线性回归:
1.目标函数增加L2正则
θ存在解析式:
使用梯度下降进行解θ:=>
代码:
import numpy as np
def regression(data, alpha, lamda):
n=len(data[0])-1
theta=np.zeros(n)
for i in range(30):
for d in data:
y_hat=np.dot(d[:-1],theta)
y_loss=y_hat-d[-1:]
theta=theta-alpha*y_loss*d[:-1]+lamda*theta
print(i,theta)
data=[[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[4,4],[5,5],[6,6],[7,7]]
regression(data,0.01,0.1)
Logistic回归:二分类
1.Logistic/sigmoid函数: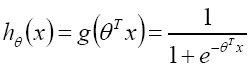 =>
=>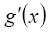
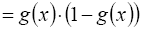
![]()
![]()
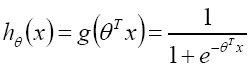 =>
=>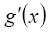
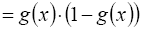
代码:
import scipy as sp import numpy as np from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression x = np.loadtxt("wine.data", delimiter=",", usecols=(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13)) # 获取属性集 y = np.loadtxt("wine.data", delimiter=",", usecols=(0)) # 获取标签集 print(x) # 查看样本 # 加载数据集,切分数据集80%训练,20%测试 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2) # 切分数据集 # 调用逻辑斯特回归 model = LogisticRegression() model.fit(x_train, y_train) print(model) # 输出模型 # make predictions expected = y_test # 测试样本的期望输出 predicted = model.predict(x_test) # 测试样本预测 # 输出结果 print(metrics.classification_report(expected, predicted)) # 输出结果,精确度、召回率、f-1分数 print(metrics.confusion_matrix(expected, predicted)) # 混淆矩阵
softmax回归:多分类
概率: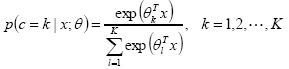
![]()
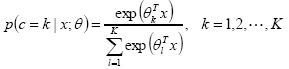
似然函数(似然函数是一种关于统计模型参数的函数。给定输出x时,关于参数θ的似然函数L(θ|x)(在数值上)等于给定参数θ后变量X的概率:L(θ|x)=P(X=x|θ)):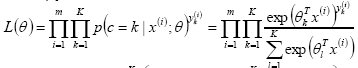
![]()
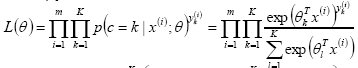
对数似然: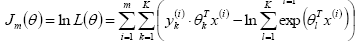
![]()
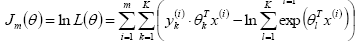
梯度:![]() =>
=>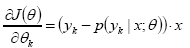
![]()
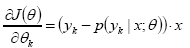
代码:








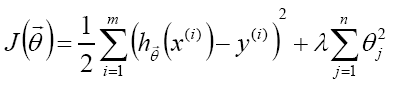
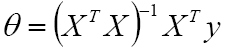
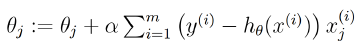














 6346
6346

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








