目录
1.将两个有序的链表合并为一个新链表,要求新的链表是通过拼接两个链表的节点来生成的。
3.设计LRU缓存结构,该结构在构造时确定大小,假设大小为K,并有如下两个功能
4.将给出的整数x翻转。例1:x=123,返回321例2:x=-123,返回-321
7.合并\ k k 个已排序的链表并将其作为一个已排序的链表返回。分析并描述其复杂度。
给出一个有n个元素的数组S,S中是否有元素a,b,c满足a+b+c=0?找出数组S中所有满足条件的三元组。
10.给定一个二叉树,返回该二叉树的之字形层序遍历,(第一层从左向右,下一层从右向左,一直这样交替)例如:给定的二叉树是{3,9,20,#,#,15,7},该二叉树之字形层序遍历的结果是
1.将两个有序的链表合并为一个新链表,要求新的链表是通过拼接两个链表的节点来生成的。
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param l1 ListNode类
* @param l2 ListNode类
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
ListNode mergeNode = null;
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
mergeNode = l1;
mergeNode.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
} else {
mergeNode = l2;
mergeNode.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
}
return mergeNode;
}
}2.给定一个二叉树和一个值\ sum sum,判断是否有从根节点到叶子节点的节点值之和等于\ sum sum 的路径,
例如:
给出如下的二叉树,\ sum=22 sum=22,
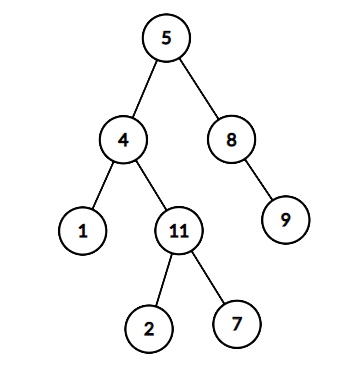
返回true,因为存在一条路径 5\to 4\to 11\to 25→4→11→2的节点值之和为 22
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)
return false;
sum -= root.val;
if (sum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum);
}
}
3.设计LRU缓存结构,该结构在构造时确定大小,假设大小为K,并有如下两个功能
- (The Least Recently Used,最近最久未使用算法)
- set(key, value):将记录(key, value)插入该结构
- get(key):返回key对应的value值
[要求]
- set和get方法的时间复杂度为O(1)
- 某个key的set或get操作一旦发生,认为这个key的记录成了最常使用的。
- 当缓存的大小超过K时,移除最不经常使用的记录,即set或get最久远的。
若opt=1,接下来两个整数x, y,表示set(x, y)
若opt=2,接下来一个整数x,表示get(x),若x未出现过或已被移除,则返回-1
对于每个操作2,输出一个答案
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* lru design
* @param operators int整型二维数组 the ops
* @param k int整型 the k
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] LRU (int[][] operators, int k) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> lruMap = new LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList();
for(int[] opat:operators){
int key = opat[1];
switch(opat[0]){
case 1:
int value = opat[2];
if(lruMap.size()<k){
lruMap.put(key,value);
}else{
Iterator ot = lruMap.keySet().iterator();
lruMap.remove(ot.next());
lruMap.put(key,value);
}
break;
case 2:
if(lruMap.containsKey(key)){
int val = lruMap.get(key);
result.add(val);
lruMap.remove(key);
lruMap.put(key,val);
}else{
result.add(-1);
}
break;
default:
}
}
int[] resultArr = new int[result.size()];
int i=0;
for(int a:result){
resultArr[i++]=a;
}
return resultArr;
}
}LFU算法
LFU(Least Frequently Used ,最近最少使用算法)
一个缓存结构需要实现如下功能。
- set(key, value):将记录(key, value)插入该结构
- get(key):返回key对应的value值
但是缓存结构中最多放K条记录,如果新的第K+1条记录要加入,就需要根据策略删掉一条记录,然后才能把新记录加入。这个策略为:在缓存结构的K条记录中,哪一个key从进入缓存结构的时刻开始,被调用set或者get的次数最少,就删掉这个key的记录;
如果调用次数最少的key有多个,上次调用发生最早的key被删除
这就是LFU缓存替换算法。实现这个结构,K作为参数给出
[要求]
set和get方法的时间复杂度为O(1)
若opt=1,接下来两个整数x, y,表示set(x, y)
若opt=2,接下来一个整数x,表示get(x),若x未出现过或已被移除,则返回-1
对于每个操作2,输出一个答案
package test;
import java.util.*;
class LFUCache {
Map<Integer, Node> cache; // 存储缓存的内容
Map<Integer, LinkedHashSet<Node>> freqMap; // 存储每个频次对应的双向链表
int size;
int capacity;
int min; // 存储当前最小频次
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
cache = new HashMap (capacity);
freqMap = new HashMap();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
freqInc(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (capacity == 0) {
return;
}
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node != null) {
node.value = value;
freqInc(node);
} else {
if (size == capacity) {
Node deadNode = removeNode();
cache.remove(deadNode.key);
size--;
}
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
cache.put(key, newNode);
addNode(newNode);
size++;
}
}
void freqInc(Node node) {
// 从原freq对应的链表里移除, 并更新min
int freq = node.freq;
LinkedHashSet<Node> set = freqMap.get(freq);
set.remove(node);
if (freq == min && set.size() == 0) {
min = freq + 1;
}
// 加入新freq对应的链表
node.freq++;
LinkedHashSet<Node> newSet = freqMap.get(freq + 1);
if (newSet == null) {
newSet = new LinkedHashSet();
freqMap.put(freq + 1, newSet);
}
newSet.add(node);
}
void addNode(Node node) {
LinkedHashSet<Node> set = freqMap.get(1);
if (set == null) {
set = new LinkedHashSet();
freqMap.put(1, set);
}
set.add(node);
min = 1;
}
Node removeNode() {
LinkedHashSet<Node> set = freqMap.get(min);
Node deadNode = set.iterator().next();
set.remove(deadNode);
return deadNode;
}
}
class Node {
int key;
int value;
int freq = 1;
public Node() {}
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
4.将给出的整数x翻转。
例1:x=123,返回321
例2:x=-123,返回-321
你有思考过下面的这些问题么?
如果整数的最后一位是0,那么输出应该是什么?比如10,100
你注意到翻转后的整数可能溢出吗?假设输入是32位整数,则将翻转10000000003就会溢出,你该怎么处理这样的样例?抛出异常?这样做很好,但是如果不允许抛出异常呢?这样的话你必须重新设计函数(比如添加一个额外的参数)。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param x int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int reverse (int x) {
//本体关键点是如何判断溢出。
//推荐解答用的是用long类型存储结果,如果结果大于0x7fffffff或者小于0x80000000就溢出
//我的解法是每次计算新的结果时,再用逆运算判断与上一次循环的结果是否相同,不同就溢出
int res=0;
while(x!=0){
//最后一位
int tail=x%10;
int newRes=res*10+tail;
//如果newRes-tail)/10!=res说明产生了溢出
if((newRes-tail)/10!=res)
return 0;
res=newRes;
x=x/10;
}
return res;
}
} 5.
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null)
return null;
//head为当前节点,如果当前节点为空的话,那就什么也不做,直接返回null;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode next = null;
//当前节点是head,pre为当前节点的前一节点,next为当前节点的下一节点
//需要pre和next的目的是让当前节点从pre->head->next1->next2变成pre<-head next1->next2
//即pre让节点可以反转所指方向,但反转之后如果不用next节点保存next1节点的话,此单链表就此断开了
//所以需要用到pre和next两个节点
//1->2->3->4->5
//1<-2<-3 4->5
while(head!=null){
//做循环,如果当前节点不为空的话,始终执行此循环,此循环的目的就是让当前节点从指向next到指向pre
//如此就可以做到反转链表的效果
//先用next保存head的下一个节点的信息,保证单链表不会因为失去head节点的原next节点而就此断裂
next = head.next;
//保存完next,就可以让head从指向next变成指向pre了,代码如下
head.next = pre;
//head指向pre后,就继续依次反转下一个节点
//让pre,head,next依次向后移动一个节点,继续下一次的指针反转
pre = head;
head = next;
}
//如果head为null的时候,pre就为最后一个节点了,但是链表已经反转完毕,pre就是反转后链表的第一个节点
//直接输出pre就是我们想要得到的反转后的链表
return pre;
}
}6.求平方根:
实现函数 int sqrt(int x).
计算并返回x的平方根
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param x int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int sqrt (int x) {
int low = 0;
int high = x;
while (low <= high) {
long mid = (low + high) / 2;
if(mid * mid == x) return (int)mid;
else if(mid * mid < x) low = (int)(mid + 1);
else high = (int)(mid - 1);
}
return high;
}
}7.合并\ k k 个已排序的链表并将其作为一个已排序的链表返回。分析并描述其复杂度。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ArrayList<ListNode> lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.size() == 0)
return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>(lists.size(), new Comparator<ListNode>() {
@Override
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
if (o1.val < o2.val)
return -1;
else if (o1.val == o2.val)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
});
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummy;
for (ListNode node : lists)
if (node != null)
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
tail.next = queue.poll();
tail = tail.next;
if (tail.next != null)
queue.add(tail.next);
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
8.
给出一个有n个元素的数组S,S中是否有元素a,b,c满足a+b+c=0?找出数组S中所有满足条件的三元组。
注意:
- 三元组(a、b、c)中的元素必须按非降序排列。(即a≤b≤c)
- 解集中不能包含重复的三元组。
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> threeSum(int[] num) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); if (num == null || num.length == 0) { return lists; } Arrays.sort(num); for (int k = 0; k < num.length - 2; k++) { if (num[k] > 0) { break; } if (k > 0 && num[k] == num[k - 1]) { continue; } int i = k + 1; int j = num.length - 1; while (i < j) { int sum = num[k] + num[i] + num[j]; if (sum > 0) { while (j > i && num[j] == num[--j]); } else if (sum < 0) { while (i < j && num[i] == num[++i]); } else { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(num[k]); list.add(num[i]); list.add(num[j]); lists.add(list); while (i < j && num[i] == num[++i]); while (j > i && num[j] == num[--j]); } } } return lists; } }9.分别按照二叉树先序,中序和后序打印所有的节点。
import java.util.*; /* * public class TreeNode { * int val = 0; * TreeNode left = null; * TreeNode right = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param root TreeNode类 the root of binary tree * @return int整型二维数组 */ public int[][] threeOrders (TreeNode root) { int[][] result = new int[3][]; preOrder(root); inOrder(root); postOrder(root); result[0] = preResult.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); result[1] = inResult.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); result[2] = postResult.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); return result; } private List<Integer> preResult = new ArrayList<>(); private List<Integer> inResult = new ArrayList<>(); private List<Integer> postResult = new ArrayList<>(); private void preOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } preResult.add(root.val); preOrder(root.left); preOrder(root.right); } private void inOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } inOrder(root.left); inResult.add(root.val); inOrder(root.right); } private void postOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } postOrder(root.left); postOrder(root.right); postResult.add(root.val); } }10.给定一个二叉树,返回该二叉树的之字形层序遍历,(第一层从左向右,下一层从右向左,一直这样交替)
例如:
给定的二叉树是{3,9,20,#,#,15,7},
该二叉树之字形层序遍历的结果是[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) { //思路:层序遍历,对lists引入一个计数器 //如果是需要逆序输出list时,引入Collections集合工具类对list进行反转 ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null) return lists; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); boolean flag = true; while(!queue.isEmpty()) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); int size = queue.size(); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); list.add(node.val); if(node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left); if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right); } if(flag) { lists.add(list); flag = false; } else { Collections.reverse(list); lists.add(list); flag = true; } } return lists; } }
11. 素数
public boolean iszhishu(int x)
{
for(int i=2;i<=x/2;i++)
if (x % 2==0 )
return false;
return true;
}12.水仙花数
13.判断回文数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex25 {
static int[] a = new int[5];
static int[] b = new int[5];
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean is =false;
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
long l = s.nextLong();
if (l > 99999 || l < 10000) {
System.out.println("Input error, please input again!"); l = s.nextLong();
}
for (int i = 4; i >= 0; i--) {
a[i] = (int) (l / (long) Math.pow(10, i));
l =(l % ( long) Math.pow(10, i));
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0,j=0; i<5; i++, j++) {
b[j] = a[i];
}
for(int i=0,j=4; i<5; i++, j--) {
if(a[i] != b[j]) {
is = false; break;
} else {
is = true;
}
}
if(is == false) {
System.out.println("is not a Palindrom!");
} else if(is == true) {
System.out.println("is a Palindrom!");
}
}
}
14.二分查找
请实现有重复数字的有序数组的二分查找。
输出在数组中第一个大于等于查找值的位置,如果数组中不存在这样的数,则输出数组长度加一。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 二分查找
* @param n int整型 数组长度
* @param v int整型 查找值
* @param a int整型一维数组 有序数组
* @return int整型
*/
public int upper_bound_ (int n, int v, int[] a) {
// write code here
int left=0;
int right=n-1;
while(left<right)
{
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;
if(a[mid]>=v)
right=mid;
else
left=mid+1;
}
if(a[left]==a[right] && a[left]==v)//这个是判断如果最后一个是目标值的话,就返回正常坐标
return left+1;
else return left==n-1?n+1:left+1;//判断其他情况,因为已经判断了最后一个,所以现在如果还是=n-1就说明找完了没找到,返回n+1,其他返回正常值。
}
}15.判断给定的链表中是否有环
对于一个给定的链表,返回环的入口节点,如果没有环,返回null
package linkedlist;
/**
* 题目描述: 链表的入环节点,如果无环,返回null
* Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, returnnull.
* Follow up: Can you solve it without using extra space?
* 思路:
* 1)首先判断是否有环,有环时,返回相遇的节点,无环,返回null
* 2)有环的情况下, 求链表的入环节点
* fast再次从头出发,每次走一步,
* slow从相遇点出发,每次走一步,
* 再次相遇即为环入口点。
* 注:此方法在牛客BAT算法课链表的部分有讲解。
*/
//nowcoder pass
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode meetNode = meetingNode(head);
if (meetNode == null) {//说明无环
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = meetNode;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
//寻找相遇节点,如果无环,返回null
public ListNode meetingNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}





















 12万+
12万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








