KMP算法是(Knuth-Morris-Pratt)提出的一种算法,其核心思想是通过分析子串来实现串匹配过程中不回溯。这样对于高频查找,还有长字串查找十分有帮助。
首先我们来看看普通的回溯查找:
朴素的查找算法最让人头疼的就是回溯,一旦一次匹配不成功,主串 字串都要回溯,主串回溯到到以前的位置的下一个位置,字串直接回溯到开始处。
所以我们可以计算其时间复杂度为: 最坏情况O(mn)其中m为主串长度,n为字串长度。
其实这是一个很可怕的复杂度,比如我们来做一下假设: 如果我们从一本书中查找一句话,假设这本书有1,000,000个负号构成,每个符号占用1个byte,所以就是1M个字节,我们来查找一句话,这句话是这样的:
The design of the Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm follows a tight analysis of the Morris and Pratt algorithm. Let us look more closely at the Morris-Pratt algorithm. It is possible to improve the length of the shifts.
呵呵,这是KMP算法的一个描述,起码得100个字符吧,算算复杂度~当然并不是每次都处于最坏的情况。
正如上面那句话所说的: KMP算法它可以解决这个问题,使得复杂度下降:
preprocessing phase in O(m) space and time complexity;
searching phase in O(n+m) time complexity (independent from the alphabet size);
呵呵,也就是处理字串的时间是 线性的,同样查找也是线性的。
让我们来看看什么是KMP算法:
首先我们来分析一下不匹配的情况:
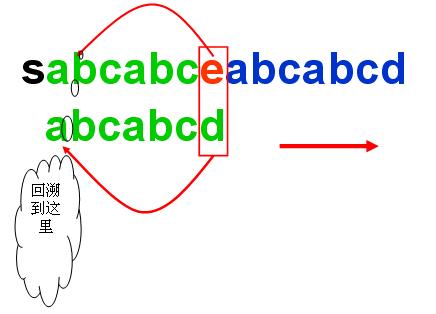
如图所示,当匹配进行到e 跟字串中的d时,匹配过程中被中断了,遇到了不匹配的情形。但是由一个有趣的现象,就是主串中的绿色部分跟字串中的绿色部分是一样的。
所以这就向我们透漏一个信息:我们可以通过分析字串来确定到底回溯多少,还是直接就不回溯!
这一点是很重要的一点,也是算法的根本出发点。所以下面的分析将主要集中在字串的分析,毕竟主串就是子串嘛!
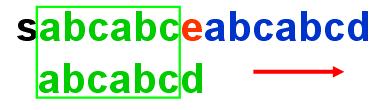
我们来分析子串什么呢?呵呵当然是在什么情况下可以子串自己根自己部分匹配。对于上面的那个子串abcabcd来说
蓝颜色下划线部分是一个很好的现象,为什么呢,因为从普通的匹配算法来说,对于子串是要回溯到开始部分的,如果我们已知开始部分跟主串中的某个部分匹配,其他全都不匹配,那么我们只要处理一下这种情况就好了。当然这个某个部分也不是乱选的,必须是已匹配子串的尾部,有点绕口,就是途中绿颜色的主串的尾部。
为什么呢?如果不是尾部我们有一个匹配,那么尾部肯定不匹配,说明这样的匹配不能进行下去,所以必须是尾部。
尾部有什么好处----主串不用回溯
看看人家大师的定义:
Consider an attempt at a left position j, that is when the the window is positioned on the text factor y[j .. j+m-1]. Assume that the first mismatch occurs between x[i] and y[i+j] with 0 < i < m. Then, x[0 .. i-1] = y[j .. i+j-1] =u and a = x[i] y[i+j]=b.
When shifting, it is reasonable to expect that a prefix v of the pattern matches some suffix of the portion u of the text. Moreover, if we want to avoid another immediate mismatch, the character following the prefix v in the pattern must be different from a. The longest such prefix v is called the tagged border of u (it occurs at both ends of u followed by different characters in x).
上面罗力巴索就是这个意思:
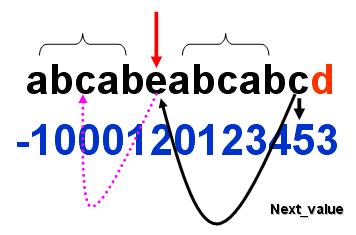
对于每一个子串的字母,都有一个next value, 这个value的是这样定义的:
-1 if j ==0
next[j]= k k= max m where a[0]...a[m-1] = a[j-m-1]...a[j-1]
0 其他
这个就是算法的精华,呵呵有了这个next——value之后我们就不用在主串回溯了,只是调整一下子串就可以了。
a[0]...a[m-1] = a[j-m-1]...a[j-1]
这句话就是我们说的开始部分跟尾部匹配.
我们来看看如何求这个next_value吧。
假设我们已经有一个串:
abcabeabcabcd
如果我们求解模式串的时候已经进行到d,呵呵前面的已经求解完成,那么我们只要判断c(d的前一个字母)是否跟其next_value是否相等就可以了,如果相等呢,说明其匹配串又长了一个, 呵呵c的next_value +1 如果不相等呢继续向前回溯,呵呵这个过程是不是很想主串中匹配子串呢??
^_^基本上就这样了。
下面是源程序:C/C++
int Kmp(const char *s, const char*d, int p, int *next )
{
if (NULL == s || NULL == d || NULL == next) return -1;
int sl = strlen(s);
int dl = strlen(d);
int j =0;
while(j<dl && p < sl){
if(s[p] == d[j] || -1 == j){
++p;++j;
}
else{
j = next[j];
}
}
if(j>=dl) return p;
else return -1;
}
void getnext(const char *s,int *next)
{
int sl = strlen(s);
int j = 0;
int i = -1;
next[0] =-1;
while( j < sl){
if(-1 ==i || s[j] == s[i]){
++i;++j;
next[j] = i;
}
else
i =next[i];
}
return ;
}
两个网址很有用,
http://www-igm.univ-mlv.fr/~lecroq/string/node8.html
http://www.cee.hw.ac.uk/~alison/ds98/node78.html







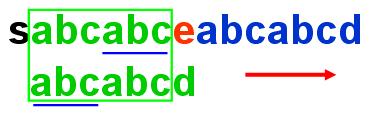















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








