 的 hash 做移位运算和位的与运算,能更广泛地分散到数组的不同位置 | ||
| 两者都会重新根据Key的hash值计算其在数组中的新位置,重新放置。算法相似,时间、空间效率相同 | compareTo()函数实现元素有序 | 和 HashMap 相似,维护循环双向链表 | ||
3.2 为什么 HashMap 的键值可以为 null,HashTable 不能为 null?
HashTable 通过 get() 获得 value 为 null 时,因为多线程的并发访问会修改值,导致无法判断 null 是值被设置为空还是从该关键字不存在。 而 Hash Map 是非线程安全的,通过 get() 获得的 value 为 null 或者 0 来判断。
3.3 HashMap 数据结构
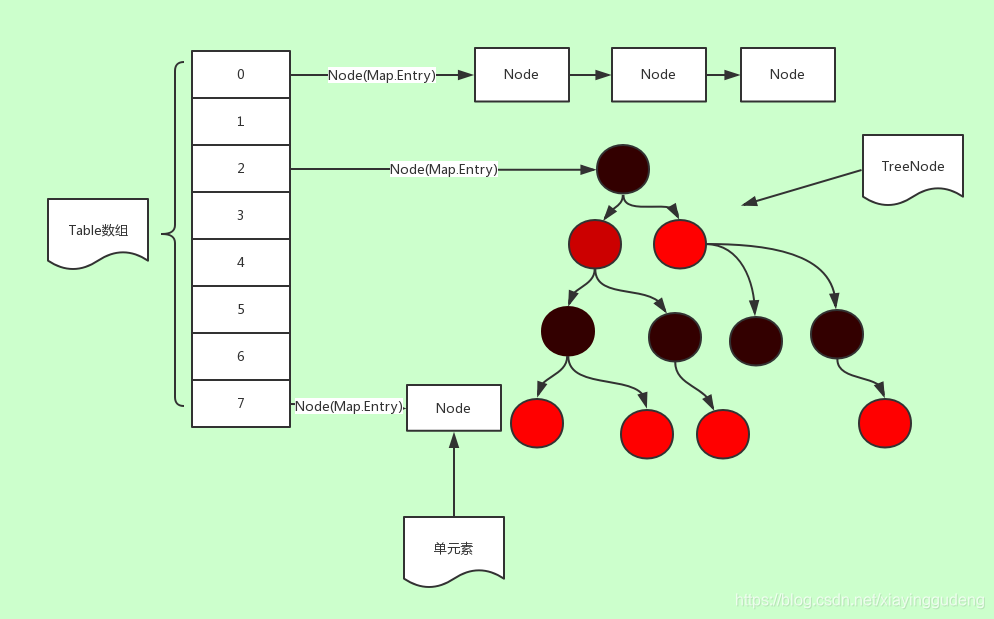
3.4 描述下 HashMap 的 put() 操作?
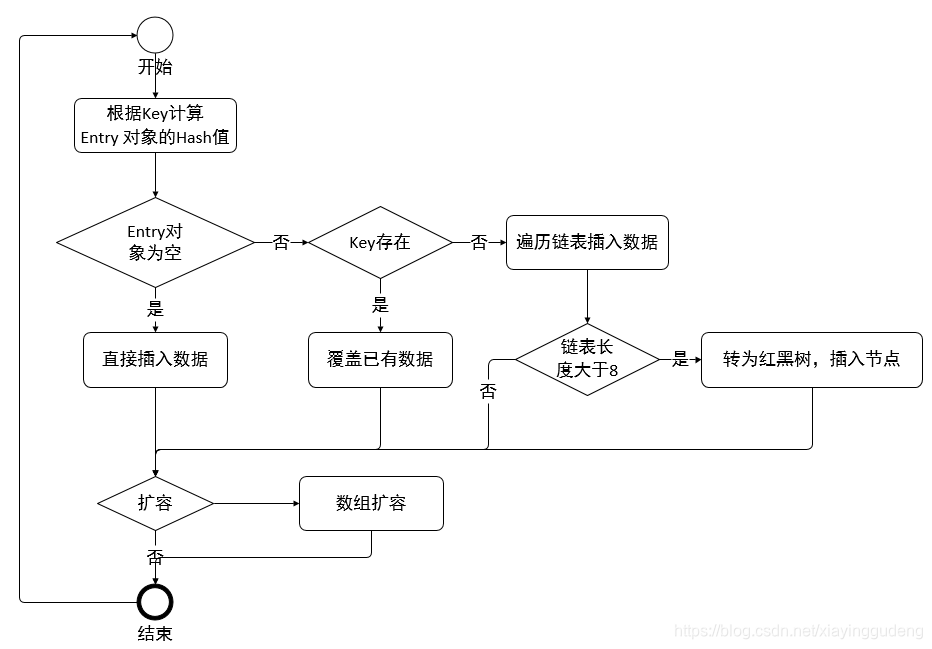
1、根据关键字 key 获得 Entry 对象的 hash 值,判断当前 Entry 对象是否为 null;
2、为 null,直接插入数据,不为 null,遍历 Entry 对象所在的链表;
3、关键字 key 存在,覆盖已有数据;关键字 key 不存在,插入数据(头插法);
4、链表长度大于8,改为红黑树插入。
说明:HashMap 1.7 版本 resize()、put() 方法采用头插法, HashMap 1.8 版本的方法采用尾插法。
// JDK 1.8 版本
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
3.5 HashMap 怎么实现线程安全?
1、Collections.synchronizedMap()函数实现;
2、使用 HashTable;
3、分段锁:CurrentHashMap。
3.6 JDK 1.7,HashMap 是怎么扩容的?
HashMap 的初始大小默认为16,加载因子为0.75,容量扩展为原来的2倍;HashMap 的容量必须是2的幂,因为性能,通过限制 HashMap 的容量是一个2的幂数,定位 Entry 在新 Hash Map 的位置时,h & (length-1) 和 h % length 结果是一致的,Java的%、/操作比&慢10倍左右。
扩容的时候,当复制旧的 HashMap 到新的 HashMap 时,遇到哈希冲突时,采用头插法将冲突的 Entry 插入到链表中。
3.7 HashMap扩容时,为什么时2的冥次方,而且要再做一次 Hash 计算?
两者的目的都是为了减少哈希冲突。
1、假设扩容后为20时(非2的冥次方),length - 1 = 19,二进制为:10011;那么,h & (length-1) 的结果的二进制倒数第三位和第四位只能是0;会增加哈希冲突。
2、不同的键的的 hash 值仅仅只能通过低位来区分,高位的信息没有被充分利用。极端情况就是:所有的 hash 值低位全相等,而高位不相等,通过一个再 Hash 来减少哈希冲突。
3.8 JDK 1.7,多线程情况下 HashMap扩容会存在什么问题?如何解决?
采用队头插入的方式,导致了HashMap在“多线程环境下”的死循环问题,JDK 1.8 采用尾插法,消除了 HashMap 多线程死循环的问题。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {//最大容量为 1 << 30
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];//新建一个新表
boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing;
useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;//是否再hash
transfer(newTable, rehash);//完成旧表到新表的转移
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {//遍历同桶数组中的每一个桶
while(null != e) {//顺序遍历某个桶的外挂链表
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;//引用next
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);//找到新表的桶位置;原桶数组中的某个桶上的同一链表中的Entry此刻可能被分散到不同的桶中去了,有效的缓解了哈希冲突。
e.next = newTable[i];//头插法插入新表中
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}3.9 LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 和 HashMap 的操作基本一致,只是,LinkedHashMap 维护一个双向链表;
LinkedHashMap 内部维护了一个双向链表,解决了 HashMap 不能随时保持遍历顺序和插入顺序一致的问题,LinkedHashMap 元素的访问顺序也提供了相关支持,也就是我们常说的 LRU(最近最少使用)原则。
// LinkedHashMap 数据结构
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
3.10 ConcurrentHashMap 底层原理?
Java 1.7版本是通过分段锁机制来实现的,ConcurrentHashMap 初始有16个分段锁Segment,后期不能再进行扩容的。每个分段锁Segment都类似于一个HashMap,继承了重入锁ReentrantLock,有了锁的功能,由数组和链表组成,当链表的长度大于8时,转化为红黑树。
Java 1.8 版本时通过数组 + 红黑树 + CAS (compare and swap) + sychronized 机制 组成,数组可以扩容。
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
3.11 HashMap遍历的三种方法
方法1:使用 For-Each 迭代 entries;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){
System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + ", value = " + entry.getValue())
}方法2 使用For-Each迭代keys和values(具体代码未给出)
方法3 使用Iterator迭代(具体代码未给出)






















 179
179

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








